By: Ken Simmons | Comments (1) | Related: > Indexing
Problem
When tuning indexes, it is somewhat difficult to tell how much impact the changes you have made will have on a query. Other than just looking at the different execution plans, is there an easy way to compare the queries using the old and new indexes?
Solution
After making index changes, I always like to use hints to see how much impact the change has on a query. Let's take the following query that uses the AdventureWorks database as an example.
USE AdventureWorks GO SELECT NationalIDNumber FROM HumanResources.Employee WHERE Title = 'Stocker' GO
As you can see by the following execution plan, the query uses a clustered index scan to retrieve the information.
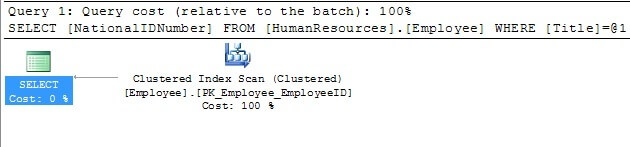
Since the query is searching by Title and returning the NationalIDNumber, you can create the following non-clustered index on Title and include the NationalIDNumber, so all of the information the query needs is located in the index. You should note that if you did not include the NationalIDNumber, the optimizer would still find it more optimal to scan the clustered index instead of seeking the non-clustered index and having to lookup the NationalIDNumber.
CREATE INDEX ix_Title_Include ON HumanResources.Employee(Title) INCLUDE (NationalIDNumber) GO
After creating the new index and rerunning the original query, you will now see that the query is performing an index seek on the new non-clustered index. That sounds good, but how much more efficient is it?
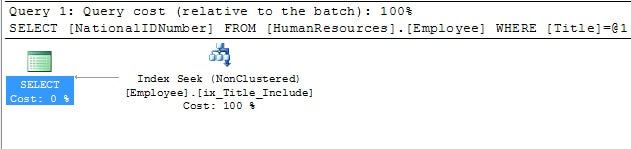
In order to answer that question, you can use a hint to force one of the queries to use the original index as shown in the following query.
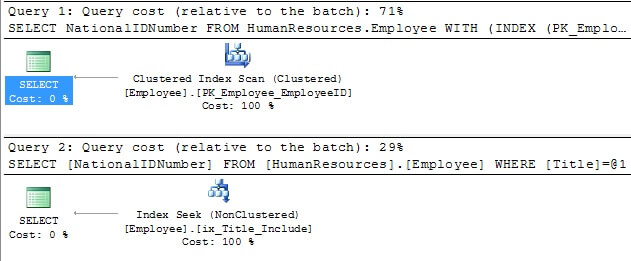
SELECT NationalIDNumber FROM HumanResources.Employee WITH (INDEX (PK_Employee_EmployeeID)) WHERE Title = 'Stocker' GO SELECT NationalIDNumber FROM HumanResources.Employee WHERE Title = 'Stocker' GO
You can now see that using the new index, the query cost is only 29% compared to the original index which is 71%. If you saw something like 50/50, you may want to rethink the new index, because it hasn't given you any performance and now you have an additional index to update and maintain.
Next Steps
-
Learn more about query plans by reviewing the tip How to read SQL Server graphical query execution plans among other tips in the category.
-
Review SQL Server Indexing Basics as well as other tips on indexing.
-
You can find the complete syntax for Table Hints in Books Online.
About the author
 Ken Simmons is a database administrator, developer, SQL Server book author and Microsoft SQL Server MVP.
Ken Simmons is a database administrator, developer, SQL Server book author and Microsoft SQL Server MVP.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips






