By: Koen Verbeeck | Comments | Related: > Analysis Services Development
Problem
With the release of SQL Server 2016, many new features and improvements were introduced for all its products. This tip continues to give an overview of all those new enhancements for the Analysis Services product. As noted in part 1, links to the original tips are provided for more details if applicable and Azure Analysis Services is not included in this overview.
Solution
Bi-directional Cross-filtering
One of my favorite enhancements is bi-directional cross-filtering. This feature allows a relationship in a Tabular model to be filtered in both directions. This solves many issues, in particular the many-to-many relationship scenario where you use a bridge tables between two other tables (called a factless fact table in dimensional modeling jargon).
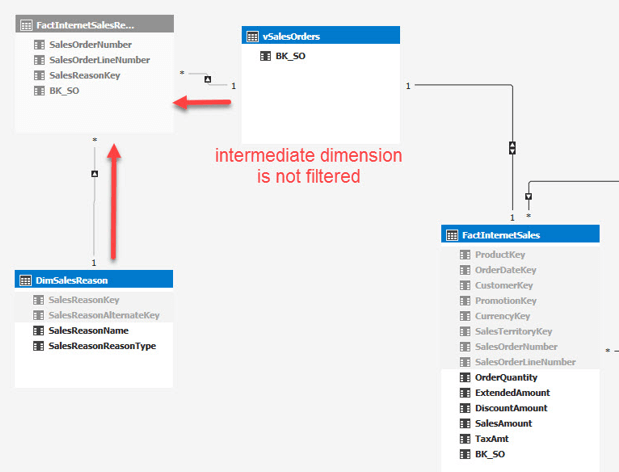
By simply enabling a property, you can solve the issue where the filters don’t propagate to the fact table, without needing to create additional complex measures.
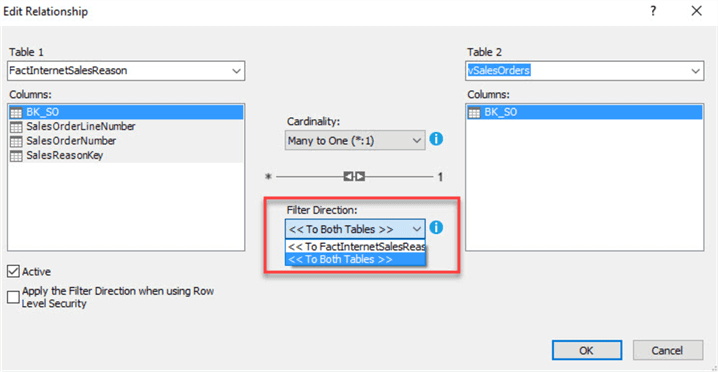
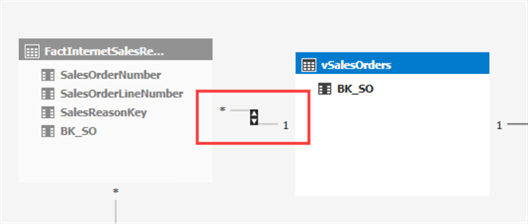
You can see the relationship now has arrows in both directions:
The bi-directional cross-filtering property has been discussed in depth for various scenarios in the following tips:
- Bi-Directional Cross-Filtering in Analysis Services Tabular 2016 - Part 1 (many-to-many relationships)
- Bi-Directional Cross-Filtering in Analysis Services Tabular 2016 - Part 2 (dynamic row-level-security)
- Bi-Directional Cross-Filtering in Analysis Services Tabular 2016 - Part 3 (measures in a dimension)
Calculated Tables
Another splendid feature is the ability to create a new table in the Tabular model as the result of a DAX query. This allows you for example to easily create a date table in your model.
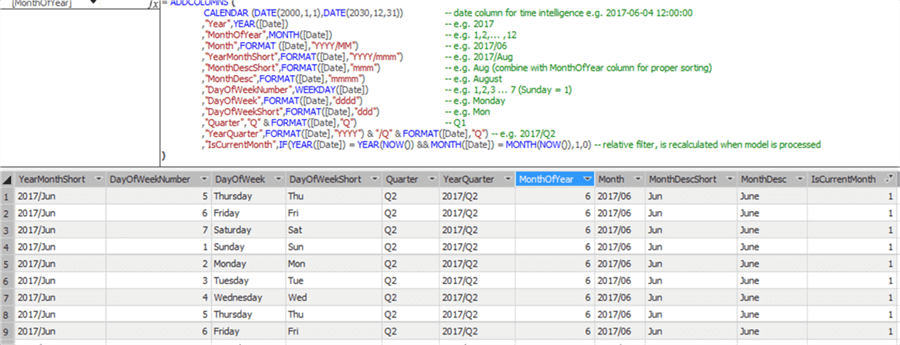
The topic of calculated tables and its various use cases has been covered in these tips:
- Scenarios for Using Calculated Tables in Analysis Services Tabular 2016 or Power BI Desktop – Part 1 (creating a small lookup table)
- Scenarios for Using Calculated Tables in Analysis Services Tabular 2016 or Power BI Desktop – Part 2 (creating a date dimension)
- Scenarios for Using Calculated Tables in Analysis Services Tabular 2016 or Power BI Desktop – Part 3 (creating an aggregate table)
Various Changes
There are many new changes and features but who don’t warrant an entire section of their own. However, it doesn’t make them less important.
- Formula Fixup. If you rename a table or column, all DAX expressions used in the model will be update. This drastically improves creation of Tabular models.
- Support for using Visual Studio configuration manager to create multiple environments. For example, you can create a test and production environment in Visual Studio to deploy the Tabular model to different servers. An example of the concept with Integration Services can be found in the tip Using Visual Studio configurations in SQL Server Integration Services projects.
- Tabular models can now process multiple partitions of a table in parallel. This is an important improvement for processing performance.
- You can now add computer accounts as members of the SSAS administrators group. You can do this through Management Studio if you are an SSAS administrator.
- Analysis Services now supports DBCC (database consistency checker) commands. DBCC can detect potential data corruption issues. It can run on demand but it also runs internally. This update is also for SSAS Multidimensional.
- This release includes a graphical user interface for SSMS to configure and maintain Analysis Services Extended Events (XE) sessions. With XE sessions, you can monitor server activity in real time, or you can load the data streams in memory or save them to disk. Extended Events is regarded as the replacement for SQL Server Profiler. More info can be found in Monitor Analysis Services with SQL Server Extended Events.
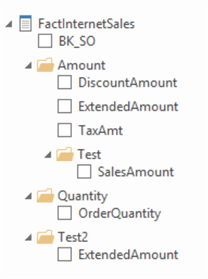
- An important usability feature has been added: display folders. With display folders, you can organize columns of a table or measures into folders. It’s possible to nest display folders (using backslashes) or to put a column into multiple folders (using semi-colons), just like in SSAS Multidimensional.
Analysis Services Tabular Service Pack 1
The first SQL Server 2016 service pack focused on bringing better performance and scalability to the product:
- NUMA awareness. The in-memory engine now maintains a separate job queue on each NUMA node, which guarantees the segment scan jobs run on the same node where the memory is allocated for the segment data. By default, NUMA awareness is only enabled for systems with at least 4 NUMA nodes.
- Memory allocation. By using Intel Threading Building Blocks, SSAS has a scalable allocator providing separate memory pools for every core. This allows the system to scale almost linearly when the number of cores increases.
- Heap fragmentation. The same allocator also reduces performance problems caused by heap fragmentation in the Windows Heap.
Next Steps
- If you want to try out all of those new features, you can download SQL Server 2016 Developer edition for free.
- You can find more SSAS 2016 features in the first part of this tip.
- The official overview of new features can be found here.
- You can find more Analysis Services tips in this overview.
- For more SQL Server 2016 tips, you can use this overview.
About the author
 Koen Verbeeck is a seasoned business intelligence consultant at AE. He has over a decade of experience with the Microsoft Data Platform in numerous industries. He holds several certifications and is a prolific writer contributing content about SSIS, ADF, SSAS, SSRS, MDS, Power BI, Snowflake and Azure services. He has spoken at PASS, SQLBits, dataMinds Connect and delivers webinars on MSSQLTips.com. Koen has been awarded the Microsoft MVP data platform award for many years.
Koen Verbeeck is a seasoned business intelligence consultant at AE. He has over a decade of experience with the Microsoft Data Platform in numerous industries. He holds several certifications and is a prolific writer contributing content about SSIS, ADF, SSAS, SSRS, MDS, Power BI, Snowflake and Azure services. He has spoken at PASS, SQLBits, dataMinds Connect and delivers webinars on MSSQLTips.com. Koen has been awarded the Microsoft MVP data platform award for many years.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips






