By: Divya Agrawal | Comments (4) | Related: > JOIN Tables
Problem
One challenge you may be faced with is the need to create running totals for query output, whether it be a straight query or for a report. Doing calculations such as this in Excel are pretty straightforward, because each cell can have a different formula. Are there any T-SQL tricks to help on calculating a running total for a fixed amount of rows?
Solution
This post is nothing new, but it contains a very short and precise solution to handle the problem at hand using CROSS JOINS.
One task we have all probably done is to create some kind of report data using SQL Server data. Reports are generally an aggregation or some calculations of some given data. It could be even calculations on calculated data.
Let's take an example from Excel. It is generally used to make some type of calculations on given data. It could be done by using arithmetic or any other sort of formula available in Excel.
My problem was that I have an Excel file with three columns called ID, Date and Balance. ID is an Identity column and Balance is the current balance on a given Date. I had to calculate the sum of the last five transactions in an iterative way, so that the computed column will give me the Running Total for the last five transactions.
As far as Excel is concerned I have just written a formula as simple as sum(C1:C5) where C1 to C5 is the balance of the last five Transactions. For the next row the formula will be sum(C2:C6)... and this will continue for all rows.
Looking at the images below you will have a better idea.
Here is the raw data and the first calculation being entered in cell D5.
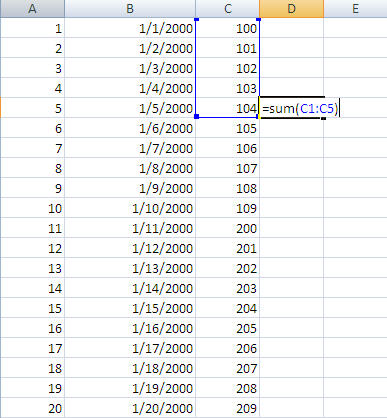
Here is the output with the formulas entered for all cells in column D.
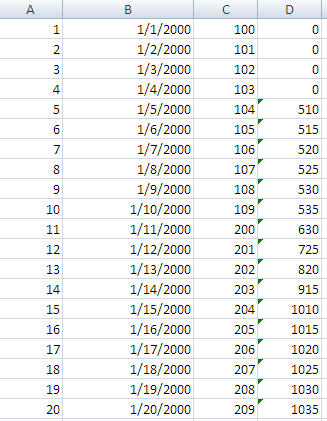
Here the RunningTotal (column D) is the computed column giving the sum of the last five transactions on an Iterative level. The sum of Transaction ID's 1 to 5 is 510, the sum of transaction ID's 2 to 6 is 515, and so on.
I needed to develop the same thing in SQL Server. But in SQL Server you might be aware it's very difficult to add such computed column which computes data on an iterative level. I had one last option of using Cursors or Loops, but as you all know it would degrade performance. So, I went for an approach that uses CROSS JOINS which was a better option.
First we will create a table name Accounts and insert some data into the table. By using this script a table named Accounts will be created and 20 rows will be inserted.
CREATE TABLE Accounts
(
ID int IDENTITY(1,1),
TransactionDate datetime,
Balance float
)
GO
insert into Accounts(TransactionDate,Balance) values ('1/1/2000',100)
insert into Accounts(TransactionDate,Balance) values ('1/2/2000',101)
insert into Accounts(TransactionDate,Balance) values ('1/3/2000',102)
insert into Accounts(TransactionDate,Balance) values ('1/4/2000',103)
insert into Accounts(TransactionDate,Balance) values ('1/5/2000',104)
insert into Accounts(TransactionDate,Balance) values ('1/6/2000',105)
insert into Accounts(TransactionDate,Balance) values ('1/7/2000',106)
insert into Accounts(TransactionDate,Balance) values ('1/8/2000',107)
insert into Accounts(TransactionDate,Balance) values ('1/9/2000',108)
insert into Accounts(TransactionDate,Balance) values ('1/10/2000',109)
insert into Accounts(TransactionDate,Balance) values ('1/11/2000',200)
insert into Accounts(TransactionDate,Balance) values ('1/12/2000',201)
insert into Accounts(TransactionDate,Balance) values ('1/13/2000',202)
insert into Accounts(TransactionDate,Balance) values ('1/14/2000',203)
insert into Accounts(TransactionDate,Balance) values ('1/15/2000',204)
insert into Accounts(TransactionDate,Balance) values ('1/16/2000',205)
insert into Accounts(TransactionDate,Balance) values ('1/17/2000',206)
insert into Accounts(TransactionDate,Balance) values ('1/18/2000',207)
insert into Accounts(TransactionDate,Balance) values ('1/19/2000',208)
insert into Accounts(TransactionDate,Balance) values ('1/20/2000',209)
GO
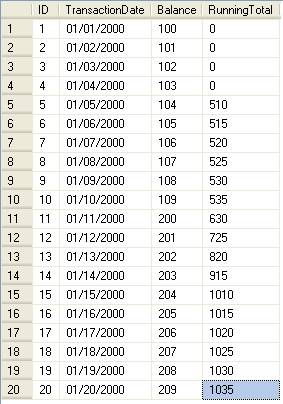
Here is what the raw data looks like.
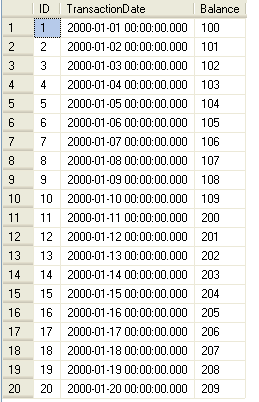
To get the running balance after every five transactions I have used a CROSS JOIN query as shown below
SELECT A.ID AS ID,
B.ID AS BID,
B.Balance
FROM Accounts A CROSS JOIN
Accounts B
WHERE B.ID BETWEEN A.ID-4 AND A.ID
AND A.ID>4
In the result set below the ID column is the first grouping after we have got our first 5 rows and the BID column is the actual row that will be used for the balance.
So for the first balance it would end on ID = 5 (since the IDs are number 1-20), the five rows that we would use for the balance are IDs (1,2,3,4,5). For the next balance it would end with ID=6, so we would use records (2,3,4,5,6) and for ID=7 we would use records (3,4,5,6,7), etc....
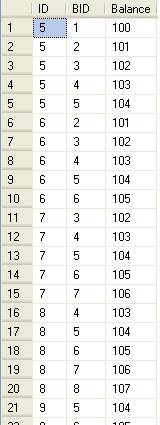
The above query is the innermost query which will fetch the balance for every five Transaction ID's from table B for a given ID of table A on an iterative level where alias names A and B are used, so we can use data from the same table.
SELECT ID,
SUM(Balance) AS RunningTotal
FROM (SELECT A.ID AS ID,
B.ID AS BID,
B.Balance
FROM Accounts A CROSS JOIN
Accounts B
WHERE B.ID BETWEEN A.ID-4 AND A.ID
AND A.ID>4 ) T
GROUP BY ID
So here we can see that the output starts with ID = 5 and if we add up the values from ID=1-5 (100+101+102+103+104+105) we get 510. Or if we look at ID=16 and up the values from ID=12-16 (201+202+203+204+205) we get 1015.
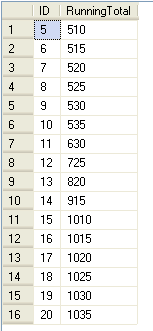
The above query would Group all the ID's and get the sum of the five transactions on an iterative level
The following query is the final product.
SELECT Acc.ID,
CONVERT(varchar(50),TransactionDate,101) AS TransactionDate,
Balance,
isnull(RunningTotal,'') AS RunningTotal
FROM Accounts Acc LEFT OUTER JOIN
(SELECT ID,
SUM(Balance) AS RunningTotal
FROM
(SELECT A.ID AS ID,
B.ID AS BID,
B.Balance
FROM Accounts A CROSS JOIN
Accounts B
WHERE B.ID BETWEEN A.ID-4 AND A.ID
AND A.ID>4 ) T
GROUP BY ID ) Bal
ON Acc.ID=Bal.ID
The outer join will give all the details of the table. By executing the query above you will get the following output. So you can see that the totals do not start until ID = 5 and from that point forward the RunningTotal is the sum of the balance for the current and previous four records.
This can be changed to do the sum after any level, by changing the fours to another number such as the following:
SELECT Acc.ID,
CONVERT(varchar(50),TransactionDate,101) AS TransactionDate,
Balance,
isnull(RunningTotal,'') AS RunningTotal
FROM Accounts Acc LEFT OUTER JOIN
(SELECT ID,
SUM(Balance) AS RunningTotal
FROM
(SELECT A.ID AS ID,
B.ID AS BID,
B.Balance
FROM Accounts A CROSS JOIN
Accounts B
WHERE B.ID BETWEEN A.ID-2 AND A.ID
AND A.ID>2 ) T
GROUP BY ID ) Bal
ON Acc.ID=Bal.ID
The one downside to this approach is that it is assumes there is a sequential ID value and there are no gaps in the IDs. This could be changed to a ROW_NUMBER() function, so you are always working with a sequential number.
I hope this gives you some ideas of what other things you may be able to do with CROSS JOINs.
Next Steps
- It is also possible to calculate the running balance on a particular date just by adding in the group by clause.
- Other conditions can also be added to the query.
- Try experimenting with other options and introducing the ROW_NUMBER() function
About the author
 Divya Agrawal's bio is coming soon...
Divya Agrawal's bio is coming soon...This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips






