By: Ahmad Yaseen | Comments (9) | Related: > Maintenance
Problem
One of the most important aspects of SQL Server database maintenance is maintaining indexes. Over time indexes can become fragmented, so to fix fragmentation indexes can either be rebuilt or reorganized and this is usually dependent upon the level of fragmentation. Index maintenance is usually a scheduled task and recently we ran into an issue where the job failed on one of the tables showing that the index can't be reorganized due to page lock issues. What is this page lock issue and why does it prevent us from reorganizing the index?
Solution
Assume we have a table named Product that requires index reorganization. If you check the index maintenance job history, the below error will be shown explaining that the reorganizing process can't complete due to page level lock issue. Here is the actual error message:
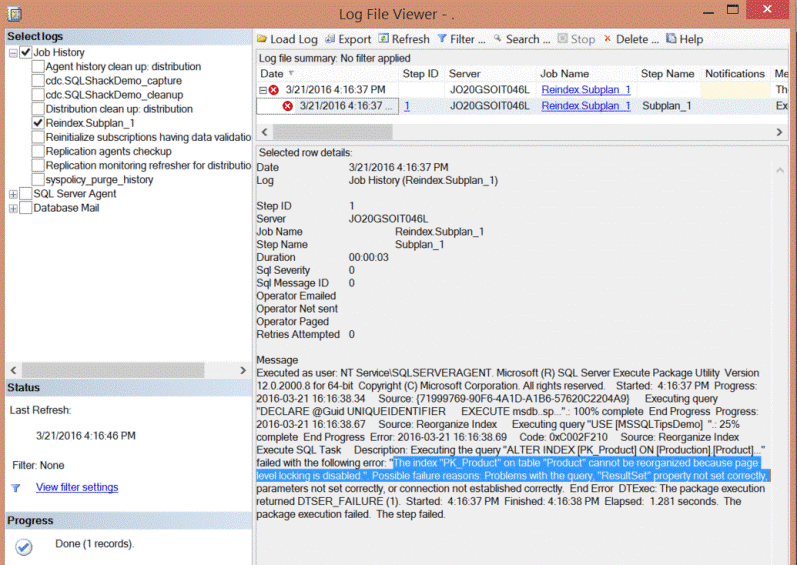
Review Index Settings on Table
Letís query the problematic tableís indexes by querying the sys.indexes system table joined with the sys.objects table as follows:
Select Indx.name, Indx.type_desc, Indx.is_disabled, Indx.allow_page_locks, Indx .allow_row_locks from sys.indexes Indx left outer join sys.objects OBJ on OBJ.object_id=Indx.Object_id where OBJ.name ='Product'
You can see from the result below that the allow_page_locks and allow_row_locks options are disabled for that index. The specific error we saw above was related to page level locking.
What are Row Level and Page Level Locks
By default the allow-page-lock and allow-row-lock options are enabled, which allows SQL Server to choose between the three locking levels: row-level locks, page-level locks, and table-level locks. By disabling these options, you limit the type of locking that can occur on the object.
The purpose of these different locking mechanisms is to limit how much of the table/index is locked at any one time, therefore allowing concurrent access to different parts of the table/index.
So, it is better to enable both allow-page-lock and allow-row-lock in order to let SQL Server decide the best locking option for each transaction.
Enable Row Level and Page Level Locks
In order to resolve the index reorganization issue, we will enable the row and page level locking by altering the index as shown below:
USE MSSQLTipsDemo GO ALTER INDEX [PK_Product] ON [Production].[Product] SET ( ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON ) ALTER INDEX [PK_Product] ON [Production].[Product] SET ( ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON )
We can also enable the row and page level locking using SSMS. If you right click on the Index and select Properties and go to the Options page you can change the values to True as follows:
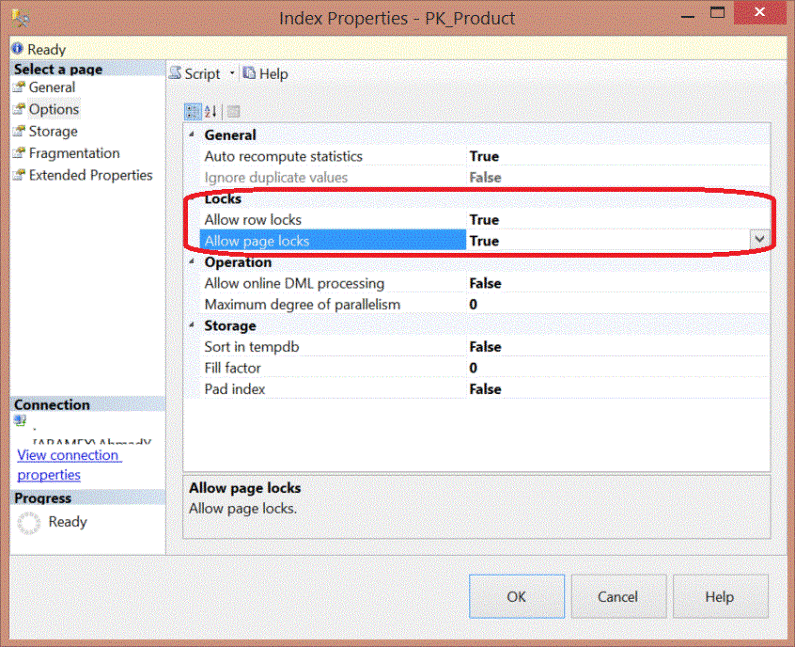
If we check the index properties again using the T-SQL code above, we will see the following result:
Retry Index Maintenance After Change
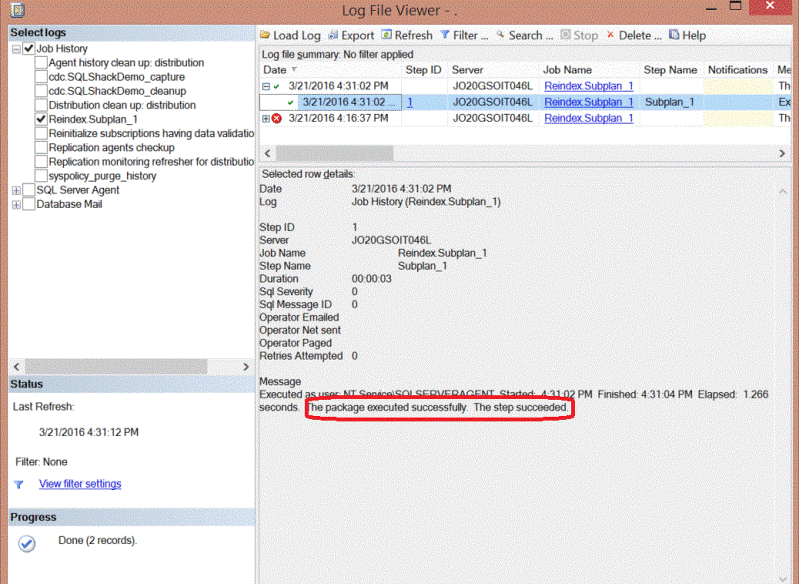
If we run the index maintenance job again, it completes successfully as shown below:
Next Steps
- It is better to keep the row level and page level locking options enabled, unless there is a specific need to disable these options.
- Check out these SQL Server Locking and Blocking Tips
- Check out these SQL Server Database Maintenance Tips
- Check out these SQL Server Fragmentation Tips
About the author
 Ahmad Yaseen is a SQL Server DBA with a bachelorís degree in computer engineering as well as .NET development experience.
Ahmad Yaseen is a SQL Server DBA with a bachelorís degree in computer engineering as well as .NET development experience.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips






