By: Diogo Souza | Comments (1) | Related: > Performance Tuning
Problem
Most of the times that we need to optimize a SQL Server query, a lot of questions and uncertainties come to our minds, just like if we could use any tool that would help with this type of improvement not only regarding the performance itself, but also in structural terms like with indexes, partitioning, DDL and DML, etc. Imagine you, being a SQL Server developer that needs to deal with lots of queries every day and still must consult the SQL Server DBA to check each of them, having such kind of optimizer in hands. That's when the Database Engine Tuning Advisor, present in SQL Server, comes to the table, providing a lot of great analysis and recommendations based on our queries and workloads. In this tip we will cover the use of this tool, especially improving the performance of our queries based on structural changes.
Solution
The famous DTA (Database Engine Tuning Advisor), basically analyzes databases and gives some recommendations. From the official docs, you can find a series of things it helps with:
- Troubleshoot the performance of a specific problem query
- Tune a large set of queries across one or more databases
- Perform an exploratory what-if analysis of potential physical design changes
- Manage storage space
For this example, we're going to use the AdventureWorks Databases and Scripts for SQL Server, which is great as a data sample for test purposes. So, first, open SQL Server Management Studio and import the database following the official steps.
Then, let's define the query we want to optimize
-- sales for group of customers by year
SELECT
year = YEAR(header.OrderDate),
sum = SUM(detail.LineTotal)
FROM
Sales.SalesOrderDetail detail
INNER JOIN
Sales.SalesOrderHeader header ON detail.SalesOrderID = header.SalesOrderID
INNER JOIN
Sales.Customer cust ON header.CustomerID = cust.CustomerID
WHERE
cust.CustomerID > 10000 and cust.CustomerID < 10000000
GROUP BY
YEAR(header.OrderDate)
Make sure to have the proper database selected in order to run the query and get the following results
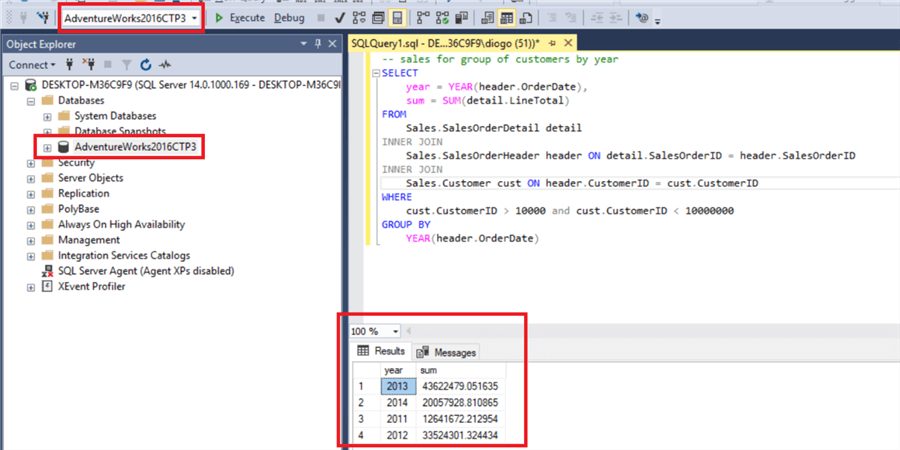
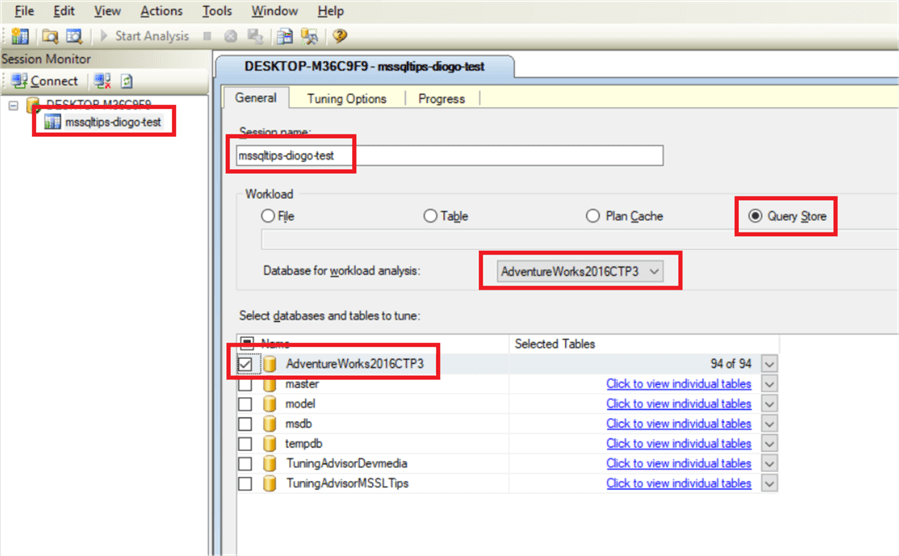
What we need to do now is to open the "SQL Server Database Engine Tuning Advisor" going to the menu Tools > Database Engine Tuning Advisor. Authenticate and create a new session name with the same options we have below.
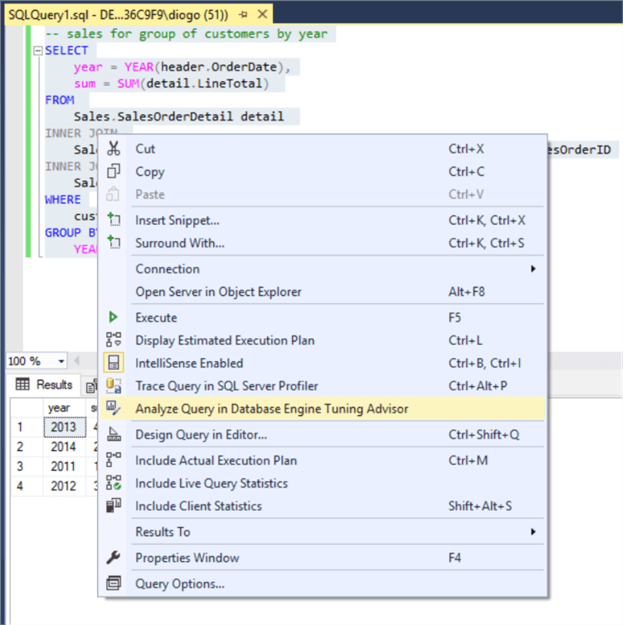
Then, get back to the query, right click it and click on the option "Analyze Query in Database Engine Tuning Advisor":
The Analyzer is going to run and give us an estimated improvement over the performance of our queries:
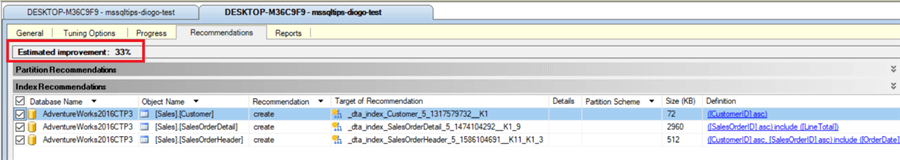
DTA includes a lot of different reports, from the performance and how costly the query is, to the way each entity relates to the other, the balance between the keys (indexes, etc.), and much more:
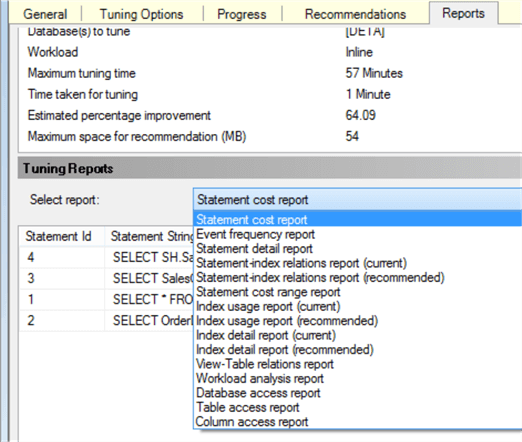
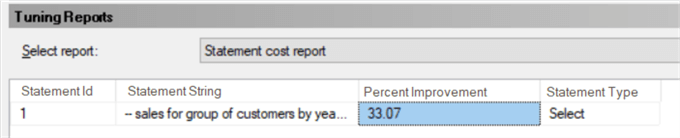
With them, we can check, for example, how much improvement we'll have when we decide to apply one of the suggested improvements. Let's look at the "Statement cost report", e.g., which says that our query can be improved by 33.07% if we apply the suggestions:
In order to check each improvement, go to the "Definition" column and click in one of them. Let's try the first one, related to an index recommendation:
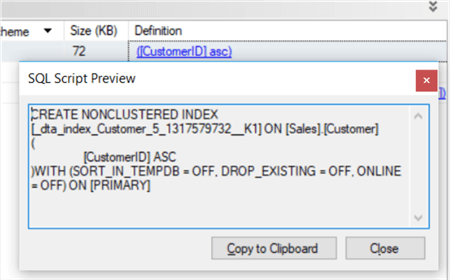
Then, go back to SQL Server Management Studio and run the recommended script that'll create a new non-clustered index to the CustomerID column, just like:
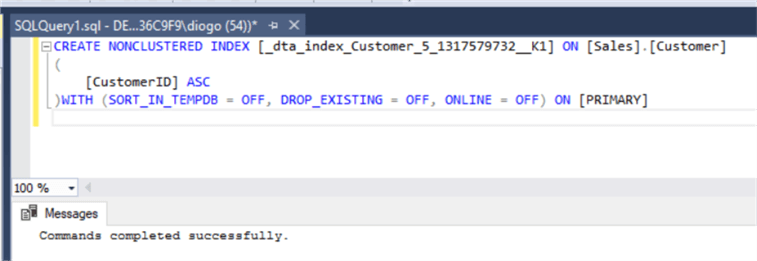
When finished, let's run the Tuning Advisor once again, go to the Reports tab and check the "Statement cost report" again:
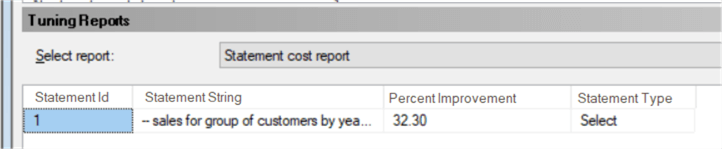
The index creation allowed our select to execute in a more optimized way. If you follow the other recommendations, you can further improve the query and the percent improvement should get smaller with each change you make.
This concludes this article, where we covered a small fraction of the range of information we will have regarding the Database Engine Tuning Advisor and how it helps us to get recommendations based on the workloads we present for performance optimization.
Next Steps
- Check out some other related content:
About the author
 Diogo Souza has been passionate about clean code, data manipulation, software design and development for almost ten years.
Diogo Souza has been passionate about clean code, data manipulation, software design and development for almost ten years.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips






