Problem
Generating random numbers from a normal distribution is essential for accuracy and realistic modeling. Used for simulation, inference, cryptography, and algorithm design for scientific, engineering, statistical, and AI domains. Is it possible to create random Gaussian numbers in SQL Server using the Ziggurat algorithm without external tools?
Solution
The Ziggurat algorithm is among the fastest and most efficient method for generating Gaussian random numbers. It uses a called rejection sampling technique speeding it up by partitioning the target probability distribution into slices which will resembling a ziggurat structure. Ziggurat is the name of an ancient Mesopotamian stepped pyramid structure. The technique randomly generates a point in the probability density function and tests if this point is inside the desired distribution, and if not, tries again.
Terms and Definitions
Before we get started, here are some things that will be helpful to understand the algorithm:
- m1 – used to scale integers to floats in SHR3 function with a constant value of 2^31 = 2147483648.
- m2 – used to normalize integer values from bitwise generators with a constant value of 2^32 = 4294967296.
- dn – X-position where the tail start for the normal distribution, defining the rightmost x boundary of the Ziggurat.
- vn – Is the area under the normal curve to the right of dn and it is used to decide when to fall back to tail sampling.
- tn – Often is equal to dn and it is used to express tail logic in code.
- kn – Integer cutoff thresholds for fast rejection.
- wn – Floating-pointing widths of rectangles for scaling.
- fn – Height of probability density function at rectangle tops calculated by
 for normal and calculated by
for normal and calculated by  exponential tables.
exponential tables. - iz – Randomly selects which Ziggurat layer to sample from, usually for normal ranges from 0 to 127 and for exponential from 0 to 255.
- hz – Random signed integer used to compute iz and x.
- x – It is a candidate sample value that can be rejected or accepted depending of the probability density function test.
- uni – Uniform random value from uni function that is used in rejection sampling logic.
- shr3 – Shift-register random number generator with 3 operations that performs bitwise XOR and shift operations on an internal state (jsr). It is fast with no use of multiplications or divisions.
- jsr – Jump shift register that must be initialized with a random or non-zero seed before calling shr3 function that will change it through the deterministic bit-shift XOR.
- Skewness – Measure of symmetry of a distribution or data set. A normal distribution has a skewness of zero and any symmetric data should have a skewness near zero.
- Kurtosis – Measure of whether the data are heavy-tailed, which tend to have outliers, or light-tailed lack of outliers, relative to a normal distribution. A normal distribution has a kurtosis of three.
- Histogram – effective graphical technique for showing both the skewness and kurtosis of a data set.
Normal distribution – probability density function
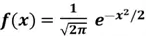
Ziggurat pre-computation
Before generating any random numbers, the algorithm sets up a table of values that defines the Ziggurat shape.
Ziggurat Method Steps for Normal Distribution
- Select a Region: A random integer i from 0 to 127 is chosen.
- Generate a Candidate: A uniform random number is generated and scaled by the pre-computed width of the selected rectangle. This produces a candidate number, x.
- Fast Path Acceptance: If the candidate number x is less than the solid part of the rectangle’s width, it’s accepted immediately. This is the most frequent outcome and avoids more complex calculations.
- Rejection Test: If the candidate falls in the small “overhang” area (the part of the rectangle that extends beyond the curve), a more precise rejection test is performed. A second random number is generated to determine a y-coordinate, and the point (x, y) is checked to see if it is actually under the normal distribution curve. The number is accepted only if this test passes.
- Tail Case: If the initial random number from step 1 corresponds to the tail region, a separate procedure is used to generate a number directly from that part of the distribution. This is a rare event.
- Apply Sign: After a positive number is successfully generated, a random sign (+ or -) is applied with a 50% probability to produce a number from the full, symmetric normal distribution.
SQL Tables
Random generated data
This table includes an extra column called src, that I used solely to trace which part of the calculation generated each value pair. This help me to identify the specific calculation step where a problem might occur and I kept it in case you encounter another flaw.
-- MSSQLTips (TSQL)
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[RndGenData](
[PointId] [int] NOT NULL,
[x] [float] NOT NULL,
[y] [float] NOT NULL,
[src] [smallint] NULL,
CONSTRAINT [PK_RndGenData_1] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED
(
[PointId] ASC
)WITH (PAD_INDEX = OFF, STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON, OPTIMIZE_FOR_SEQUENTIAL_KEY = OFF) ON [PRIMARY]
) ON [PRIMARY]
GOPre-computed Normal distribution values
-- MSSQLTips (TSQL)
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[RndZigguratNor](
[PointId] [int] IDENTITY(0,1) NOT NULL,
[kn] [bigint] NULL,
[wn] [float] NULL,
[fn] [float] NULL,
CONSTRAINT [PK_RndZigguratNor] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED
(
[PointId] ASC
)WITH (PAD_INDEX = OFF, STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON, OPTIMIZE_FOR_SEQUENTIAL_KEY = OFF) ON [PRIMARY]
) ON [PRIMARY]
GOSQL Function
Table-valued function SHR3
-- =============================================
-- Author: SCP - MSSQLTips
-- Create date: 20250718
-- Description: SHR3 pseudo-random generator
-- =============================================
CREATE OR ALTER FUNCTION [dbo].[tvfRndGenSHR3]
(@jsr bigint
,@rectangles int)
RETURNS TABLE
AS
RETURN
(
WITH step1 AS
(SELECT jsr1 = (@jsr ^ (@jsr << 13)) & 0xFFFFFFFF),
step2 AS
(SELECT jsr2 = (jsr1 ^ (jsr1 >> 17)) & 0xFFFFFFFF
FROM step1),
step3 AS
(SELECT jsr_final = (jsr2 ^ (jsr2 << 5)) & 0xFFFFFFFF
FROM step2)
,result AS
(SELECT shr3 = (@jsr + jsr_final) & 0xFFFFFFFF
,jsr_new = jsr_final
FROM step3)
SELECT shr3
,jsr_new
,CONVERT(float,0.5 + shr3 / 4294967296.0) AS uni
,CASE WHEN shr3 >= 2147483648
THEN CONVERT(int, shr3 - 4294967296)
ELSE CONVERT(int, shr3)
END AS hz
,CASE WHEN shr3 >= 2147483648
THEN CONVERT(int, shr3 - 4294967296) & @rectangles
ELSE CONVERT(int, shr3) & @rectangles
END AS iz
FROM result
);
GOSQL Stored Procedures
Generating pre-computed values for Normal distribution
-- =============================================
-- Author: SCP - MSSQLTips
-- Create date: 20250804
-- Description: Ziggurat RNOR precomputed Tables
-- =============================================
CREATE OR ALTER PROCEDURE [dbo].[uspRandGenZigguratRNorIni]
WITH EXECUTE AS CALLER
AS
BEGIN;
SET NOCOUNT ON;
BEGIN TRY
DECLARE @jsr bigint
,@jsrseed bigint
,@m1 float = 2147483648.0
,@dn float = 3.442619855899
,@tn float
,@vn float = 0.00991256303526217
,@q float
,@i int = 0
,@NumRects int = 128;
SET @jsrseed = FLOOR(RAND(CHECKSUM(NEWID())) * (@m1 - 1));
SET @tn = @dn;
SET @jsr ^= @jsrseed & 0xFFFFFFFF;
TRUNCATE TABLE [dbo].[RndZigguratNor];
SET @q = @vn / Exp(-0.5 * @dn * @dn);
WHILE @i < @NumRects BEGIN
INSERT INTO [dbo].[RndZigguratNor]
([kn])
VALUES (0);
SET @i += 1;
END
UPDATE [dbo].[RndZigguratNor]
SET kn = @dn / @q * @m1
,wn = @q / @m1
,fn = 1.0
WHERE PointId = 0;
UPDATE [dbo].[RndZigguratNor]
SET wn = @dn / @m1
,fn = Exp(-0.5 * @dn * @dn)
WHERE PointId = 127;
SET @i = @NumRects - 2;
WHILE @i > 0 BEGIN
SET @dn = SQRT(-2.0 * LOG(@vn / @dn + EXP(-0.5 * @dn * @dn)));
UPDATE [dbo].[RndZigguratNor]
SET kn = @dn / @tn * @m1
WHERE PointId = @i + 1;
SET @tn = @dn;
UPDATE [dbo].[RndZigguratNor]
SET wn = @dn / @m1
,fn = EXP(-0.5 * @dn * @dn)
WHERE PointId = @i;
SET @i -= 1;
END;
RETURN;
END TRY
BEGIN CATCH
PRINT 'Error: ' + CONVERT(varchar(50), ERROR_NUMBER()) +
', Severity: ' + CONVERT(varchar(5), ERROR_SEVERITY()) +
', State: ' + CONVERT(varchar(5), ERROR_STATE()) +
', Procedure: ' + ISNULL(ERROR_PROCEDURE(), '-') +
', Line: ' + CONVERT(varchar(5), ERROR_LINE());
PRINT ERROR_MESSAGE();
END CATCH;
END
GOGenerating RNOR values
-- =============================================
-- Author: SCP - MSSQLTips
-- Create date: 20250719
-- Description: Ziggurat RNOR
-- =============================================
CREATE OR ALTER PROCEDURE [dbo].[uspRandGenZigguratRNor]
(@Points int)
WITH EXECUTE AS CALLER
AS
BEGIN;
SET NOCOUNT ON;
BEGIN TRY
TRUNCATE TABLE [dbo].[RndGenData];
IF (SELECT COUNT(*) FROM [dbo].[RndZigguratNor]) = 0
EXEC [dbo].[uspRandGenZigguratRNorIni];
DECLARE @shr3 bigint
,@jsr bigint = FLOOR(RAND(CHECKSUM(NEWID())) * 2147483647)
,@kn bigint
,@src smallint
,@wn float
,@fn float
,@fnPrevious float
,@x float
,@y float
,@r float = 3.442619855899
,@hz int
,@iz bigint
,@rectangles int
,@i int = 0
,@uni float;
SET @rectangles = (SELECT COUNT(*) - 1
FROM [dbo].[RndZigguratNor]);
WHILE @i < @Points BEGIN
SET @src = 0;
SELECT @shr3 = shr3
,@jsr = jsr_new
,@hz = hz
,@iz = iz
,@uni = uni
FROM [dbo].[tvfRndGenSHR3] (@jsr,@rectangles);
SELECT @kn = kn
,@wn = wn
,@fn = fn
FROM [dbo].[RndZigguratNor]
WHERE [PointId] = @iz;
IF ABS(@hz) < @kn AND @iz <> 0 BEGIN
SET @x = @hz * @wn;
IF @fn < EXP(-0.5 * @x * @x)
SET @y = @fn;
ELSE
SET @y = EXP(-0.5 * @x * @x);
END ELSE BEGIN
SET @src = 3;
WHILE 1 = 1 BEGIN
SELECT @shr3 = shr3
,@jsr = jsr_new
,@hz = hz
,@iz = iz
,@uni = uni
FROM [dbo].[tvfRndGenSHR3] (@jsr,@rectangles);
SELECT @kn = kn
,@wn = wn
,@fn = fn
FROM [dbo].[RndZigguratNor]
WHERE [PointId] = @iz;
SET @x = @hz * @wn;
SET @y = EXP(-0.5 * @x * @x);
IF @iz = 0 BEGIN
SET @src = 5;
WHILE @y + @y < @x * @x OR @y = 1 BEGIN
SELECT @x = -LOG(uni) / @r
,@jsr = jsr_new
FROM dbo.[tvfRndGenSHR3] (@jsr,@rectangles);
SELECT @y = -LOG(uni)
,@jsr = jsr_new
FROM dbo.[tvfRndGenSHR3] (@jsr,@rectangles);
END
IF @hz > 0
SET @x = @r + @x;
ELSE
SET @x = -@r - @x;
SET @y = EXP(-0.5 * @x * @x);
BREAK;
END ELSE BEGIN
SET @src = 7;
SELECT @fnPrevious = fn
FROM [dbo].[RndZigguratNor]
WHERE [PointId] = @iz - 1;
IF @fn + (@uni * (@fnPrevious - @fn)) < EXP(-0.5 * @x * @x) BEGIN
SET @y = EXP(-0.5 * @x * @x);
BREAK;
END;
END
IF ABS(@hz) < @kn
BREAK;
END
END
INSERT INTO [dbo].[RndGenData]
([PointId]
,[X]
,[Y]
,[src])
VALUES (@i
,@x
,@y
,@src);
SET @i += 1;
END
DECLARE @xMean float;
SELECT @xMean = AVG(x) FROM [dbo].[RndGenData];
DECLARE @xStd float;
SELECT @xStd = STDEV(x) FROM [dbo].[RndGenData];
SELECT COUNT(*) AS n
,AVG(x) AS mean
,STDEV(x) AS std
,SUM(POWER((x - @xMean) / @xStd, 3)) / COUNT(*) AS skewness
,SUM(POWER((x - @xMean) / @xStd, 4)) / COUNT(*) AS kurtosis
FROM [dbo].[RndGenData];
RETURN;
END TRY
BEGIN CATCH
PRINT 'Error: ' + CONVERT(varchar(50), ERROR_NUMBER()) +
', Severity: ' + CONVERT(varchar(5), ERROR_SEVERITY()) +
', State: ' + CONVERT(varchar(5), ERROR_STATE()) +
', Procedure: ' + ISNULL(ERROR_PROCEDURE(), '-') +
', Line: ' + CONVERT(varchar(5), ERROR_LINE());
PRINT ERROR_MESSAGE();
END CATCH;
END
GOHistogram
-- =============================================
-- Author: SCP - MSSQLTips
-- Create date: 20250809
-- Description: Histogram
-- =============================================
CREATE OR ALTER PROCEDURE [dbo].[uspRandGenHistogram]
(@BarWidth float = 0.09
,@Ratio float = 100)
WITH EXECUTE AS CALLER
AS
BEGIN;
BEGIN TRY
DECLARE @Histogram
TABLE (x float
,y int
,id int DEFAULT 0);
INSERT INTO @Histogram
(x
,y)
SELECT round(X,1)
,COUNT(*)
FROM [dbo].[RndGenData]
GROUP BY round(X,1)
ORDER BY 1;
DECLARE @Scale float = (SELECT COUNT(*) FROM [dbo].[RndGenData]) / @Ratio;
SELECT id
,geometry::CollectionAggregate(SpatialLocation) AS [Geom]
FROM (SELECT id
,geometry::STPolyFromText(
'POLYGON((' +
CAST(X - @BarWidth/2 AS VARCHAR(10)) + ' 0, ' +
CAST(X - @BarWidth/2 AS VARCHAR(10)) + ' ' + CAST(ROUND(y / @Scale, 2) AS VARCHAR(10)) + ', ' +
CAST(X + @BarWidth/2 AS VARCHAR(10)) + ' ' + CAST(ROUND(y / @Scale, 2) AS VARCHAR(10)) + ', ' +
CAST(X + @BarWidth/2 AS VARCHAR(10)) + ' 0, ' +
CAST(X - @BarWidth/2 AS VARCHAR(10)) + ' 0))',0) AS SpatialLocation
FROM @Histogram) AS D
GROUP BY id;
RETURN;
END TRY
BEGIN CATCH
PRINT 'Error: ' + CONVERT(varchar(50), ERROR_NUMBER()) +
', Severity: ' + CONVERT(varchar(5), ERROR_SEVERITY()) +
', State: ' + CONVERT(varchar(5), ERROR_STATE()) +
', Procedure: ' + ISNULL(ERROR_PROCEDURE(), '-') +
', Line: ' + CONVERT(varchar(5), ERROR_LINE());
PRINT ERROR_MESSAGE();
END CATCH;
END
GOExample 1
Let´s starting generating 10,000 random normal points.
-- MSSQLTips (TSQL)
EXEC [dbo].[uspRandGenZigguratRNor] @Points = 10000;
GOResulting in
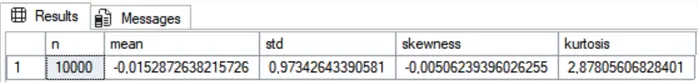
Observe the values and the ideal ones are mean = 0, std = 1, skewness = 0, and kurtosis = 3. If you are not comfortable with the values, run again or increase the number of points.
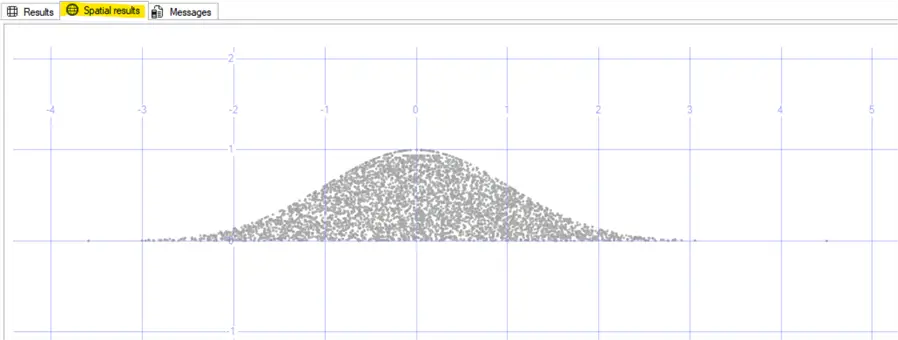
To have a look at the Spatial results of our data run the following. There is a limitation in how much data points can be shown on the Spatial results tab.
-- MSSQLTips (TSQL)
SELECT top 5000 [PointId]
,[X]
,[Y]
,[src]
,([geometry]::Point([x],[y],(0))).STBuffer(0.01)
FROM [MsSqlTips].[dbo].[RndGenData];
GOResulting in
Or if you want to see the histogram:
-- MSSQLTips (TSQL)
EXECUTE [dbo].[uspRandGenHistogram]
GOResulting in
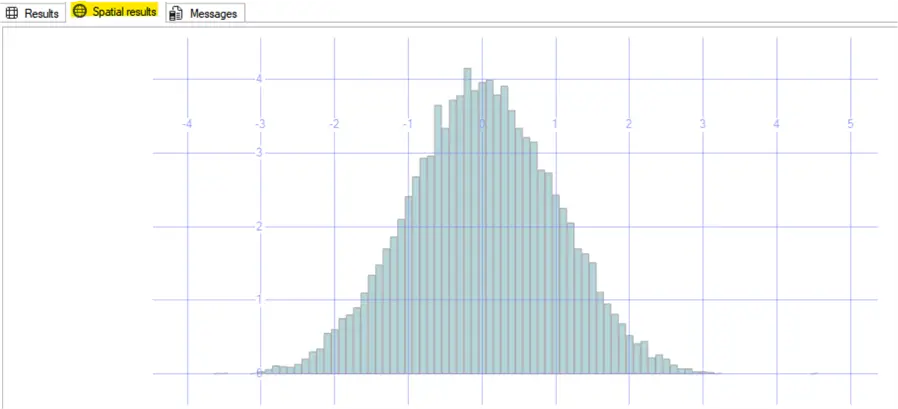
You can adjust the generated values stored at the table RndGenData applying to the x values the mean as x-offset and the standard deviation as x-scale and them obtain the data that you need.
Random Human Height Values Example
Let´s say that I need a table of random values of human height distribution, I will assume a standard deviation of 7 cm and a mean of 170 cm.
-- MSSQLTips (TSQL)
UPDATE [dbo].[RndGenData]
SET [x] = [x] * 7 + 170;
GO
EXECUTE [dbo].[uspRandGenHistogram] 0.09,1000;
GOResulting in
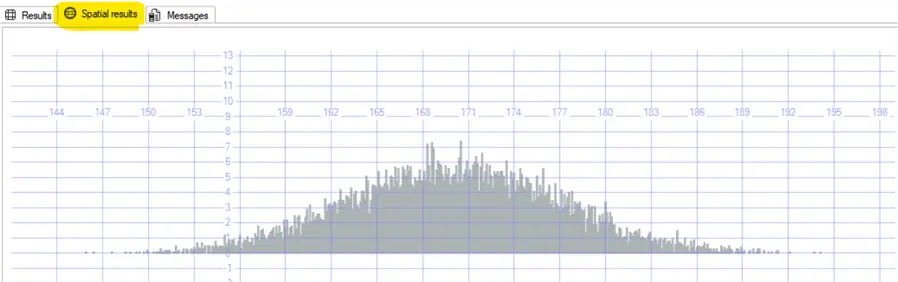
Next Steps

 for normal and calculated by
for normal and calculated by  exponential tables.
exponential tables.
