By: Jeremy Kadlec | Comments (1) | Related: > Performance Tuning
Problem
Capturing performance monitor counters is of great value to understand how SQL Server is behaving at a macro level, that being how overall resources are being used within the engine. Without this data it is difficult to determine where the performance issues are occurring. Capturing the metrics has been traditionally from Performance Monitor either on an ad-hoc basis or setting up a log to capture the values on a predefined basis.
If you dug a little further in SQL Server 2000's system tables you probably found the dbo.sysperfinfo table in the master database. Unfortunately, this table has been converted to a view for SQL Server 2005 and later versions and dbo.sysperfinfo is only available for backward compatibility. Since this is the case, how can I capture the Performance Monitor values on an as needed basis for SQL Server?
Solution
In SQL Server, one of the dynamic management objects is sys.dm_os_performance_counters. This DMV makes it possible to query a view directly to capture the SQL Server counters related to the instance. This offers DBAs a great deal of flexibility to capture the metrics in real time as an issue is occurring. It is as simple as a SELECT statement to determine the SQL Server performance metrics. What could be easier?
What is the result set?
A simple SELECT statement against the sys.dm_os_performance_counters view will result in a 5 column result set and 500+ counters. On my particular instance close to a 1000 counters are being captured and you can expect more with large numbers of databases and by installing all of the SQL Server application components.
SELECT * FROM sys.dm_os_performance_counters; GO
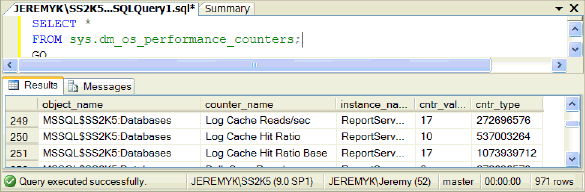
| Column | Explanation |
|---|---|
| object_name | Counter category i.e. MSSQL + $ + InstanceName: + Databases (if you
have an instance)
NOTE - Depending on the applications and services installed, 20+ categories
will be captured for the SQL Server instance. |
| counter_name | Counter name relative to the category, which may overlap between various
object_name values. |
| instance_name | Instance of the counter which is either a database value or if it is
a NULL value than the instance name is related to the overall SQL Server. |
| cntr_value | The captured or calculated value for the counter. |
| cntr_type | Counter type defined by Performance Monitor. |
What are the counters?
Depending on the services and applications installed the number of counters will vary, but expect to be able to query at least 500 counters. These counters range from memory usage toSQL Server application specific counters to include:
- MSSQL:CLR
- MSSQL:Access Methods
- MSSQL:User Settable
- MSSQL:Buffer Manager
- MSSQL:Broker Statistics
- MSSQL:SQL Errors
- MSSQL:Latches
- MSSQL:Buffer Partition
- MSSQL:SQL Statistics
- MSSQL:Locks
- MSSQL:Buffer Node
- MSSQL:Plan Cache
- MSSQL:Cursor Manager by Type
- MSSQL:Memory Manager
- MSSQL:General Statistics
- MSSQL:Databases
- MSSQL:Catalog Metadata
- MSSQL:Broker Activation
- MSSQL:Broker/DBM Transport
- MSSQL:Transactions
- MSSQL:Cursor Manager Total
- MSSQL:Exec Statistics
- MSSQL:Wait Statistics
What are the limitations?
Unfortunately, the sys.dm_os_performance_counters is limited to SQL Server counters, so if you want system, physical disk, network interface card, etc. you need to run performance monitor to capture these counters.
Next Steps
- With the sys.dm_os_performance_counters DMV you can start to query the Performance Monitor values directly from SQL Server to troubleshoot the instance's performance issues. So keep these in mind as a future resource.
- The sys.dm_os_performance_counters is a replacement to dbo.sysperfinfo from SQL Server 2000 that is available for backward compatibility.
- Check out these related MSSQLTips:
About the author
 Jeremy Kadlec is a Co-Founder, Editor and Author at MSSQLTips.com with more than 300 contributions. He is also the CTO @ Edgewood Solutions and a six-time SQL Server MVP. Jeremy brings 20+ years of SQL Server DBA and Developer experience to the community after earning a bachelor's degree from SSU and master's from UMBC.
Jeremy Kadlec is a Co-Founder, Editor and Author at MSSQLTips.com with more than 300 contributions. He is also the CTO @ Edgewood Solutions and a six-time SQL Server MVP. Jeremy brings 20+ years of SQL Server DBA and Developer experience to the community after earning a bachelor's degree from SSU and master's from UMBC.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips






