Problem
You know how to manage logins and users on on-premises SQL Servers with SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS), but now you’ve created an Azure SQL Database and are now ready to add users.
It’s presumed you are not and will not have users and / or applications using the server level “sa” like server admin credentials chosen when the Azure SQL Database server was built. What is the best way to manage users in Azure SQL Databases?
Solution
Let’s do a quick review. With traditional on-premises SQL Server, you have a login to the SQL Server. The login can be an Active Directory account or created in the SQL Server using local SQL authentication. The login gets you access to the SQL Server only. Then you map a user to the login in each database. This gives access to a databases(s) with permissions typically granted by putting the user in a specific security group(s).
Security at a server / database level with on-premises SQL Server and Azure SQL Database are similar but with some differences.
SQL Server and Azure SQL Database Security Differences
The first difference is the concept of a contained user, which is a user not mapped to a login. Authentication is done in Azure Active Directory or in the database itself. Traditional logins to SQL Server with a user in a database mapped to it still exists, but this breaks from the concept of the required login that gets you access to the server and the user gets you access to the database. Contained users make the database more easily portable.
The traditional database level roles like db_datareader, db_datawriter, db_ddladmin, etc. are the same. But the traditional server level roles like sysadmin, serveradmin, etc. don’t exist in Azure SQL Database. There are two server admin roles, dbmanager (similar to dbcreator) to create and drop databases, and loginmanager (similar to securityadmin) to create new logins.
In SSMS, when you right click on Logins or Users from Object Explorer and choose New it opens a new query window. This will show the command syntax instead of the familiar GUI options.
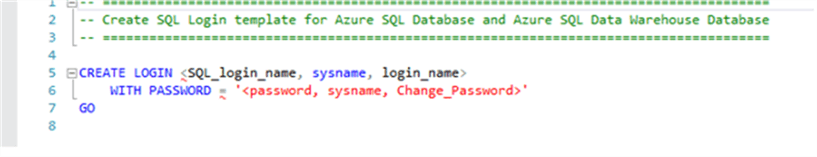

Now that we have reviewed the basics, have some background, know the differences and what to expect, here are our options:
- Create a SQL authentication login and add a user(s) to a database(s) that is mapped to the login. This would be used when you want to manage one login and password for users in multiple databases. This is just like an on-premises SQL Server.
- Create a contained SQL Authentication user in a database(s) not mapped to any login.
- Create a contained Azure Active Directory user for a database(s).
- Create a SQL authentication login, add a user mapped to it in master and add the user to a server level admin role.
- Create a user mapped to an Azure Active Directory user and add the user to a server level admin role.
Examples
Following are examples of our options listed above:
- Connect to your Azure SQL Database server with SSMS as an admin in master.
- Create a SQL authentication login called ‘test’ with a password of ‘SuperSecret!’.
- Create a user mapped to the login called ‘test’ in a database, and add it to db_datareader and db_datawriter roles.
-- create SQL auth login from master
CREATE LOGIN test
WITH PASSWORD = 'SuperSecret!' - Open another query window and choose your user database in the dropdown.
-- select your db in the dropdown and create a user mapped to a login
CREATE USER [test]
FOR LOGIN [test]
WITH DEFAULT_SCHEMA = dbo;
-- add user to role(s) in db
ALTER ROLE db_datareader ADD MEMBER [test];
ALTER ROLE db_datawriter ADD MEMBER [test]; - Repeat second step for all databases you are adding ‘test’ to. Note, you will need to open a new connection(s).
- Connect to your Azure SQL Database server with SSMS as an admin and choose the database you want to add the user(s) to in the dropdown. Create a SQL authentication contained user called ‘test’ with a password of ‘SuperSecret!’ then adding it to the db_datareader and db_datawriter roles.
-- select your db in dropdown and create a contained user
CREATE USER [test]
WITH PASSWORD = 'SuperSecret!',
DEFAULT_SCHEMA = dbo;
-- add user to role(s) in db
ALTER ROLE db_datareader ADD MEMBER [test];
ALTER ROLE db_datawriter ADD MEMBER [test]; - Connect to your Azure SQL Database server with SSMS as an admin and choose the database you want to add a user to in the dropdown. Add Azure Active Directory user ‘name@domain.com’ then add it to the db_datareader and db_datawriter roles.
-- add contained Azure AD user
CREATE USER [name@domain.com]
FROM EXTERNAL PROVIDER
WITH DEFAULT_SCHEMA = dbo;
-- add user to role(s) in db
ALTER ROLE db_datareader ADD MEMBER [test];
ALTER ROLE db_datawriter ADD MEMBER [test]; - Next, we’ll create a login and user in master that can manage databases and logins. Connect to your Azure SQL Database server with SSMS as an admin in master. Add a SQL authentication login called ‘test2’ and a password of ‘SuperSecret!’, create a user mapped to it in master and add the user to the dbmanager and login manager roles.
-- add login
CREATE LOGIN [test2]
WITH PASSWORD='SuperSecret!';
-- add user
CREATE USER [test2]
FROM LOGIN [test2]
WITH DEFAULT_SCHEMA=dbo;
-- add user to role(s) in db
ALTER ROLE dbmanager ADD MEMBER [test2];
ALTER ROLE loginmanager ADD MEMBER [test2]; - Lastly, we’ll add an Azure Active Directory user that can also manage databases and logins. Connect to your Azure SQL Database server with SSMS as an admin in master. Add a contained user ‘name@domain.com’ and add it to the dbmanager and login manager roles.
-- add contained Azure AD user
CREATE USER [name@domain.com]
FROM EXTERNAL PROVIDER
WITH DEFAULT_SCHEMA = dbo;
-- add user to role(s) in db
ALTER ROLE dbmanager ADD MEMBER [name@domain.com];
ALTER ROLE loginmanager ADD MEMBER [name@domain.com]; Next Steps
Hopefully this tip has given you everything you need to know to create logins and users in SQL Azure Database, but you can find further information here:
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/sql-database/
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/sql-database/sql-database-manage-logins
- https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/blog/adding-users-to-your-sql-azure-database/
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/security/authentication-access/create-a-database-user
- https://blogs.msdn.microsoft.com/azuresqldbsupport/2016/10/05/create-sql-login-and-sql-user-on-your-azure-sql-db/


