By: Graham Okely | Comments (4) | Related: > Backup
Problem
How often do you execute a SQL Server backup on a remote server and then say to yourself, "Oh I need to copy that backup to another server" then go try to find it? Or how often do you want to clean out some old backup files off a SQL Server drive, but not sure which backups should be removed? Check out this tip to learn more about identifying and managing your backups on disk.
Solution
To answer the first question, we can use two system tables in the MSDB database. The first system table is called msdb.dbo.backupset and it has a row for each backup executed. The second system table is msdb.dbo.backupmediafamily and this table has a row for each media family. Let's build a query that reveals where the backups are located to learn more about identifying the backup location.
Query for Locating SQL Server Backups
-- File name : Where are the backups.sql -- Author : Graham Okely B App Sc -- Scope : OK on SQL Server 2000,2005,2008R2,2012 -- Select the information we require to make a decision about which backup we want to use select top 5 a.server_name, a.database_name, backup_finish_date, a.backup_size, CASE a.[type] -- Let's decode the three main types of backup here WHEN 'D' THEN 'Full' WHEN 'I' THEN 'Differential' WHEN 'L' THEN 'Transaction Log' ELSE a.[type] END as BackupType ,b.physical_device_name from msdb.dbo.backupset a join msdb.dbo.backupmediafamily b on a.media_set_id = b.media_set_id where a.database_name Like 'master%' order by a.backup_finish_date desc
You can adjust the where clause in the query above to display your database backup. Note that a full list of database backup types is discussed here.
The screen shot below displays the top 5 results. It lists the following columns:
- Server name
- Database name
- Backup finish date
- Backup type
- Backup path
Building a better query to analyze SQL Server Backups
The image above shows the answer to our initial question, however let's try to gather more useful information from the query below:
-- File name : Where is my specific backup located.sql
-- Author : Graham Okely B App Sc
-- Scope : OK on SQL Server 2000,2005,2008R2,2012
-- Select the information we require to make a decision about which backup we want to use
select top 5 a.server_name, a.database_name, backup_finish_date, a.backup_size,
CASE a.[type] -- Let's decode the three main types of backup here
WHEN 'D' THEN 'Full'
WHEN 'I' THEN 'Differential'
WHEN 'L' THEN 'Transaction Log'
ELSE a.[type]
END as BackupType
-- Build a path to the backup
,'\\' +
-- lets extract the server name out of the recorded server and instance name
CASE
WHEN patindex('%\%',a.server_name) = 0 THEN a.server_name
ELSE substring(a.server_name,1,patindex('%\%',a.server_name)-1)
END
-- then get the drive and path and file information
+ '\' + replace(b.physical_device_name,':','$') AS '\\Server\Drive\backup_path\backup_file'
from msdb.dbo.backupset a join msdb.dbo.backupmediafamily b
on a.media_set_id = b.media_set_id
where a.database_name Like 'master%'
order by a.backup_finish_date desc
Now we can see more helpful data. We can use the full path and database backup name when we use SQL Server Management Studio to recover a database or when we restore via T-SQL code. If you use SQL Server Management Studio, to restore a database you can paste the path and database backup name into the GUI when you are asked to supply the location of the backup.
A query to generate the location of the SQL Server Backup files
However let's say we want to copy that file or delete it after we copied the file from production to our test environment. How do we do that? Well let's modify our query.
-- File name : A query to a pathway.sql
-- Author : Graham Okely B App Sc
-- Select the information we require to make a decision about which backup we want to use
select top 5 a.server_name, a.database_name, backup_finish_date, a.backup_size,
CASE a.[type] -- Let's decode the three main types of backup here
WHEN 'D' THEN 'Full'
WHEN 'I' THEN 'Differential'
WHEN 'L' THEN 'Transaction Log'
ELSE a.[type]
END as BackupType
-- Browse to the file
,'\\' +
-- lets extract the server name out of the recorded server and instance name
CASE
WHEN patindex('%\%',a.server_name) = 0 THEN a.server_name
ELSE substring(a.server_name,1,patindex('%\%',a.server_name)-1)
END
-- then get the drive information
+ '\' + left(replace(b.physical_device_name,':','$'),2) AS '\\Server\Drive'
from msdb.dbo.backupset a join msdb.dbo.backupmediafamily b
on a.media_set_id = b.media_set_id
where a.database_name Like 'master%'
order by a.backup_finish_date desc
On the very right you can see the server name and drive listed.
To use the information from this query to copy or delete a file follow these instructions:
- In SQL Server Management Studio, click in the results field for the data you wish to browse to.
- Alternate click and copy the data from the \\Server\Drive column.
- Click on Start then Run on your workstation or current server.
- Windows key + R will do the same thing.
- Then paste the data from the \\Server\Drive column into the run command.
- Press enter and then, given you have permission, Windows Explorer will open up that drive.
- Then browse down the folders to move or remove the backup files.
- You will know the folder from the results of the previous queries.
- If you wish you can search for *.bak (or *.trn, etc.) using the Windows Explorer search box. See the image below and note the search box in the top right hand corner.
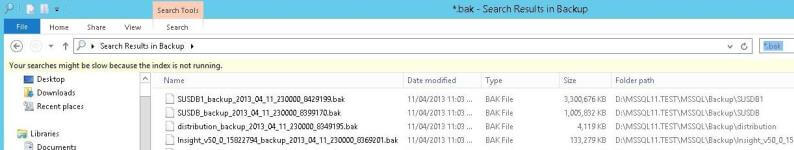
At this point you should be able to click on a backup file and press delete to clean up and create space. However be careful...usually your maintenance plans should clear up those old backups. So ask yourself "Why is it there?" first. Sometimes on a test environment or development environment you may find stray backups taking up space. They are the ones you should target as potential clean up items.
SQL Server Query for all Available Drives on a Server
Since we have been talking about backup storage, here is a handy query that will show all the drives on an instance. The xp_fixeddrives command will list the available drives on an instance. Most DBAs know that, all I have done is added some formatting that produces a useful path for each drive. I like to see the free space in gigabytes so I added that formatting.
-- File name : Space the final frontier.sql
-- Author : Graham Okely B App Sc
-- Purpose : Create the path for each drive on a SQL Server instance
-- Scope : OK on SQL Server 2000,2005,2008R2,2012
USE [Master]
GO
-- 2000 specific drop temp table
IF Object_id('tempdb..#Drives') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE #Drives
-- Make a space for data
CREATE TABLE #Drives ( Drive_Letter CHAR(1), mb_Free_Space int )
-- Collect the data
INSERT INTO #Drives EXEC xp_FixedDrives
-- Display a path to the drives
SELECT '\\' + CAST(Serverproperty('MachineName') AS NVARCHAR(128)) +
'\' + Drive_Letter + '$' AS 'Server and Drive'
,mb_Free_Space/1024 AS 'GB Free space'
FROM #Drives
-- Clean up
DROP TABLE #Drives
Example results
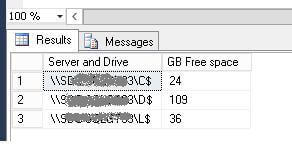
Next Steps
- Could you include one of these reports into an email to let a user know where their backup was located?
- SQL Server 2012 has a nice wizard to copy databases. However it does not always work across versions of SQL Server.
- If you are new see this restoration tutorial for command line restores.
- General advice from Microsoft about copying databases with backup and restore.
- Check out tip 2444 by Jugal Shah "Script to Get Available and Free Disk Space for SQL Server".
- Check out tip 1263 by Jeremy Kadlec "Accessing the Windows File System from SQL Server".
- Here is a link to a stored procedure version of determining free disk space. Tip 1706 by Jeremy Kadlec
About the author
 Graham Okely is a SQL Server DBA and has been working with database systems since 1984 and has been specializing in SQL Server since 2007.
Graham Okely is a SQL Server DBA and has been working with database systems since 1984 and has been specializing in SQL Server since 2007.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips






