By: Edwin Sarmiento | Comments (27) | Related: More > Database Administration
Problem
Microsoft products such as Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) 3.0 and Windows Sharepoint Services (WSS) 3.0 ship with SQL Server 2005 Embedded Edition. Now called the Windows Internal Database, more and more system administrators charged with managing WSUS and WSS are faced with the challenge of managing these databases. Since most of these system administrators are not full-fledged DBAs, how do they manage the Windows Internal Database?
Solution
The Windows Internal Database is an embedded data service that can only be used by a handful of Windows Services. It is designed in such a way that you are not allowed to connect to and use this particular database service for non-Microsoft products. By default, installing either WSUS 3.0 or WSS 3.0 will create the databases on the C:\ partition and will cause administration issues such as insufficient disk space. It is quite confusing to manage this SQL Server instance as it does not appear as a SQL Server service nor are there management tools included with the products. The easiest way is to use SQL Server Management Studio Express. You can install a copy of SQL Server Management Studio Express on the server running your WSUS 3.0 or WSS 3.0. You then register this instance using Named Pipes as this is the only configuration for connectivity. Use this server name when you register this instance
\\.\pipe\MSSQL$MICROSOFT##SSEE\sql\query
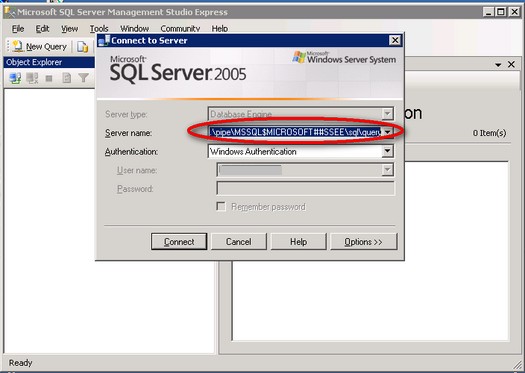
Once you've managed to register this instance in SQL Server Management Studio Express, you can now administer the WSUS 3.0 and WSS 3.0 databases like shrinking the database files or moving them to a different disk partition dedicated for them to avoid insufficient disk space issues.
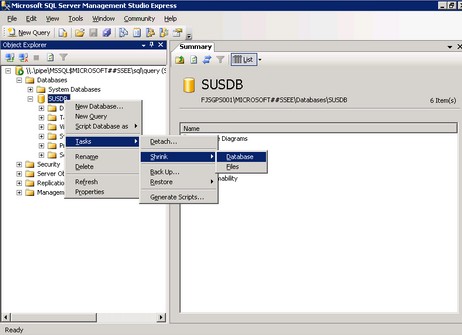
If you prefer to use scripts to manage these databases, you can download and install the SQL Server 2005 Command Line Query Utility - sqlcmd . This tool will be installed, by default, on this directory C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\90\Tools\binn.
To connect to the database instance, you need to run the sqlcmd.exe utility, passing the instance name and your credentials
sqlcmd -S \\.\pipe\MSSQL$MICROSOFT##SSEE\sql\query -E
You can then run your administrative T-SQL scripts once connected to this database instance.
Considerations
While these are possible reasons to administer the Windows Internal Database, it is not recommended to do anything beyond performing backups, moving or shrinking the database files. Modifying database schema or database properties would break supportability of these products. Plus, any changes made to these databases can be overwritten by the products' service packs or cumulative updates.
Next Steps
- Install SQL Server Management Studio Express on your WSUS 3.0 and WSS 3.0 servers
- Take control of your WSUS 3.0 and WSS 3.0 databases
About the author
 Edwin M Sarmiento is a Microsoft SQL Server MVP and Microsoft Certified Master from Ottawa, Canada specializing in high availability, disaster recovery and system infrastructures.
Edwin M Sarmiento is a Microsoft SQL Server MVP and Microsoft Certified Master from Ottawa, Canada specializing in high availability, disaster recovery and system infrastructures.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips






