By: John Garcia | Comments (6) | Related: More > Database Administration
Problem
There's an excellent tip about SQL Server Services, Checking SQL Service Status - An Evolution Part 1, by Robert Pearl. Indeed, this a helpful article, but a very critical piece was missing from it: Which user runs the service. I needed to check which account was associated with the SQL Services very quickly. Not only is the DBA responsible for the running status of the Services, they are responsible that the Service is running with a proper owner.
Solution
Although with SQL Server 2012 a new DMV is used to find the status of the services, sys.dm_server_services: You will be able to query the ServiceName, Startup_Type, Startup_Type_Desc, Status, Status_Desc,Process_ID, and Last_Startup_Time.
However, the code below will give us more detail information for each service(s). There's more flexibility with service control manager, SC, since you can use different options that you may require.
We will use the xp_cmdshell and sc.exe for the code below and we will pass the qc option, which queries the configuration information for the service. You can also use the queryex option, which queries the extended status for a service, this option will give you the Process_ID if needed.
Here are all the options for the SC command:
DESCRIPTION:
SC is a command line program used for communicating with the Service Control Manager and services.
USAGE:
sc <server> [command] [service name] <option1> <option2>...
The option <server> has the form "\\ServerName"
Further help on commands can be obtained by typing: "sc [command]"
Commands:
- query - Queries the status for a service, or enumerates the status for types of services.
- queryex - Queries the extended status for a service, or enumerates the status for types of services.
- start - Starts a service.
- pause - Sends a PAUSE control request to a service.
- interrogate - Sends an INTERROGATE control request to a service.
- continue - Sends a CONTINUE control request to a service.
- stop - Sends a STOP request to a service.
- config - Changes the configuration of a service (persistent).
- description - Changes the description of a service.
- failure - Changes the actions taken by a service upon failure.
- failureflag - Changes the failure actions flag of a service.
- sidtype - Changes the service SID type of a service.
- privs - Changes the required privileges of a service.
- qc - Queries the configuration information for a service.
- qdescription - Queries the description for a service.
- qfailure - Queries the actions taken by a service upon failure.
- qfailureflag - Queries the failure actions flag of a service.
- qsidtype - Queries the service SID type of a service.
- qprivs - Queries the required privileges of a service.
- qtriggerinfo - Queries the trigger parameters of a service.
- qpreferrednode - Queries the preferred NUMA node of a service.
- delete - Deletes a service (from the registry).
- create - Creates a service. (adds it to the registry).
- control - Sends a control to a service.
- sdshow - Displays a service's security descriptor.
- sdset - Sets a service's security descriptor.
- showsid - Displays the service SID string corresponding to an arbitrary name.
- triggerinfo - Configures the trigger parameters of a service.
- preferrednode - Sets the preferred NUMA node of a service.
- GetDisplayName - Gets the DisplayName for a service.
- GetKeyName - Gets the ServiceKeyName for a service.
- EnumDepend - Enumerates Service Dependencies.
The following commands don't require a service name:
- sc <server> <command> <option>
- boot - (ok | bad) Indicates whether the last boot should be saved as the last-known-good boot configuration
- Lock - Locks the Service Database
- QueryLock - Queries the LockStatus for the SCManager Database
T-SQL Script to Check the SQL Server Services Owner
Below is a script that calls xp_cmdshell and the sc.exe application to check the status for the SQL Server services:
SET NOCOUNT ON
-- Temporary Tables
CREATE TABLE #tmpServices
(oOutput VARCHAR(1024))
CREATE TABLE #tmpServicesDetail
(oOutput VARCHAR(1024))
CREATE TABLE #tmpServicesFinal
(ServiceName VARCHAR(100),
ServiceOwner VARCHAR(100),
ServiceStartTp VARCHAR(100),
ServiceBinary VARCHAR(150))
-- sc query is used to query the entire service control manager and then filters
-- by anything with "SQL" in it's name. /I option ignores Case.
INSERT INTO #tmpServices EXEC xp_cmdshell 'sc query |find /I "sql"|find /I "service_name"'
-- Remove NULL records
DELETE FROM #tmpServices WHERE oOutput IS NULL
-- Cursor variables
DECLARE @curServNm VARCHAR(100)
DECLARE @cCMD VARCHAR(100)
DECLARE @cBinary VARCHAR(150)
DECLARE @cOwner VARCHAR(100)
DECLARE @cStartTp VARCHAR(100)
DECLARE cCursor CURSOR FOR
SELECT RTRIM(LTRIM(SUBSTRING(oOutPut,PATINDEX('%:%', oOutPut)+1, LEN(oOutPut)) )) AS ServiceName
FROM #tmpServices
OPEN cCursor
FETCH NEXT FROM cCursor INTO @curServNm
WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0
BEGIN
-- You can use different Options to query SC. For Example, use sc queryex to pull PID
SET @cCMD = 'sc qc "#SERVICENAME#"'
SET @cCMD = REPLACE(@cCMD, '#SERVICENAME#', @curServNm)
INSERT INTO #tmpServicesDetail EXEC xp_cmdshell @cCMD
DELETE FROM #tmpServicesDetail WHERE oOutput IS NULL
-- To extract any other piece of data, you should modify/add variable:
-- For Example: If I use sc queryex to get PID, then I would make the following changes:
-- Then You can Insert it into Temp Table
-- SELECT @cPID = RTRIM(LTRIM(SUBSTRING(oOutPut,PATINDEX('%:%', oOutPut)+1, LEN(oOutPut)) ))
-- FROM #tmpServicesDetail
-- WHERE PATINDEX('%PID%', oOutPut) > 0
SELECT @cBinary = RTRIM(LTRIM(SUBSTRING(oOutPut,PATINDEX('%:%', oOutPut)+1, LEN(oOutPut)) ))
FROM #tmpServicesDetail
WHERE PATINDEX('%BINARY_PATH_NAME%', oOutPut) > 0
SELECT @cOwner = RTRIM(LTRIM(SUBSTRING(oOutPut,PATINDEX('%:%', oOutPut)+1, LEN(oOutPut)) ))
FROM #tmpServicesDetail
WHERE PATINDEX('%SERVICE_START_NAME%:%', oOutPut) > 0
SELECT @cStartTp = RTRIM(LTRIM(SUBSTRING(oOutPut,PATINDEX('%:%', oOutPut)+1, LEN(oOutPut)) ))
FROM #tmpServicesDetail
WHERE PATINDEX('%START_TYPE%:%', oOutPut) > 0
INSERT INTO #tmpServicesFinal (
ServiceName,
ServiceOwner,
ServiceStartTp,
ServiceBinary)
VALUES(
@curServNm,
@cOwner,
@cStartTp,
@cBinary)
FETCH NEXT FROM cCursor INTO @curServNm
END
CLOSE cCursor
DEALLOCATE cCursor
-- Final result set
SELECT * FROM #tmpServicesFinal
-- Clean-up objects
IF OBJECT_ID('TempDB.dbo.#tmpServices') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE #tmpServices
IF OBJECT_ID('TempDB.dbo.#tmpServicesDetail') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE #tmpServicesDetail
IF OBJECT_ID('TempDB.dbo.#tmpServicesFinal') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE #tmpServicesFinal
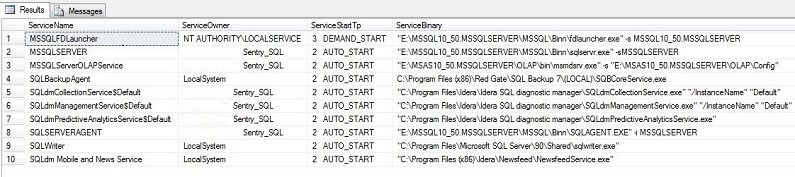
Here are some sample results from my test environment:
Next Steps
- Familiarize yourself with the SC windows command and run through some tests in your environment.
- Walk through the code and modify it to meet your needs.
- Check out these related resources:
About the author
 John Garcia is a SQL Server Database Administrator in Alpharetta, GA with over 12 years of experience.
John Garcia is a SQL Server Database Administrator in Alpharetta, GA with over 12 years of experience. This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips






