By: Siddharth Mehta | Comments | Related: More > Database Administration
Problem
PowerShell is evolving as a task management framework in the Microsoft technology stack. As Microsoft started its adoption of open-source into different Microsoft products and platforms, PowerShell has also joined the open-source alliance and its supported on non-Microsoft platforms like Linux. Python on the other hand is arguably one of the most popular and widely adopted languages with programming constructs and features to interface with platforms, devices, network, storage and much more, like PowerShell. Another interesting part of both languages is that SQL Server too has support for both languages though for different purposes. For those who are new to these languages, it creates a dilemma of which language to consider for task automation as well as how both languages play a role in the SQL Server ecosystem. In this tip we will discuss points that will clarify the answer to this question.
Solution
PowerShell is a native task management and automation framework from Microsoft with cross-platform support. Python is a multi-purpose programming language with capabilities to interface with the system. Let's understand the detail of these languages to understand their applicability for the right use-case.
PowerShell is a command-line based shell which enables task execution using a scripting language. PowerShell uses .NET core in the background and can work on Windows, MacOS and Linux based operating systems. You can find more information on installing PowerShell from here. Let's investigate Windows PowerShell in more detail. Windows PowerShell is a Windows command line shell for Windows administrators. Our interest lies in the use of PowerShell in the context of SQL Server, though PowerShell functionality covers a much wider range of tasks like accessing the file system, registry, databases, software installations and much more.
PowerShell like every other command line shell has many commands, many of which are similar to Unix shell commands, which you can read from here. So, for someone who is new to PowerShell, the first question that arises is how to learn which all commands are available and how to use them. You can find PowerShell Language Reference Cheat Sheet from here, which can be used to get a quick overview of things like operators, functions, variables and other programming related functionality. PowerShell organizes commands, which are known as commandlets (cmdlets), in the form of "verb-noun" naming system. There are a set of one of more standard verbs for ever cmdlets like Get, Set, New, Start, Stop, Suspend, Resume, Restart, etc. And nouns can be items like Windows, Process, Drive, Service, Job, Event, etc. There are several modules in PowerShell like Utility, NetSecuirty, Management, PKI, Azure, SqlServer, SQLPS and more. A SQL Server professional's interest would lie in the PowerShell modules related to SQL Server, which is also known as SQL PowerShell.
There are two SQL PowerShell modules: SQLPS (previous / older version) module and the SqlServer module which is the latest module and is a superset of the SQLPS module.
- Depending upon your version of SQL Server, SQL PowerShell modules may or may not be installed on your system. Consider referring to this article to make sure SQL PowerShell is installed on your system to try out some examples explained in this tip.
- To ensure as well as explore the different commandlets (cmdlet) in the SqlServer module, type the command as shown below from Windows PowerShell and you would be able to see a list of all commandlets under the SqlServer module.
- To understand the functionality of these commandlets (cmdlet), consider using this reference which details out its use.
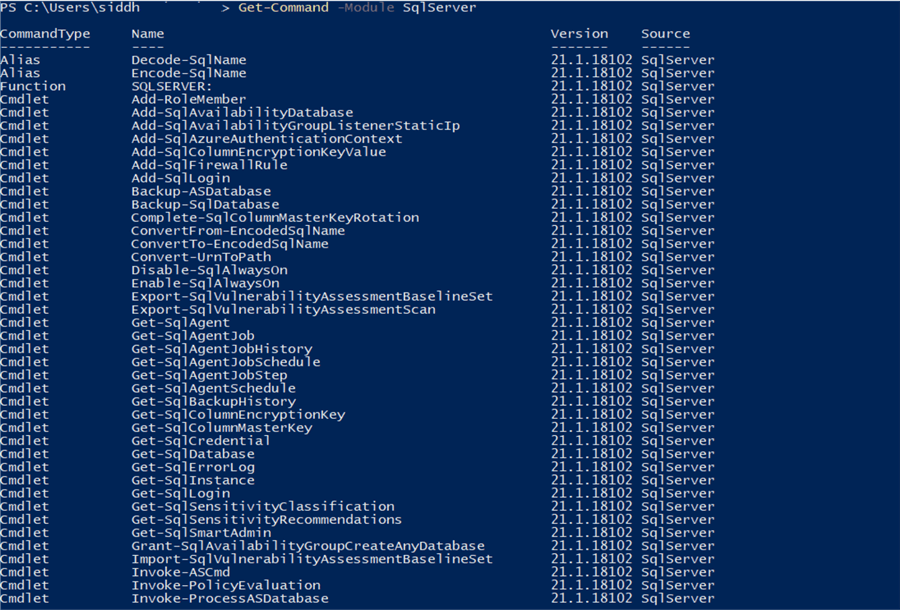
To use PowerShell from SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS), select the object on which you intend to use PowerShell, right-click and select the menu option "Start PowerShell" as shown below.
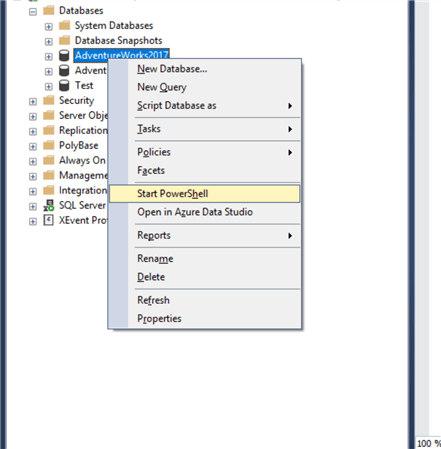
Upon selecting, a new screen opens as shown below and the path would be set to the object hierarchy of the database object.
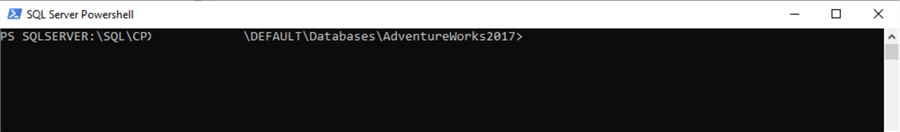
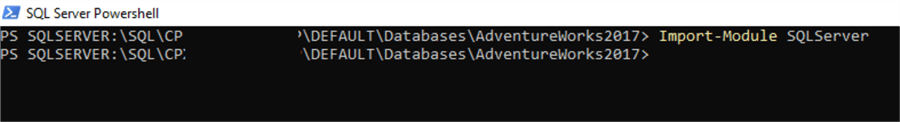
Before we can start using the cmdlets from the SqlServer module, we need to import this module in the PowerShell environment as shown below.
To understand the syntax of the cmdlet, you can type the Get-Help cmdlet along with the one for which you intend to learn the syntax with some examples. In the below case, we are executing the command to get information and examples about the Read-SqlTableData cmdlet, which enables querying of data from a table.
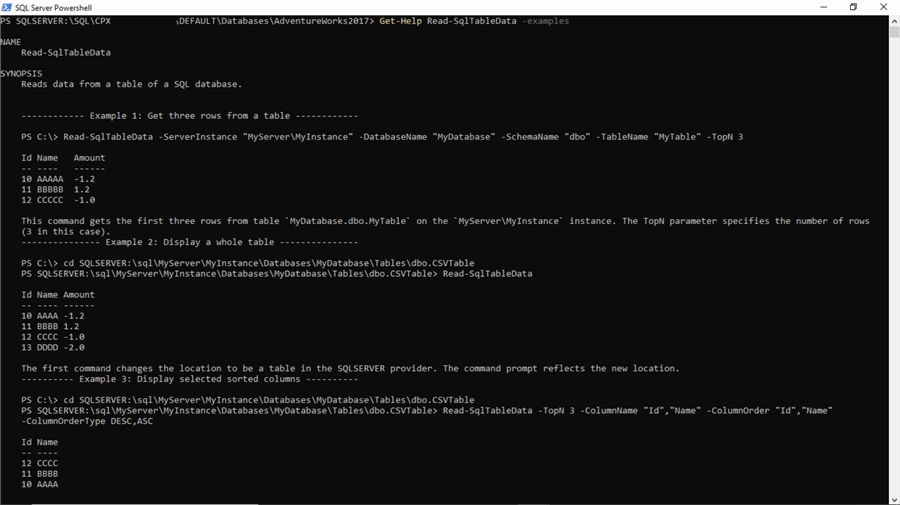
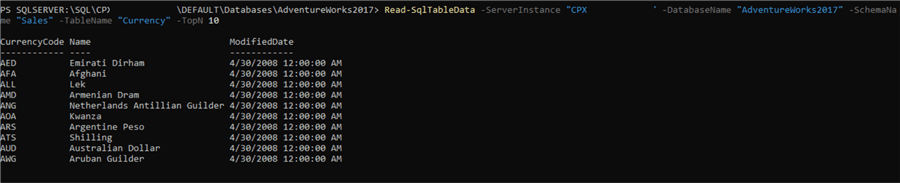
Execute the Read-SqlTableData function with the relevant parameters as shown below, and you are able to retrieve the query results from the table as per the parameters passed to the cmdlet. PowerShell contains many such cmdlets using which can automate a lot of administrative tasks
Now that we understand the basics of PowerShell scripting and its use, let's move on to analyze Python from the context of comparing it with PowerShell.
Firstly, PowerShell to Python is not an equal or an apple to apple kind of comparison. Let's understand the reasons for this.
- Python is a general-purpose programming language which can be used for a variety of purposes ranging from administration, web development to even machine learning. Whereas PowerShell is a scripting language and task automation framework aimed to automate administrative tasks programmatically.
- The object model of Python is feature rich for supporting programming constructs, data manipulation, graphics and is supported by a wide variety of community developed packages and compilers. The PowerShell framework is feature rich with constructs for supporting automation of tasks like jobs, cmdlets, scripting language, etc.
- PowerShell is natively supported on the Windows platform along with its support for other platforms like Linux. PowerShell contains modules for automating tasks on Windows as well as working with SQL Server. Similar functionality can be achieved with Python as well with specialized packages or custom programming, as Python is not designed for automating administrative tasks though it can access the same objects as PowerShell. So, on Linux based environments, if the need is for task automation at system level, then Python would be a comparatively more efficient choice than PowerShell.
- SQL Server is supported in Windows as well as Linux environments. The commands, cmdlets and SQL Server modules that we tried using PowerShell on Windows, will work on Linux as well. Python on the other hand will require custom programming for automating or even operating administrative tasks on SQL Server.
Python is an integral part of SQL Server and can be used from T-SQL to execute Python code for processing data. So, Python is interoperable from SQL Server so is PowerShell. From a task automation perspective, PowerShell has hundreds of commands especially for interfacing with Windows system, whereas in Python, one would have to use Python system packages for interfacing with the system and develop custom logic for automating system tasks. To understand this, we can look at a very simple example. Let's say that we need to find system information using Python, for which we can use the Python's "platform" package and extract various attributes of the OS as shown below on a Windows system.
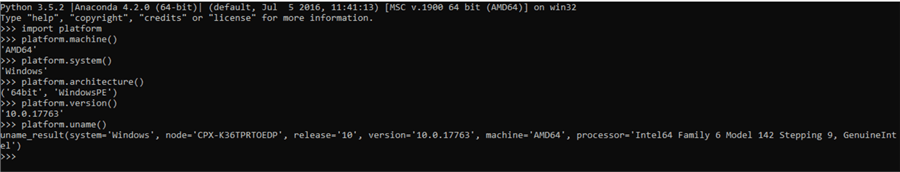
Whereas using Windows PowerShell, we can execute a single cmdlet Get-ComputerInfo and it extracts a very large number of attributes related to OS, Processor, Network, Storage and other detailed and sensitive information. You can read through the list of attributes from here.
I hope this simple comparison will make it clear that how PowerShell is much more powerful for administrative task automation on Windows platform as well as on SQL Server. And on platforms like Linux, Python can be powerful for system administration related tasks, though Microsoft has number of products in its ecosystem that use PowerShell as the administrative and management framework as a core part of the product. One should make a comparative analysis and make an informed decision based on this analysis when consider PowerShell vs Python for task automation.
Next Steps
- Consider trying out the examples demonstrated in this tip on a Linux system to understand the effectiveness of PowerShell vs Python on Linux vs Windows.
- Check out the PowerShell tips.
- Check out the Python tips.
- Check out the SQL Server and Python Tutorial.
About the author
 Siddharth Mehta is an Associate Manager with Accenture in the Avanade Division focusing on Business Intelligence.
Siddharth Mehta is an Associate Manager with Accenture in the Avanade Division focusing on Business Intelligence.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips






