By: Daniel Farina | Comments (4) | Related: > SQL Server Configurations
Problem
When I tried to start the SQL Server service, I received the following error message: "SQL Server could not spawn FRunCommunicationsManager thread. Check the SQL Server error log and the Windows event logs for information about possible related problems." See how I managed to solve this with the help of Microsoft's Sysinternals TCPView tool.
Solution
Sometimes error messages provide little to no information, but in other cases like this, information is included in several error messages to help troubleshoot the issue.
System Event Log:
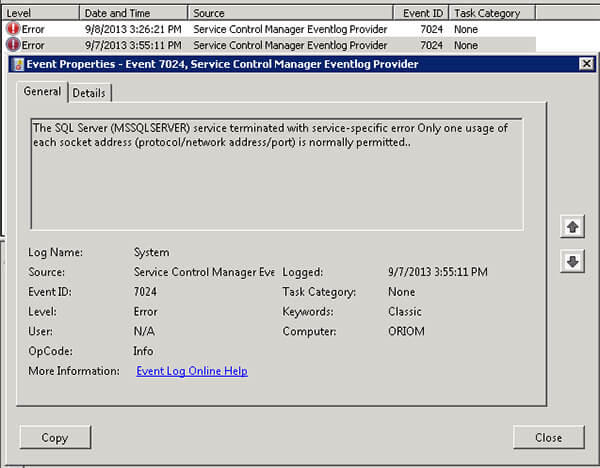
Application Event Log:
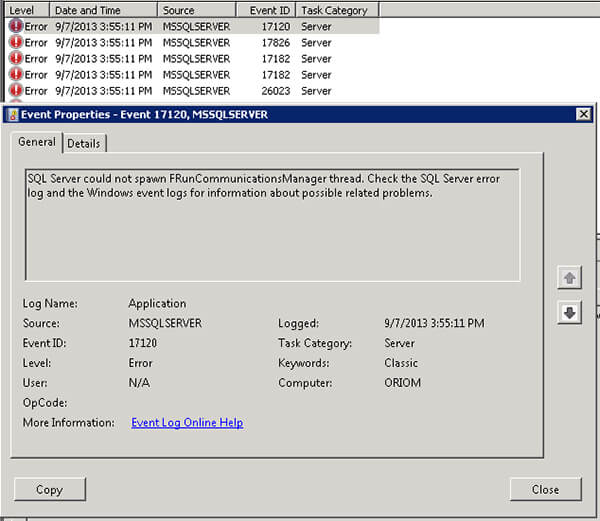
These are the event log error messages in question:
Event ID: 17120 Task Category: Server Level: Error Keywords: Classic User: N/A Computer: ORIOM Description: SQL Server could not spawn FRunCommunicationsManager thread. Check the SQL Server error log and the Windows event logs for information about possible related problems.
Event ID: 17826 Task Category: Server Level: Error Keywords: Classic User: N/A Computer: ORIOM Description: Could not start the network library because of an internal error in the network library. To determine the cause, review the errors immediately preceding this one in the error log.
Event ID: 17182 Task Category: Server Level: Error Keywords: Classic User: N/A Computer: ORIOM Description: TDSSNIClient initialization failed with error 0x2740, status code 0x1. Reason: Initialization failed with an infrastructure error. Check for previous errors.
Event ID: 17182 Task Category: Server Level: Error Keywords: Classic User: N/A Computer: ORIOM Description: TDSSNIClient initialization failed with error 0x2740, status code 0xa. Reason: Unable to initialize the TCP/IP listener.
Event ID: 26023 Task Category: Server Level: Error Keywords: Classic User: N/A Computer: ORIOM Description: Server TCP provider failed to listen on [ 'any'1433]. Tcp port is already in use.
Looking at the last error message we can see why the SQL Server process could not start. The error message says that port 1433 is already in use and this is the port that SQL Server uses by default.
How can the port be in use if the SQL Server process is not running?
The first thing that I did was to execute "netstat -a" at a command prompt to check for connections using the SQL Server ports.
As you can see in the image below there were two connections with CLOSE_WAIT status using the default SQL Server ports: port 1433 which is used by the SQL Server Service and port 1434 which is used by the SQL Server Browser.
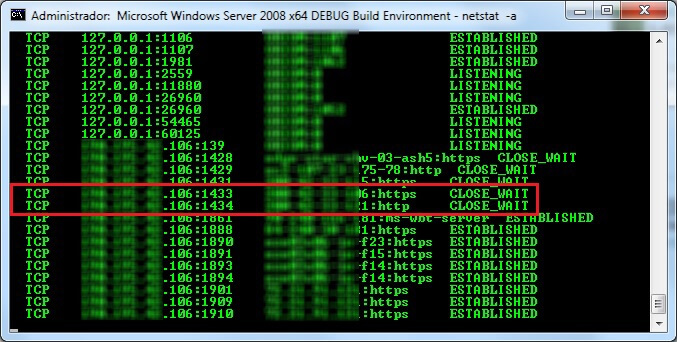
Without going into too much detail, CLOSE_WAIT status means that the remote machine has ended the connection, but the local application keeps the socket opened, probably for reuse later on.
Now that I confirmed a process was using these ports, how do I know what application is using these ports?
What application is using these ports?
To answer this I executed TCPView which is a free Microsoft Sysinternals tool you can download here: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/bb897437.aspx.
This utility shows a detailed listing of TCP and UDP connections along with details about the connections, owner, processes, etc.
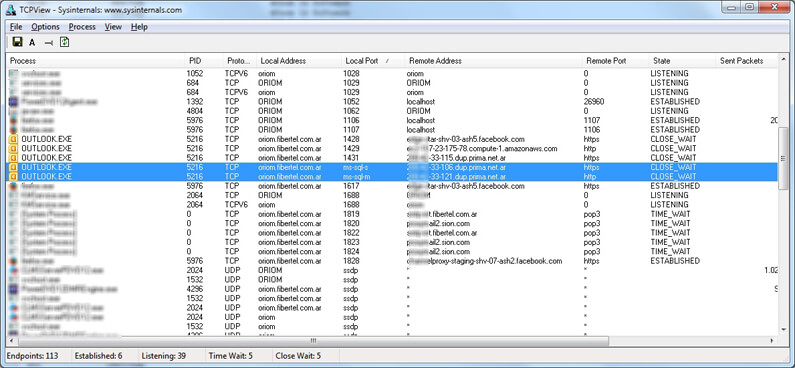
In the image above, you can see that the process using those ports was Microsoft Outlook. Doing some research I found that the connections remote host was an Akamai server. So I killed the Outlook process by clicking End Process from the Process menu.
How do you avoid this situation from happening again?
Windows allows us to set reserved ports and in the remainder of this tip I will explain how you can reserve SQL Server ports depending on your Windows version.
How to reserve a port in Windows 2003?
To reserve a port or a range of ports on Windows 2003 we need to edit the following registry subkey:
Simply add a new Multi-Line String value called ReservedPorts and enter the range of ports in the following format:
For example: 1433-1434
Also if you want to reserve a single port use the same value for StartPort and EndPort: 1433-1433
How to reserve a port in Windows 2008 and beyond?
On Windows 2008 the previous registry key is not supported. In order to reserve a range of ports you may need to apply hotfix KB2665809 http://support.microsoft.com/kb/2665809. After you installed this Hotfix you can manage port ranges with Netshell (netsh) as follows.
Reserving a range of ports
This is the syntax to exclude a port range with netsh:
Example: This will reserve ports 1433 and 1434.
netsh int ipv6 Add excludedportrange protocol=tcp startport=1433 numberofports=2 store=persistent
Querying excluded ports
You can query excluded ports with this command:
Example: This will show persistent reserved ports for IPv4 and IPv6 protocols.
netsh int ipv6 show excludedportrange protocol=tcp store=persistent
Deleting an excluded port range
This is the command to delete an excluded port range:
Example: This will remove the reserved port range 1433 - 1434.
netsh int ipv6 delete excludedportrange protocol=tcp startport=1433 numberofports=2 store=persistent
Checking a dynamic port range
For those of you who don't know, dynamic ports are assigned to the client end of a connection. So it is better to keep these ports above the ports at are used most often.
Example: To check the dynamic port range, execute the following commands:
netsh int ipv4 show dynamicport udp
netsh int ipv6 show dynamicport tcp
netsh int ipv6 show dynamicport udp
Setting the dynamic port range
The suggested range of dynamic ports according to the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) is 49152 to 65535.
Example: These are the commands to set the dynamic port range to an IANA recommended value:
netsh int ipv4 set dynamicport udp start=49152 num=16383
netsh int ipv6 set dynamicport tcp start=49152 num=16383
netsh int ipv6 set dynamicport udp start=49152 num=16383
Next Steps
- Download the free tool I used in this tip: TCPView.
- In this tip you will learn how to Start, Stop, Pause and Query Windows SQL Server Services Remotely.
- This is something every DBA needs to know: DOS Commands for the SQL Server DBA.
- In this tip I used the Event Log to read the error messages, but you can also use the SQL Server error log. Here is a tip to fine errors in the error log Simple way to find errors in SQL Server error log.
- To troubleshoot SQL Server service start use this tip to Read the end of a large SQL Server Error Log.
- Also check the Error Logs Tips category for additional tips
- In this tip you will get a SQL Server DBA Checklist to see what things need your concern.
- Since I mentioned the SQL Server Browser service, you may want to get an Overview of the SQL Server Browser service.
- Microsoft Sysinternals tools are very useful. You can read my previous tip about Solving SQL Server Database Physical File Fragmentation to see another one of these tools in action.
- Talking about Tools? Here you have looked at these Free SQL Server tools from Microsoft.
- You may want to use this Free SQL Server Troubleshooting Tool from Microsoft for other issues regarding SQL Server Troubleshooting.
- Also check the Tools Tips Category.
About the author
 Daniel Farina was born in Buenos Aires, Argentina. Self-educated, since childhood he showed a passion for learning.
Daniel Farina was born in Buenos Aires, Argentina. Self-educated, since childhood he showed a passion for learning.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips






