Problem
SQL Server Linked servers can introduce a security risk if not configured properly. Some settings out of the box can make Linked Servers more secure, like using proper logins mappings. In this article, we look at how to enable encryption between linked servers.
Solution
In this tip, we provide information for a security review and/or SQL Server patching process and describe the steps how SQL Server linked servers can be secured by encrypting network traffic.
Linked Servers Default Drivers
By default, SQL Server Linked Servers that provide connections to another SQL Server use one of the old legacy drivers: the SQL Server Native Client (SQLNCLI or SQLNCL11) is one of them.
Let’s look at the basic Linked Server properties. Let’s create a linked server that will connect to another SQL Server using SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS). Note: An older version of SQL Server is used for this demonstration, so results might be different in your environment:
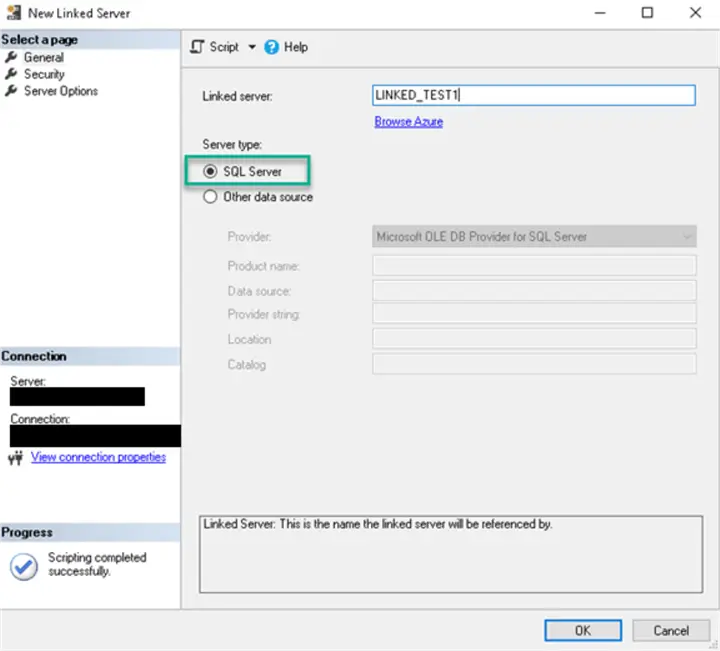
Use the sys.servers catalog view to see if the old SQLNCLI (SQL Native Client) provider is used by default:
USE [master]
GO
SELECT name, product, provider from sys.servers WHERE name = N'LINKED_TEST1'
GO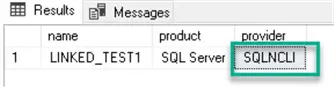
The Latest MSOLEDBSQL Driver Versions Support and SQL Server Compatibility
The SQL Server Native Client driver is not installed during the latest version of SQL Server installation (for example, when you install SQL Server 2022). The SQL Server Native Client driver (SQLNCLI11) and another old SQLOLEDB provider are not recommended by Microsoft to use for new development.
Read more about Support Policies for the SQL Server Native Client. Below are a few important notes from the Microsoft documentation:
- In the Driver history article Microsoft recommends to use newer providers/drivers (Microsoft ODBC Driver for SQL Server, Microsoft OLE DB Driver (MSOLEDBSQL) for SQL Server) instead of the old SQL Server drivers (SQLNCLI/SQLNCLI11, SQLOLEDB) for the new development projects.
- The “Support Lifecycle exception” section of the Support Policies article mentions the limited support to the SQL Server Native Client 11.0. The exception is the older provider usage with SQL Server Linked Servers.
Ensure the driver and SQL Server version are supported. Use the following OLE DB driver version or higher on these versions of SQL Server:
- SQL Server 2014/2016/2017 – 18.0 or higher.
- SQL Server 2019 – 18.2 or higher.
- SQL Server 2022 – 18.6 or higher.
- MSOLEDBSQL driver 19.3.5 is the latest and supported on SQL Server versions starting with SQL Server 2016.
- Full support matrix: Support policies for OLE DB Driver for SQL Server – OLE DB Driver for SQL Server | SQL version support.
- Support matrix for the drivers versions on different Operating Systems versions
Note: Even though the older provider is still supported with SQL Server Linked Servers, it’s still a good idea to use the latest drivers. The exceptions are for remote servers and linked servers created by/for the Replication.
Known Issues
Microsoft OLE DB Driver for SQL Server known issues:
- Microsoft supports MSOLEDBSQL19 provider for the linked servers only starting with SQL Server 2022.
- At this point, MSOLEDBSQL19 provider for the linked servers requires encryption support and a valid certificate (from a trusted Certificate Authority, not the self-signed one).
Check out the note about Linked servers and MSOLEDBSQL19 here.
Note: Even though Microsoft only supports MSOLEDBSQL19 provider for linked servers on the newer versions of SQL Server, you should be able to configure it on the older versions of SQL Server as well.
Additional steps might be required:
- DTC service configuration and distributed transaction start when there is a cross-server join.
- Some code changes might be required to the collations for the character fields when there is a cross server join.
This tip does not cover detailed steps for these additional configurations as this is not an officially supported solution.
Network Traffic Encryption with MSOLEDBSQL19
The new Microsoft OLE DB Driver for SQL Server (MSOLEDBSQL19) has some new features, including Encryption and certificate validation in OLE DB. Also, starting with version 19.2, the new driver supports TDS 8.0 (strict encryption) and TLS 1.3. This makes this driver more secure than the previous versions.
The next sections describe the steps required to install and configure the new MSOLEDBSQL19 driver.
Prerequisites (Trusted Certificate)
In order to use MSOLEDBSQL19 with SQL Server Linked Servers, SQL Server needs to be configured with a certificate issued by a trusted certificate authority.
The certificate creation and configuration steps can be found here.
Here are some points that could be useful when a certificate is used:
- SQL Server service requires a restart.
- Encryption does not have to be “forced” for the rest of the SQL Server traffic, but it will be “forced” for the linked server.
- SQL Server service account requires “Read” permissions to the certificate.
- Note: If there is a mismatch during the linked server creation between @datasrc (“Data Source”) parameter value and the Common Name (CN) in the certificate, then linked server may not work. The solution is either to recreate the linked server with the same server’s name as the certificate’s CN or to add Subject Alternate Name to the certificate during its creation. (This article has more information about SQL Server certificates requirements and troubleshooting.) Here is an example of the @datasrc (“Data Source”) parameter for the server that has a Fully Qualified Domain name in the certificate:

If we used this linked server creation i.e. host name for the Data Source (“LINKED_TEST1\DEMO1” vs. “LINKED_TEST1.domain.com\DEMO1”), then during the linked server testing and usage, we would get this error:

OLE DB provider "MSOLEDBSQL19" for linked server "LINKED_TEST1" returned message "Client unable to establish connection".
Msg -2146893022, Level 16, State 1, Line 0
SSL Provider: The target principal name is incorrect.MSOLEDBSQL19 Installation and Linked Server Configuration
The latest version of the Microsoft OLE DB Driver for SQL Server can be downloaded from this page.
In the following steps, we will use server “DEMO1” to create the linked server and use server “LINKED_TEST1” as the linked server data source:
- Step 1: Install MSOLEDBSQL19 driver on DEMO1 host.
- Step 2: Configure the driver for secure/encrypted connection through the registry on DEMO1 host as per this article:
- Force protocol encryption:
- Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\MSSQLServer\Client\SNI19.0\GeneralFlags\Flag1
- Value=1
- Trust Server Certificate:
- Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\MSSQLServer\Client\SNI19.0\GeneralFlags\Flag2
- Value=1
- Force protocol encryption:
- Step 3: On DEMO1 SQL Server, set MSOLEDBSQL19 driver’s property to “Allow inprocess” using this script:
USE [master]
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_MSset_oledb_prop N'MSOLEDBSQL19', N'AllowInProcess', 1
GOYou can do it with SSMS as well:

- Step 4: Create a linked server to the LINKED_TEST1.domain.com\DEMO1 SQL Server:
EXEC master.dbo.sp_addlinkedserver @server = N'LINKED_TEST1',
@srvproduct=N'',
@provider=N'MSOLEDBSQL19',
@datasrc=N'LINKED_TEST1.domain.com\DEMO1'Note: You will also need to add linked server logins under “Security” tab of the linked server and grant appropriate permissions on the linked server itself (LINKED_TEST1.domain.com\DEMO1 in our example script).
Make sure that only authorized users have access to the linked server:

Test Environment Setup
After creating our linked server, we’ll set up a test database and logins.
LINKED_TEST1 SQL Server
These steps are performed on the LINKED_TEST1 SQL Server:
Step 1: Create SQL Server login:
USE [master]
GO
CREATE LOGIN [user2] WITH PASSWORD=N'<NNNNNNNN>', DEFAULT_DATABASE=[master], CHECK_EXPIRATION=ON, CHECK_POLICY=ON
GOStep 2: Create a test database and a table, grant access to this table to the new login:
CREATE DATABASE [_demo_lnk_1]
GO
USE [_demo_lnk_1]
GO
CREATE USER user2 FROM LOGIN user2
GO
CREATE TABLE tbl_demo_lnk (c1 int , c2 char(2))
GO
INSERT INTO tbl_demo_lnk VALUES (1,'AB')
INSERT INTO tbl_demo_lnk VALUES (2,'CD')
GO
GRANT SELECT ON tbl_demo_lnk TO user2
GODEMO1 SQL Server
These steps will be performed on the DEMO1 SQL Server:
Step 1: Create a SQL Server login:
USE [master]
GO
CREATE LOGIN [user1] WITH PASSWORD=N'<NNNNNNNNN>', DEFAULT_DATABASE=[master], CHECK_EXPIRATION=ON, CHECK_POLICY=ON
GOStep 2: Create a linked server login:
USE [master]
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_addlinkedsrvlogin
@rmtsrvname = N'LINKED_TEST1',
@locallogin = N'user1',
@useself = N'False',
@rmtuser = N'user2',
@rmtpassword = N'<NNNNNNN>'
GOTesting
To test our connection, we need to run a test query using SSMS as the user1 from DEMO1 SQL Server.
Before running the query to the linked server, we must start a “watcher” query on LINKED_TEST1 SQL Server. This is done because the linked server query may run very fast, and we may not be able to capture connection information if we switch between the windows.
Connect with SSMS to the LINKED_TEST1 SQL Server and start the “watcher” query. This query will run until it captures the connection that we are monitoring. If it doesn’t stop (filter information won’t match the connection information, for example), then stop it manually. Start the “watcher” query on LINKED_TEST1:
SET NOCOUNT ON
CREATE TABLE #watcher (connect_time datetime,
net_transport nvarchar(50),
protocol_type nvarchar(50),
encrypt_option nvarchar(50),
auth_scheme nvarchar(50),
login_name nvarchar(50),
[host_name] nvarchar(50),
[program_name] nvarchar(150)
)
a:
INSERT INTO #watcher
SELECT c.connect_time, c.net_transport, c.protocol_type, c.encrypt_option, auth_scheme, login_name, [host_name], s.[program_name]
FROM sys.dm_exec_connections c
JOIN sys.dm_exec_sessions s ON c.session_id=s.session_id
WHERE
--comment out the next line if you are not sure if the connection is encrypted or not
encrypt_option = 'TRUE' OR
login_name like 'user%' OR
host_name like 'DEMO1%'
IF (SELECT @@rowcount) = 0
BEGIN
WAITFOR DELAY '00:00:00.011'
GOTO a
END
SELECT * FROM #watcher
DROP TABLE #watcherAfter the “watcher” started in another window, run the query from the DEMO1 SQL Server. Execute it multiple times to make sure the “watcher” has enough time to get the connection information:
SET NOCOUNT ON
SELECT * FROM LINKED_TEST1.[_demo_lnk_1].dbo.tbl_demo_lnk
GO 10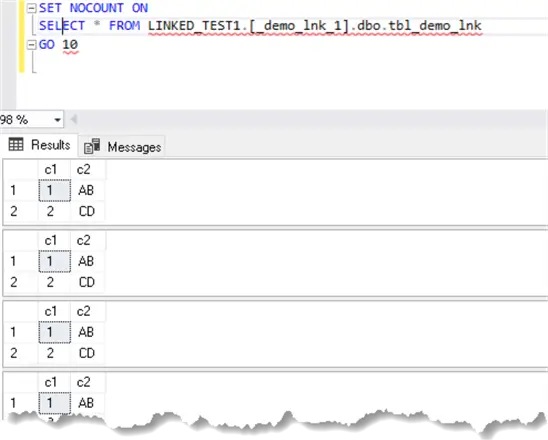
You may need to run the test query on DEMO1 a couple of times if you still don’t see any output or decrease the delay in the “watcher” query.
Make sure you run this in your test environment first.
We can see the SQL login connection is encrypted after switching to a secure driver:

Conclusion
Security reviews and patching often overlook database drivers. There were several SQL Server security patches related to the SQL Server Native Client OLE DB provider released recently, so adding the drivers versions review is a good step to add to your DBA procedures.
The new drivers make your system less vulnerable to attacks and it’s a good idea to keep an eye on the new features (for example, stronger protocols support in case with MSOLEDBSQL19).
SQL Server logins connections encryption during linked servers’ queries is also an excellent improvement to your SQL Servers security.
Next Steps
Review your linked servers’ drivers (with the exception of the replication linked/remove servers) and make sure that you take advantage of the latest security features.
If you are still on SQL Server 2019 or earlier, you may want to start planning a transition to the new providers.
- Older drivers might still be in use.
- Linked servers’ dependencies (for example, SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) packages connections) may be in use, so it is important to review and test your systems before removing any old database drivers.
- Older versions of drivers are supported for linked servers, but it’s better to replace them for services like SSIS for example.
Additional Reading
- SQL Server Linked Server basics
- Create linked servers
- SQL Server Linked Servers Tips, Tutorials, Webinars and more
- Linked Servers Security
- How to set and use encrypted SQL Server connections (sqlshack.com)
- Configure SQL Server Database Engine for encryption
- Linked Servers Security Configuration
- Read about end-to-end Oracle and SQL Server connections encryption
- Find other security-related tips


