By: Daniel Farina | Comments | Related: > SQL Server on Linux
Problem
You installed SQL Server on Linux and need to customize the default installation, for instance change its default port, instance collation or even add trace flags. In this tip I will show you how easy it is.
Solution
With the arrival of SQL Server to Linux came new ways for us to do our DBA tasks. On Windows we are used to using SQL Server Configuration Manager as the de facto configuration tool for SQL Server, because of its simplicity compared with other ways like PowerShell scripting. Now on Linux we don't have that graphical interface to interact with and we must rely on the console, but surprisingly it's not too hard to use. Microsoft included on the Linux edition of SQL Server a configuration tool named mssql-conf which you may find on the /opt/mssql/bin/ folder.
mssql-conf
This script configuration tool receives the arguments listed on the table below. All the arguments are case sensitive.
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
|
set |
Sets the value of a SQL Server setting. You can get the list of available settings with the list argument (mssql-conf list). |
|
unset |
Used to remove a setting added with the set option. |
|
traceflag |
Use this argument to set trace flags on or off. |
|
set-sa-password |
This argument is used to change the sa password while the service is not running. |
|
set-collation |
Used to change the instance collation |
|
validate |
Validates the contents of SQL Server configuration file mssql.conf found in /var/opt/mssql/ folder. |
|
list |
Lists the available settings to set / unset. |
|
setup |
Runs the installation script. |
|
start-service |
Starts the SQL Server service, but I suggest that you use systemctl start mssql-server instead. |
|
stop-service |
Stops the SQL Server service, but I suggest that you use systemctl stop mssql-server instead. |
|
enable-service |
Enables SQL Server service automatic start on system start up. |
|
disable-service |
Disables SQL Server service automatic start on system start up. |
set / unset Arguments
You can use this argument to set or unset one option at a time by using the following command.
mssql-conf set [option] [option value] mssql-conf unset [option]
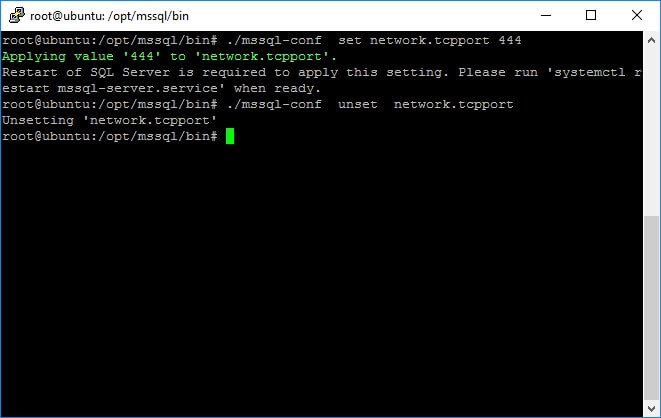
For example, if you want to configure SQL Server to use port 444 you need to execute the following statement on an elevated prompt.
mssql-conf set network.tcpport 444
Also, if you want to let SQL Server to use the default port instead of 444 you have to run the following command.
mssql-conf unset network.tcpport
The following screen capture illustrates the previous statements.
traceflag Argument
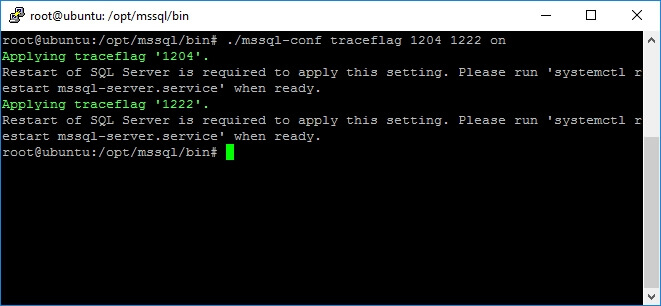
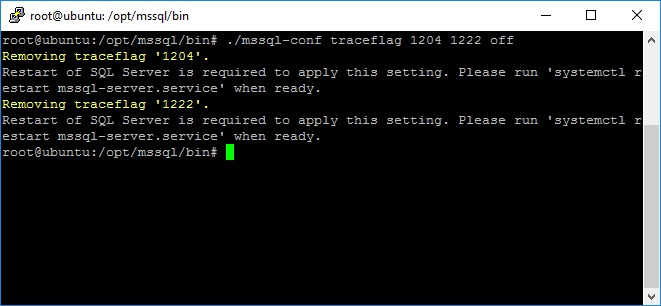
You can use this argument to set on or off one or more trace flags at a time with the following commands.
mssql-conf traceflag traceflag01 traceflag02 ... traceflagn on mssql-conf traceflag traceflag01 traceflag02 ... traceflagn off
Take a look at the following screen captures that shows how to set on / off trace flags 1204 (returns the resources and types of locks participating in a deadlock and also the current command affected) and 1222 (returns the resources and types of locks that are participating in a deadlock and also the current command affected, in an XML format that does not comply with any XSD schema).
list Argument
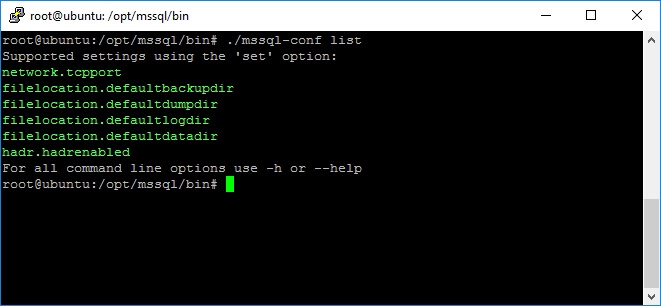
As previously stated, you can get the list of available settings to use with set and unset arguments by running the following command:
mssql-conf list
The following image is a screen capture that shows the execution of this command.
set-sa-password
If you run mssql-conf with this argument while the instance is running it will not work.
set-collation
This argument is used to change the instance collation to one of the available collations listed on file /opt/mssql/lib/mssql-conf/collations.txt. The SQL Server service must be offline in order for this command to work.
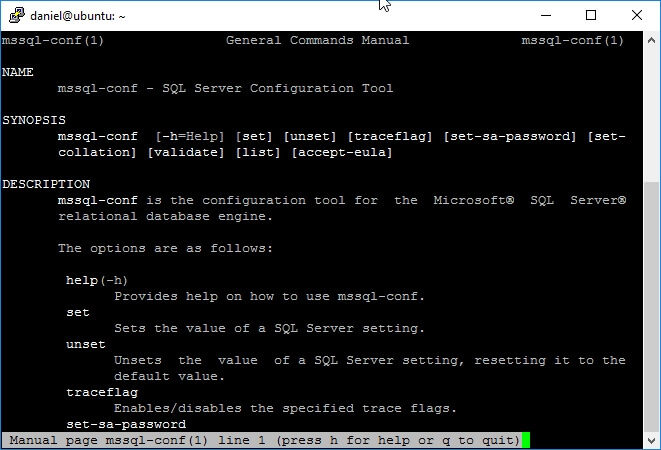
Additional help on mssql-conf (The Linux Way)
There is a command on Linux named man (from the English word Manual) that receives as an argument another command, and displays what is known as the Manual Pages. Yes, Microsoft knew about that and added a reference into the Manual pages about mssql-conf that you can query with the following command.
Next Steps
- Check out the SQL Server 2016 tips.
- For more information about configuring SQL Server, take a look at SQL Server Configurations Tips Category.
- Learn how to install SQL Server vNext on Mac: Run SQL Server vNext (CTP1) as a Docker Container on a Mac.
- Stay tuned for more SQL Server on Linux Tips.
About the author
 Daniel Farina was born in Buenos Aires, Argentina. Self-educated, since childhood he showed a passion for learning.
Daniel Farina was born in Buenos Aires, Argentina. Self-educated, since childhood he showed a passion for learning.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips






