Overview
The GETUTCDATE() function returns the system timestamp using the datetime format. This function returns the date and time in UTC format. UTC stands for Coordinated Universal Time and is the successor to Greenwich Mean Time (GMT).
Explanation
Syntax
GETUTCDATE()Parameters
- No parameters required
Simple GETUTCDATE() Example
The following example will show the current server datetime in UTC format.
SELECT GETUTCDATE() as date
Difference between GETUTCDATE() , CURRENT_TIMESTAMP and GETDATE()
The following example shows the difference of 5 hours on my machine between GETUTCDATE() and GETDATE().
SELECT DATEDIFF(HOUR, GETDATE(), GETUTCDATE()) as difference
Following is the output from each of these functions.
SELECT GETUTCDATE() as getutcdate, GETDATE() as getdate, CURRENT_TIMESTAMP as current_timestamp
We can see that GETDATE() and CURRENT_TIMESTAMP are the same, but CURRENT_TIMESTAMP is 5 hours ahead.
How to set the GETUTCDATE() in a custom format
The following example will show the GETUTCDATE() in dddd-MMMM yyyy hh:mm:ss tt format.
SELECT FORMAT(GETUTCDATE(), 'dddd-MMMM yyyy hh:mm:ss tt') as formatdate
How to set the GETUTCDATE() with a different Cultural Format
The following example will set the GETUTCDATE to the Spanish date format.
SELECT FORMAT(GETUTCDAY(), 'dddd dd, MMMM, yyyy', 'ES-es') as spanish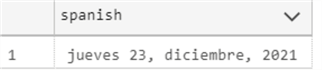
Use GETUTCDATE() with Table Data
The following example, will show the products with startdate between 7 and 8 years ago.
SELECT Productid, DATEDIFF(YEAR, StartDate, GETUTCDATE()) as years
FROM Production.ProductCostHistory
WHERE DATEDIFF(YEAR, StartDate, GETUTCDATE()) BETWEEN 7 AND 8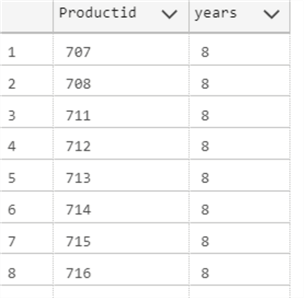
Additional Information


