By: Greg Robidoux | Comments (15) | Related: > Replication
Problem
When setting up replication there are many things to think about and many options you can choose from when setting up your publications and subscriptions. In most cases replication is an after thought and not part of the original database or application design, so there may be some required changes that need to be done when replication is setup. The most important part is that the table has a primary key. All tables should have a primary key when they are created, but sometimes this is not addressed and for replication to work this needs to be setup. In addition, if you are using merge replication you need to have a RowGuid column. Also, if you use identity columns you need to make sure the not for replication parameter is turned on.
Luckily when setting up replication SQL Server will handle the RowGuid and the not for replication settings for your identity columns. but the primary key issue is something you still need to address manually. Although it is great that SQL Server handles the not for replication setting for you, what is the process to turn this off or turn this on for tables?
Solution
The "Not For Replication" setting for identity columns allows replication to pass the ID value from the publisher to the subscriber without the subscriber creating a new ID. Since identity columns will always generate a new number when records are inserted, this setting allows you to ensure the values on both your publisher and subscribers stay in synch.
For SQL Server 2005 and later this option can be set when designing or creating a new table as shown below in the highlighted section.
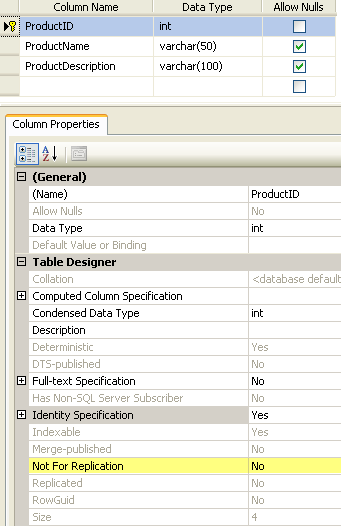
For SQL Server 2000 this option can be set when designing or creating a new table as shown below in the highlighted section.
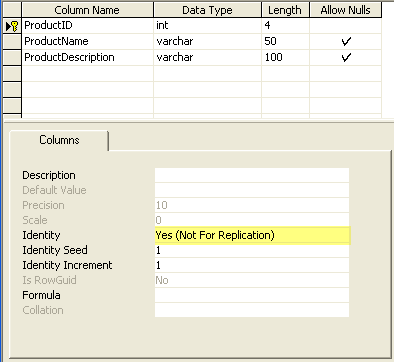
To create a table with the not for replication syntax using a script you would do something as follows:
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Table_1]( [ProductID] [int] IDENTITY(1,1) NOT FOR REPLICATION NOT NULL, [ProductName] [varchar](50) COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS NULL, [ProductDescription] [varchar](100) COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS NULL, CONSTRAINT [PK_Table_1] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED
As mentioned above, replication is not always thought about when tables are first created and therefore this "Not For Replication" option is not usually set to YES. Also, I mentioned that when replication is setup these options are changed for you by the replication setup process. But if you remove replication this setting stays as yes or if you need to keep a development schema (which is not replicated) in synch with your production schema (which is replicated) how can you do this without having to manually change each table via the table designer?
Set Tables Identity Column to Not For Replication for SQL Server 2008 and later
In SQL Server 2008 a new option for the ALTER TABLE command allows you to turn on and off the "Not For Replication" setting. Thanks to one of our readers for pointing this out.
This script turns it to YES for all tables that have an identity column where the setting is currently off.
DECLARE @cmd varchar(max) = '' SELECT @cmd = @cmd + 'alter table [' + object_schema_name( col.object_id ) + '].[' + object_name( col.object_id ) + '] alter column [' + col.name + '] add not for replication; ' FROM sys.identity_columns as col INNER JOIN sys.objects as obj on obj.object_id = col.object_id WHERE obj.is_ms_shipped = 0 and is_not_for_replication = 0 SELECT @cmd EXEC (@cmd)
This script turns it to NO for all tables that have an identity column and the setting is currently on.
DECLARE @cmd varchar(max) = '' SELECT @cmd = @cmd + 'alter table [' + object_schema_name( col.object_id ) + '].[' + object_name( col.object_id ) + '] alter column [' + col.name + '] drop not for replication; ' FROM sys.identity_columns as col INNER JOIN sys.objects as obj on obj.object_id = col.object_id WHERE obj.is_ms_shipped = 0 and is_not_for_replication = 1 SELECT @cmd EXEC (@cmd)
Set Tables Identity Column to Not For Replication for SQL Server 2005 and later
In SQL Server 2005 and later a system stored procedure has been created to allow you to turn on or turn off this "Not For Replication" setting. This new stored procedure is sys.sp_identitycolumnforreplication. Following is the code of this new SP. As you can see it makes a call to a some process %%ColumnEx which is a bit cryptic.
--
-- Name:
-- sp_identitycolumnforreplication
--
-- Description:
-- This procedure allows customers to set the NFR on
-- identity columns for a particular table.
--
-- Returns:
-- 0-Success 1-Failure
--
-- Security: DBO check
--
-- Requires Certificate signature for catalog access
--
CREATE PROCEDURE [sys].[sp_identitycolumnforreplication]
(
@object_id INT,
@value bit
)
AS
BEGIN
DECLARE @identity_column sysname
IF IS_SRVROLEMEMBER('sysadmin') = 0
AND IS_MEMBER('db_owner') = 0
BEGIN
RAISERROR(21050, 14, -1)
RETURN 1
END
SELECT @identity_column = NULL
SELECT @identity_column = name
FROM sys.columns
WHERE OBJECT_ID = @object_id
AND COLUMNPROPERTY(OBJECT_ID, name, 'IsIdentity') = 1
IF @identity_column IS NOT NULL
BEGIN
EXEC %%ColumnEx(ObjectID = @object_id, Name = @identity_column).SetIdentityNotForRepl(Value = @value)
IF @@ERROR <> 0
RETURN 1
END
RETURN 0
END
By using this new SP along with the sp_msforeachtable which iterates through all tables you can turn this on for all tables or off for all tables as follows:
This script turns it to YES for all tables that have an identity column.
EXEC sp_msforeachtable @command1 = '
declare @int int
set @int =object_id("?")
EXEC sys.sp_identitycolumnforreplication @int, 1'
This script turns it to NO for all tables that have an identity column.
EXEC sp_msforeachtable @command1 = '
declare @int int
set @int =object_id("?")
EXEC sys.sp_identitycolumnforreplication @int, 0'
Set Tables Identity Column to Not For Replication for SQL Server 2000
In SQL Server 2000 it is not quite as simple to make this change. There is not a stored procedure like there is for SQL Server 2005 and later. The following code snippet will allow you to change this value across the board for all tables in a database as well, but this is updating the system table syscolumns directly. Most of what you read will tell you not to update the system tables directly.
This script turns it YES for all tables that have an identity column.
update syscolumns set colstat = colstat | 0x0008 where colstat & 0x0008 = 0 -- ie not already "not for replication" and colstat & 0x0001 <> 0 -- ie identity column
When trying to run this you may get the following error message. You need to make this change in order to run these queries.
Ad hoc updates to system catalogs are not enabled. The system administrator must reconfigure SQL Server to allow this.
Next Steps
- If the need arises to turn on or turn off the not for replication setting now you now how to go about making the change
- Keep in mind that when changing this value using the table designer, SQL Server creates a temporary table, drops the existing table and renames the new table. This is not a simple update.
- Be careful changing system tables. A wrong update could be disastrous. Make sure you have database backups prior to changing any system tables directly.
About the author
 Greg Robidoux is the President and founder of Edgewood Solutions, a technology services company delivering services and solutions for Microsoft SQL Server. He is also one of the co-founders of MSSQLTips.com. Greg has been working with SQL Server since 1999, has authored numerous database-related articles, and delivered several presentations related to SQL Server. Before SQL Server, he worked on many data platforms such as DB2, Oracle, Sybase, and Informix.
Greg Robidoux is the President and founder of Edgewood Solutions, a technology services company delivering services and solutions for Microsoft SQL Server. He is also one of the co-founders of MSSQLTips.com. Greg has been working with SQL Server since 1999, has authored numerous database-related articles, and delivered several presentations related to SQL Server. Before SQL Server, he worked on many data platforms such as DB2, Oracle, Sybase, and Informix.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips






