By: Diogo Souza | Comments (2) | Related: > Monitoring
Problem
Automated SQL Server database monitoring is a very important task for the DBA, because information about the availability and health of the environment (instances availability, use of data files and transaction logs, resource consumption: CPU, disk and memory, etc.) is obtained when the professional is not in his or her working hours.
Obviously, this data is used to alert the administrator of a problem that is occurring or to prevent a problem that may occur. This tip will discuss the combination of T-SQL scripts that generate HTML reports for an environment analysis, SQL Server Agent to schedule this analysis at regular intervals, and Database Mail to send the generated report.
Solution
To resolve the issue, let’s take the following steps:
Step 1 - Profile configuration and account in Database Mail
You must first configure Database Mail.
When you setup Database Mail, you need to configure a Profile to be used for sending emails. The profile must have a name. After naming the profile, you must add a SMTP account with the authentication data. For this, it is necessary to know the data of the SMTP server: its name, port and if it requires SSL (i.e. a secure connection).
In the image below, the profile was configured with the name SQLAgentDBA and the SMTP account is already added:
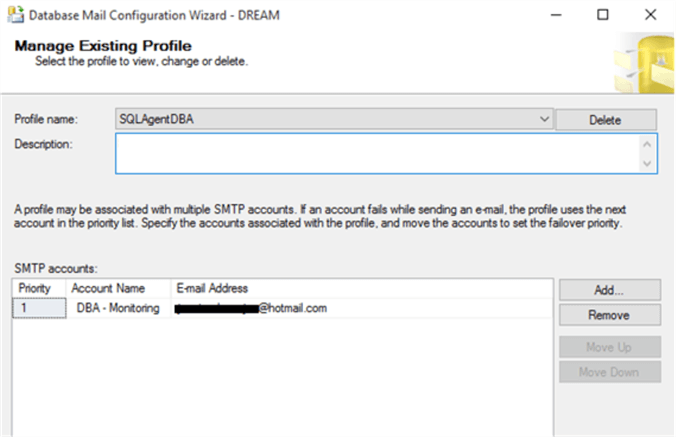
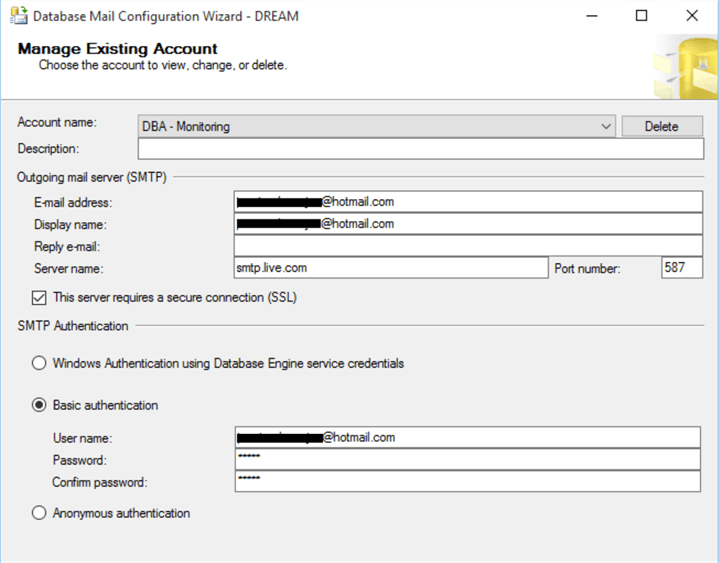
The SMTP account also requires a name. In this case, DBA - Monitoring.
We will also have the authentication settings: Windows (credentials configured for the SQL Server service), basic and anonymous.
- The Windows Authentication option causes Database Mail to use the user name and password that starts the SQL Server service. This user must have an associated e-mail address and the settings are set on the domain controller (Active Directory).
- In Basic authentication, the user name and password associated with the server is defined in the SMTP settings that are specified.
- And Anonymous authentication does not require a user name and password, but the SMTP server must be configured to not require authentication.
Step 2 - SQL Server T-SQL Disk Space Monitoring Script
The following query will pull the free disk space information and below I explain how this was put together and how this is used.
We will initially create a query against tempdb.sys.tables to check if the temporary table named #Drives exists. If it exists, it is deleted and created with the drive, freespace, totalsize, and percentfree fields along with their respective data types. Remembering that the tempdb database stores the temporary tables and these are deleted when the connection is closed.
In the second block the information in the temporary table is inserted from the sys.dm_os_volume_stats DMF query. Calculation is done on the available_bytes and total_bytes columns to get the values in megabytes. Then, the HTML is assembled and treated within a SELECT statement with the CASE expression that defines the color of the fields in red when the free percentage is less than or equal to 15% of the total space of each unit.
In the sequence, the sp_monitor_disk procedure was created within the master system database, where we have the following parameters: @to variable will receive the recipient's email, the variable @subject will be responsible for the subject of the email and @PercentFree will determine how the report returns the data based on the actual percentage free values compared to this value.
USE [master]
GO
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[sp_monitor_disk_free_space]
@to varchar(200),
@subject varchar(100),
@PercentFree int
AS
SET NOCOUNT ON
-- Create the temp table #Drives
IF EXISTS ( SELECT name
FROM tempdb.sys.tables
WHERE name LIKE '#Drives%' )
DROP TABLE #Drives
CREATE TABLE #Drives
(
Drive CHAR(3) PRIMARY KEY ,
FreeSpace INT NULL ,
TotalSize INT NULL ,
[PercentFree] AS ( CONVERT(FLOAT, FreeSpace) / TotalSize ) * 100
)
-- Insert the info on the table by DMF sys.dm_os_volume_stats
INSERT #Drives
( Drive ,
FreeSpace ,
TotalSize
)
SELECT DISTINCT
dovs.volume_mount_point ,
CONVERT(INT, dovs.available_bytes / 1048576.0) ,
CONVERT(INT, dovs.total_bytes / 1048576.0)
FROM sys.master_files mf
CROSS APPLY sys.dm_os_volume_stats(mf.database_id, mf.file_id) dovs
ORDER BY dovs.volume_mount_point ASC
-- Variables for mail send
DECLARE @tableHTML NVARCHAR(MAX)
-- Creates the HTML to the report sending with the total free space info
SET @tableHTML = N'<H1>Disk usage</H1>' + N'<table border="1">'
+ N'<tr><th>Drive</th><th>Total (MB)</th><th>Free (MB)</th><th>% Free</th></tr>'
+ CAST(( SELECT CASE WHEN [PercentFree] <= @PercentFree THEN '#FF0000'
END AS 'td/@BGCOLOR' ,
td = Drive ,
'' ,
'right' AS 'td/@align' ,
CASE WHEN [PercentFree] <= @PercentFree THEN '#FF0000'
END AS 'td/@BGCOLOR' ,
td = TotalSize ,
'' ,
'right' AS 'td/@align' ,
CASE WHEN [PercentFree] <= @PercentFree THEN '#FF0000'
END AS 'td/@BGCOLOR' ,
td = FreeSpace ,
'' ,
'right' AS 'td/@align' ,
CASE WHEN [PercentFree] <= @PercentFree THEN '#FF0000'
END AS 'td/@BGCOLOR' ,
td = CONVERT (NUMERIC(10, 2), [PercentFree])
FROM #Drives
FOR
XML PATH('tr') ,
TYPE
) AS NVARCHAR(MAX)) + N'</table>';
-- Calls the procedure sp_send_dbmail to send the email using the SQLAgentDBA profile created on
SET @Subject = @Subject + @@Servername
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_send_dbmail @profile_name = 'SQLAgentDBA',
@recipients = @to, @body = @tableHTML,
@subject = @Subject, @body_format = 'HTML'
RETURN 0
GO
Step 3 - Create a New SQL Server Agent Job
In SQL Server Agent, a new job must be created. In this example, the DBA - Disk Space job is created.
In the Steps tab we will add a new step that will receive the script.
The type, in this case, must be a T-SQL script and the database must be set to the master.
In the Schedules tab, the scheduling must be configured according to each environment. In our case, the job is recurring and it will run every day, every hour between 00:00 to 23:59. You can configure as needed in your environment.
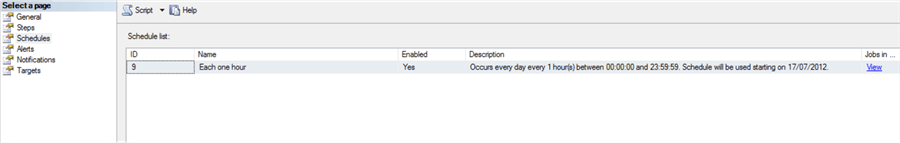
That's all there is to it. This is a pretty simple and straightforward way to automate an email to alert you about available disk space.
Next Steps
- Make sure database mail is enabled on the SQL Server where this script is executed.
- Check out some other related content:
About the author
 Diogo Souza has been passionate about clean code, data manipulation, software design and development for almost ten years.
Diogo Souza has been passionate about clean code, data manipulation, software design and development for almost ten years.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips






