Overview
The GETDATE() function returns the current server time stamp using the datetime format. This function returns the same value as the CURRENT_TIMESTAMP function. GETDATE() is used mostly in SQL Server, but CURRENT_TIMESTAMP is the ANSI SQL standard.
Explanation
Syntax
GETDATE()Parameters
- No parameters required
Simple GETDATE() Example
The following example will show the current server datetime.
SELECT GETDATE() as date
Difference between SQL GETDATE() and CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
The following example shows that there is no difference between the GETDATE() function and CURRENT_TIMESTAMP.
SELECT DATEDIFF(SECOND, GETDATE(), CURRENT_TIMESTAMP) as difference
How to use a Custom Format with GETDATE()
The following example will show GETDATE() in the dd-MM-yyyy hh:mm:ss tt format.
SELECT FORMAT(GETDATE(),'dd-MM-yy hh:mm:ss tt') as formatdate
How to use a Cultural Format with GETDATE
The following example will set the GETDATE() in a Spanish date format.
SELECT FORMAT(GETDATE(), 'dddd dd, MMMM, yyyy', 'ES-es') as spanish
Using SQL GETDATE() with Table Data
The following example will show the ProductIDs with a startdate between 7 and 8 years ago using GETDATE() as the current time.
SELECT Productid, DATEDIFF(YEAR, StartDate, GETDATE()) as years
FROM Production.ProductCostHistory
WHERE DATEDIFF(YEAR, StartDate, GETDATE()) BETWEEN 7 AND 8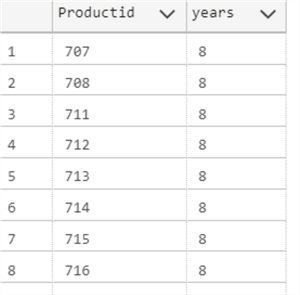
Additional Information


