By: Eli Leiba | Comments (3) | Related: > Security
Problem
You are a SQL DBA responsible for many instances of SQL Server running many versions of SQL Server from 2005 to 2016. You get a requirement from the IT security department to get a list of all failed login attempts from last week from all servers. You need a consistent method to capture this data from all of these servers and in this tip we will cover one approach.
Solution
The method for solving this problem involves a stored procedure that will be compiled and executed on the master database of each SQL Server instance.
The stored procedure declares two table variables @EnumErrorLogs and @ErrorLogInfo. The first, @EnumErrorLogs will store the list of the SQL Server error log values like; archive number, change date and file size. The second, @ErrorLogInfo will store the message lines from the logs.
We will use the system stored procedure sp_enumerrorlogs to fill the first table and then we will loop over each of these files using sp_readerrorlog system stored procedure to fill the second table. We will then filter this data to find login information and specifically where there were failures for the last 7 days.
Code to Find Failed Logins
If you want to go back further than 7 days, you change the 7 values below to match your needs.
CREATE PROC usp_GetFailedLoginsListFromLastWeek
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON
DECLARE @ErrorLogCount INT
DECLARE @LastLogDate DATETIME
DECLARE @ErrorLogInfo TABLE (
LogDate DATETIME
,ProcessInfo NVARCHAR (50)
,[Text] NVARCHAR (MAX)
)
DECLARE @EnumErrorLogs TABLE (
[Archive#] INT
,[Date] DATETIME
,LogFileSizeMB INT
)
INSERT INTO @EnumErrorLogs
EXEC sp_enumerrorlogs
SELECT @ErrorLogCount = MIN([Archive#]), @LastLogDate = MAX([Date])
FROM @EnumErrorLogs
WHILE @ErrorLogCount IS NOT NULL
BEGIN
INSERT INTO @ErrorLogInfo
EXEC sp_readerrorlog @ErrorLogCount
SELECT @ErrorLogCount = MIN([Archive#]), @LastLogDate = MAX([Date])
FROM @EnumErrorLogs
WHERE [Archive#] > @ErrorLogCount
AND @LastLogDate > getdate() - 7
END
-- List all last week failed logins count of attempts and the Login failure message
SELECT COUNT (TEXT) AS NumberOfAttempts, TEXT AS Details, MIN(LogDate) as MinLogDate, MAX(LogDate) as MaxLogDate
FROM @ErrorLogInfo
WHERE ProcessInfo = 'Logon'
AND TEXT LIKE '%fail%'
AND LogDate > getdate() - 7
GROUP BY TEXT
ORDER BY NumberOfAttempts DESC
SET NOCOUNT OFF
END
Example of how to use the stored procedure
We execute the procedure:
exec usp_GetFailedLoginsListFromLastWeek
We get the following failed logins from last week list (as it was recorded on my server)
NumberOfAttempts Details ---------------- --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 3 Login failed for user 'NT SERVICE\ReportServer$SQL2K14'. Reason: Failed to open the explicitly specified database 'ReportServer$SQL2K14'. [CLIENT: <local machine>] 3 Login failed for user 'NT SERVICE\ReportServer$SQL2K14'. Reason: Failed to open the explicitly specified database 'ReportServer$SQL2K14'. [CLIENT: 10.1.22.32] 2 Login failed for user '222'. Reason: Could not find a login matching the name provided. [CLIENT: <local machine>] 1 Login failed for user '222222'. Reason: Could not find a login matching the name provided. [CLIENT: <local machine>] 1 Login failed for user '11'. Reason: Could not find a login matching the name provided. [CLIENT: <local machine>] 1 Login failed for user '111'. Reason: Could not find a login matching the name provided. [CLIENT: <local machine>]
Repeat these steps on all reported SQL Servers.
SQL Server Setting to Capture Failed Logins
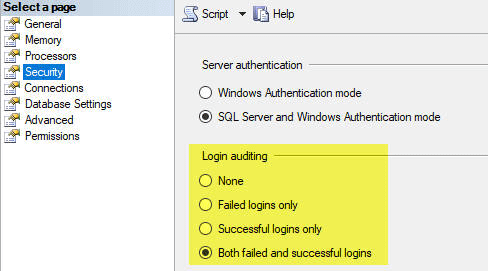
Make sure the server security auditing property is set to monitor Failed Logins only or Both Failed and Successful Logins.
To set for just "Failed Logins" do the following:
USE [master]
GO
EXEC xp_instance_regwrite N'HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE',
N'Software\Microsoft\MSSQLServer\MSSQLServer',
N'AuditLevel',
REG_DWORD, 2
GO
For both "Failed and Successful Logins" do the following:
USE [master]
GO
EXEC xp_instance_regwrite N'HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE',
N'Software\Microsoft\MSSQLServer\MSSQLServer',
N'AuditLevel',
REG_DWORD, 3
GO
These settings can also be changed in SSMS, by right clicking on the instance name, select Properties and go to the Security page. These options are under the Login Auditing section on this page.
Next Steps
- If you liked this solution you can compile and use this procedure in order to report failed logins.
- The procedure was tested on SQL Server 2014 Standard Edition, but should work for SQL Server 2005 and later.
About the author
 Eli Leiba is a senior application DBA, a teacher and a senior database consultant with 19 years of RDBMS experience.
Eli Leiba is a senior application DBA, a teacher and a senior database consultant with 19 years of RDBMS experience.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips






