By: John Sterrett | Comments (9) | Related: > Dates
Problem
I saw this tip on new date types provided with SQL Server 2008. I am interested in using the datetimeoffset because we support end users around the world. How do I convert the datetime data types to the datetimeoffset data type in SQL Server 2008?
Solution
Converting data in a datetime column to datetimeoffset is straight forward, but it will probably give you an unexpected conversion. By default the time zone offset is zero. Unless all your data resides in Iceland or the other countries with a time zone of UTC-0 this is going to be a problem.
The following example shows you how to convert your time through a set of scripts.
Note: DateTimeOffset is a new feature in SQL Server 2008. If your instance of SQL Server is before SQL Server 2008 this code will not work.
Step 0 - Create an example table and insert sample date time values as shown in the script below.
CREATE TABLE dbo.DateTimeDemo (DateTimeExample DATETIME, -- current date type DateTimeOffsetExample DATETIMEOFFSET) -- new date type -- Insert current date to convert to datetimeoffset INSERT INTO dbo.DateTimeDemo (DateTimeExample) VALUES (GETDATE()) GO
Step 1 - We will convert the DateTimeExample column to DateTimeOffset data type and store it in the DateTimeOffsetExample column. You will notice that the offset is zero. This is the default. Unless your data resides in Iceland or another country with a time zone of UTC-0 this is going to be a problem. We will show you this step because we want to make sure you don't do this in your conversion. We will correct the time zone a little later in the demo.
UPDATE dbo.DateTimeDemo SET DateTimeOffsetExample = DateTimeExample -- time zone = 00:00 GO -- Let's look at our conversion. You should see (+00:00) time zone SELECT DateTimeExample, DateTimeOffsetExample FROM dbo.DateTimeDemo
You should see something similar to the screenshot provided below.
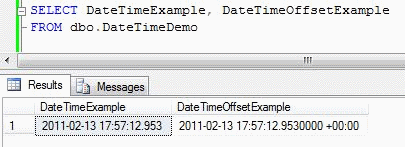
Step 2 - For this example we will assume that the data resides on the east coast. We will convert the data to East Standard Time. This is done by converting the data to a varchar and appending the time zone value.
UPDATE dbo.DateTimeDemo
SET DateTimeOffsetExample =
CONVERT(varchar(50), DateTimeExample, 120)+ ' -5:00'
SELECT DateTimeExample,
DateTimeOffsetExample
FROM dbo.DateTimeDemo
You should see something similar to the screenshot provided below.
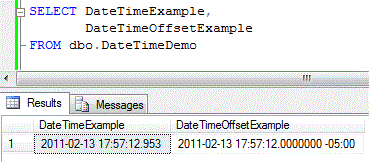
Step 3 Now that the DateTimeOffset is stored with the correct time zone lets show the time to the user as local time. In this example we will assume that the application us running by a user in Central Standard Time. We will use the SWITCHOFFSET function to change the time.
SELECT DateTimeExample,
DateTimeOffsetExample,
SWITCHOFFSET (DateTimeOffsetExample , '-06:00')
AS DateTimeSavingsOffsetExample
FROM dbo.DateTimeDemo
You should see something similar to the screenshot provided below. Notice that the time shown for the DateTimeSavingsOffsetExample column is in Central Standard Time (1 hour behind Eastern Standard Time) and the offset changed by one hour.
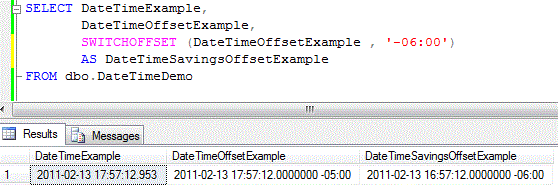
Next Steps
- If you have users in different time zones, consider this tip as a means to manage the time zone specific date\times.
- Experiment with the code from this tip based on the time zones your applications support to see what sorts of code changes would be necessary.
- Check out these related tips:
About the author
 John Sterrett is a DBA and Software Developer with expertise in data modeling, database design, administration and development.
John Sterrett is a DBA and Software Developer with expertise in data modeling, database design, administration and development.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips






