By: K. Brian Kelley | Comments | Related: > SQL Server Agent
Problem
We have notifications configured to let us know when a backup job fails. However, that doesn’t tell me if we successfully re-ran the backup job and now have a good backup. As a result, trying to determine what databases have outstanding failed backups with no later successful backups is a problem. Is there an easy way to do this?
Solution
If you’re performing SQL Server native backups via SQL Server Agent, there are two tables in msdb that you can query to get information on job runs:
- sysjobs
- sysjobhistory
Determining which jobs belong to backups can be difficult if we’re relying strictly on the job name, especially if there are issues with consistency in the names. The easiest way to deal with this is to ensure we create a job category specifically for backups.
Here’s how you go about it if you’re using the SQL Server Management Studio. First, right click on the Jobs folder under SQL Server Agent. Then select Manage Job Categories:
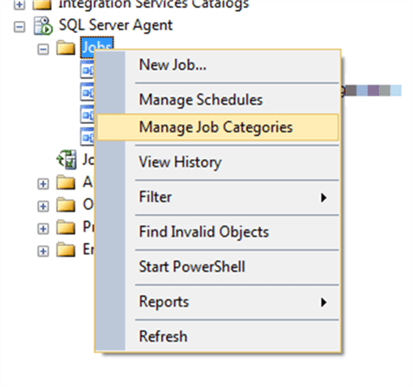
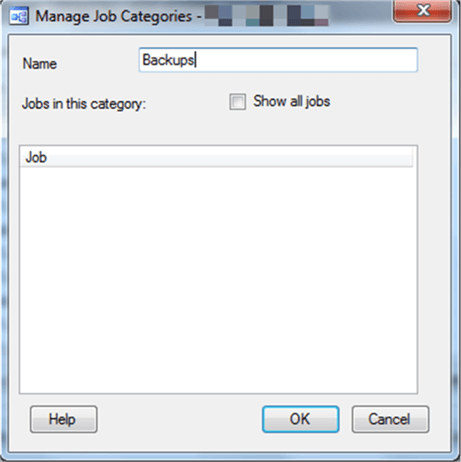
Next, choose to add a category. Type in the name you want to use, such as Backups, and click OK. When you go to create your backup jobs (or if you have existing backup jobs already), make sure they use that category.
Alternately, you could simply add the category using a script. I do this for all my categories when I build a new SQL Server. It ensures consistency:
IF NOT EXISTS(SELECT name FROM msdb.dbo.syscategories WHERE name = 'Backups') EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_add_category @name = 'Backups';
With that new category, we need to add another table: syscategories.
This gets us to the following query:
SELECT j.job_id, j.name
FROM msdb.dbo.sysjobs j
JOIN msdb.dbo.syscategories c
ON j.category_id = c.category_id
JOIN (SELECT h1.job_id, h1.run_status
FROM msdb.dbo.sysjobhistory AS h1
JOIN (SELECT job_id, MAX(instance_id) AS instance_id
FROM msdb.dbo.sysjobhistory
WHERE step_id = 0
GROUP BY job_id) AS h2
ON h1.job_id = h2.job_id AND h1.instance_id = h2.instance_id) AS h
ON j.job_id = h.job_id
WHERE j.[enabled] = 1
AND h.run_status = 0
AND c.[name] = 'Backups';
Why This Works
Let’s step through the WHERE clause first. We’re filtering on three things:
- Enabled jobs (j.[enabled] = 1)
- Jobs that have a failed status (h.run_status = 0)
- Jobs in the Backups category (c.[name] = ‘Backups’)
Once we’ve filtered to that level, we need to be able to identify what was the last attempt to run a particular job. That’s the clause we call h2 in the query above. We’re getting step_id = 0 because that’s the overall result of the job. We can’t retrieve the run_status yet. We need the absolute last result. If we include run_status at this point, and we have multiple run_status values, say one for failed and one for completed successfully, we’ll get two rows because of the way GROUP BY works. Therefore, we get the max, meaning the last execution of the job.
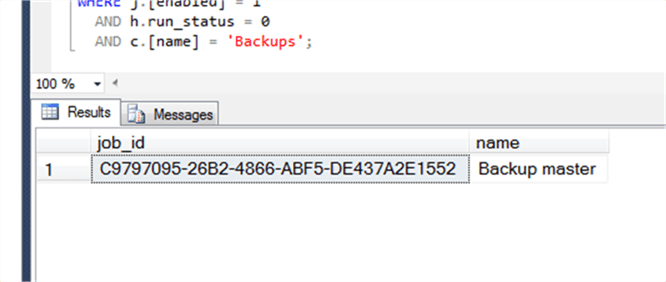
Have each job and its last execution, we join back to sysjobhistory and retrieve the run_status at this point. Then we join to syscategories in order to filter to just backups. Then we apply the filter and what we should have left are the backup jobs which failed the last time they ran:
What This Doesn’t Handle
This method of finding failed backups only encompasses looking at SQL Server Agent. If someone runs a backup outside of the SQL Server Agent Jobs, you won’t have all the information. For instance, if someone gets the failed job notification and then manually backs up the database, say by right-clicking on it in SSMS, then we won’t have this information reflected in the job history. Similarly, if someone ran a backup manually outside of the jobs and that attempt failed, we won’t know. There are other scenarios where backups could be attempted. Anything outside of the SQL Server Agent Job execution won’t be captured. You will have to determine some other way of reconciling the information.
Next Steps
- Learn how to back up all your databases with a single script.
- Create an SSRS report which can show when each database was last backed up.
- Know which databases have not had any backups taken at all.
About the author
 K. Brian Kelley is a SQL Server author and columnist focusing primarily on SQL Server security.
K. Brian Kelley is a SQL Server author and columnist focusing primarily on SQL Server security.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips






