By: Atif Shehzad | Comments (4) | Related: More > DBA Best Practices
Problem
Databases whose architecture or data is not required to be updated should be considered to be set as READ ONLY databases. For one of my archival databases, I am looking to make it READ ONLY and would like to know what steps I should take. In this tip I go over some best practices before setting a database to READ ONLY.
Solution
In this section we would go through best practices for preparing a database for READ ONLY status. Databases can be set to READ ONLY mode and back using T-SQL and SSMS. For our testing we will use the sample database AdventureWorks to carry out all operations.
Preparing a database for READ ONLY state
Once a database is changed to READ ONLY nothing will change in your database. So based on this, certain changes should be made to optimize the performance of a READ ONLY database.
Consider these facts:
- Statistics will not be automatically updated (nor required) and you would not be able to update statistics of a READ ONLY database
- READ ONLY databases will not shrink automatically or manually
- You will not be able to create indexes
- You will not be able to defragment indexes of a READ ONLY database
- READ ONLY databases will not allow you to add any extended properties on any of its objects
- Permissions may not be edited and users may not be added or removed from a READ ONLY database
So it is required to complete such tasks before we set the database to READ ONLY mode. The following script provides an outline to start with. You may add or remove certain steps in the script according to your specific requirements. The script assumes that your database is in the FULL recovery mode and also you have a prior full backup as a base for transactional log backups. If that is not the case then you may skip step 1 and 2 in the following script
-- Script 1: Prepare database for READ ONLY status Use AdventureWorks GO
-- Step 1. Assuming that DB has recovery model FULL and has a prior full backup. --Create transactional log backup BACKUP LOG AdventureWorks TO disk = 'D:\AdventureWorksTLog' GO
-- Step 2. Assuming that DB has recovery model FULL. Set Recovery model to Simple ALTER DATABASE AdventureWorks SET RECOVERY SIMPLE GO
-- Step 3. Shrink the database DBCC SHRINKDATABASE (AdventureWorks, TRUNCATEONLY) GO
-- Step 4. Create/rebuild/reorganize indexes where required -- Step 5. De-fragment indexes where required
-- Step 6. Add extended properties for database if required EXEC [AdventureWorks].sys.sp_addextendedproperty @name=N'Purpose ', @value=N'DB made READ ONLY for testing purpose.' GO
-- Step 7. Modify permissions if required and add/remove users appropriately
-- Step 8. Update all statistics EXEC sp_updatestats GO
Set database to READ ONLY status
Setting your database to READ ONLY itself is quite simple, but demands prior considerations and preparation. After completing tasks in script 1, we are ready to change the status of AdventureWorks to READ ONLY. This task may be accomplished through the system stored procedure sp_dboption or through and ALTER DATABASE command.
Using ALTER DATABASE command is recommended as sp_dboption may be excluded from newer versions of SQL Server.
The following script would set AdventureWorks to READ ONLY state
-- Script 2: Set AdventureWorks to READ ONLY status -- Set DB to READ ONLY status through ALTER DATABASE ALTER DATABASE AdventureWorks SET READ_ONLY GO
The same task may be performed through SSMS. Right click on the database and go to properties. Click on Options in left panel and scroll to 'state' related options at end. Here you can manage the READ ONLY property of the database.
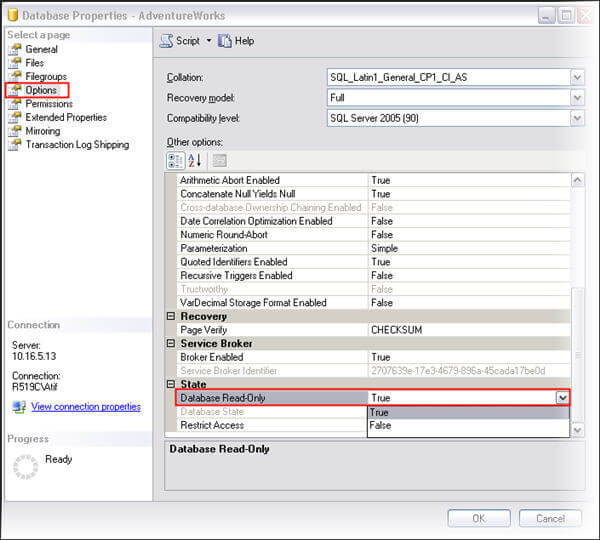
Verify the READ ONLY state of database
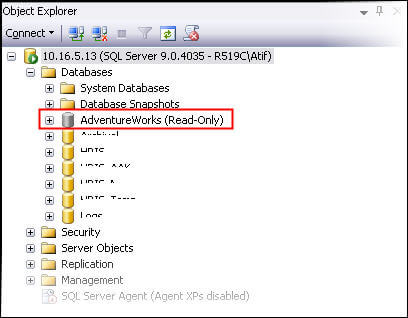
As a database changes to READ ONLY through SSMS, the color of the database folder in SSMS will instantly change and it would look as follows. If the database is changed to READ ONLY through T-SQL then a refresh of your databases may be required to show the color change in SSMS.
You can also verify the READ ONLY property of a database using this T-SQL,
-- Script 3: Verify that DB is READ ONLY or not -- A value of 1 corresponds to READ ONLY state SELECT name, is_read_only FROM sys.databases WHERE name = 'AdventureWorks' GO
Working with backups of READ ONLY databases
There are couple of important points that should be kept in view while working with backups of READ ONLY databases.
- You can create any type of backup (full, differential, log) of a database in READ only state. However considering the READ ONLY state you may want to have a different backup plan than that of a READ WRITE database. Consider using simple recovery mode along with only full backups.
- A full backup of READ ONLY database would be recovered as a READ ONLY database. Recovered databases may be changed to READ WRITE mode later.
- A full backup of READ WRITE database over a READ ONLY database would make the target database READ WRITE, so you would need to change the state of the database again.
Performance benefits of READ ONLY state
- As there would be no data modifications in a READ ONLY state, SQL Server would not have to bother with locks.
- You can create additional indexes to optimize data retrieval without worrying about degradation of data modifications and index maintenance.
- You can copy data and log files of a READ ONLY database while the database is online
Change READ ONLY database to READ WRITE
If there is a need to change a READ ONLY database to READ WRITE this task can be performed both through T-SQL or SSMS.
-- Script 4: Change state of READ ONLY database to READ WRITE -- Set DB to READ WRITE status through ALTER DATABASE ALTER DATABASE AdventureWorks SET READ_WRITE GO
SSMS may also be used for changing database state in the same way as mentioned in first image above. If task is performed through T-SQL then you will need to refresh the databases in SSMS to see the color change of the database folder back to normal.
Next Steps
- Do not forget to disable application features that previously were being used to update the database
- Click here to read more about updating statistics in SQL Server databases or read this tip
- Click here to read more about index maintenance operations
- Click here to read more about shrinking database
- Click here to read more about using extended properties on SQL Server objects
- Click here to read more about working with recovery models for SQL Server databases or read this tip
About the author
 Atif Shehzad is a passionate SQL Server DBA, technical reviewer and article author.
Atif Shehzad is a passionate SQL Server DBA, technical reviewer and article author.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips






