By: Joe Gavin | Comments (2) | Related: > Data Types
Problem
SQL Server has many different data types and it is not always a given as which data type to use, so this outline gives you a quick overview of the different data types you can use in SQL Server.
Solution
Following are commonly used data types organized by category with a brief description, range of values, storage size, and an example.
Exact Numerics SQL Server Data Types
Int Data Type
- Int is used to store a whole number and is the primary integer data type
- Range of values: -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647
- Storage size: 4 Bytes
-- declare an int variable, assign it a value, and increment it DECLARE @MyInt int = 0 SET @MyInt += 1 SELECT @MyInt AS [MyInt]

BigInt Data Type
- Bigint is used to store a whole number that is outside of the range of an int
- Range of values: -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807
- Storage size: 8 Bytes
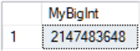
-- make the variable a bigint DECLARE @MyBigInt bigint = 2147483648 SELECT @MyBigInt AS [MyBigInt]
Smallint Data Type
- Smallint takes less space than an INT and can be used when a whole number is guaranteed to be between -32,768 to 32,767
- Range of values: -32,768 to 32,767
- Storage size: 2 Bytes
-- smallint example DECLARE @MySmallInt smallint = 32000 SELECT @MySmallInt AS [MySmallInt]

Tinyint Data Type
- Tinyint can be used when a whole number is guaranteed to be between 0 and 255, i.e. number of years of a mortgage
- Range of values: 0 to 255
- Storage size: 1 Byte
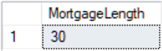
-- tinyint example of length of a mortgage in years DECLARE @MortgageLength tinyint = 30 SELECT @MortgageLength AS [MortgageLength]
Bit Data Type
- Bit can be used to represent a Boolean value such as a switch is either on or off, a process is done or it isn’t, etc.
- Range of values: 0 or 1, or a NULL
- Storage size = 1 Byte per every 8-bit column in a table
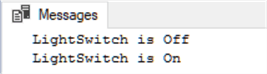
-- BIT example as an on / off value of a light switch DECLARE @LightSwitch bit = 0 IF @LightSwitch = 1 PRINT 'LightSwitch is On' ELSE PRINT 'LightSwitch is Off' SET @LightSwitch = 1 -- turn on IF @LightSwitch = 1 PRINT 'LightSwitch is On' ELSE PRINT 'LightSwitch is Off'
Decimal Data Type
- Decimal is a fixed precision and scale type
- Range of values: 10^38 +1 to 10^38
- Storage size:
- Precision 1-9 5 Bytes
- Precision 10-19 9 Bytes
- Precision 20-28 13 Bytes
- Precision 29-38 17 Bytes
- Functionally the same as numeric
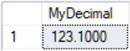
/* decimal (p,s) p = precision = maximum total number of digits to be stored including both sides of decimal point - must 1 thru 38 - default = is 18 s = scale = number of digits to the right of the decimal point - default = 0 */ DECLARE @MyDecimal decimal(8,4) = 123.1 -- 8 total digits with 4 to the right of the decimal SELECT @MyDecimal AS MyDecimal
Numeric Data Type
- Numeric is a fixed precision and scale type
- Range of values: 10^38 +1 to 10^38
- Storage size:
- Precision 1-9 5 Bytes
- Precision 10-19 9 Bytes
- Precision 20-28 13 Bytes
- Precision 29-38 17 Bytes
- Functionally the same as decimal
/* numeric (p,s) p = precision = maximum total number of digits to be stored including both sides of decimal point - must 1 thru 38 - default = is 18 s = scale = number of digits to the right of the decimal point - default = 0 */ DECLARE @MyNumeric numeric(8,4) = 123.1 -- 8 total digits with 4 to the right of the decimal SELECT @MyNumeric AS MyNumeric

Money Data Type
- Money represents a monetary value
- Range of values: -922,337,203,685,477.5808 to 922,337,203,685,477.5807
- Storage size: 8 Bytes
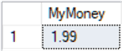
/* numeric (p,s) p = precision = maximum total number of digits to be stored including both sides of decimal point - must 1 thru 38 - default = is 18 s = scale = number of digits to the right of the decimal point - default = 0 */ --declare variable and set to $1.99 DECLARE @MyMoney money = 1.99 SELECT @MyMoney AS MyMoney
Smallmoney Data Type
- Smallmoney represents a monetary value
- Range of values: - 214,748.3648 to 214,748.3647
- Storage size: 4 Bytes
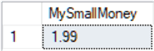
--declare variable and set to $1.99 DECLARE @MySmallMoney smallmoney = 1.99 SELECT @MySmallMoney AS MySmallMoney
Approximate Numerics SQL Server Data Types
Float Data Type
- Float is an approximate number data type used to store a floating-point number
- float (n) - n is the number of bits that are used to store the mantissa in scientific notation
- Range of values: - 1.79E+308 to -2.23E-308, 0 and 2.23E-308 to 1.79E+308
- Storage size: 4 Bytes if n = 1-9 and 8 Bytes if n = 25-53 – default = 53
-- float DECLARE @MyFLoat float = 0.1111111111111111111111111111111111111 -- 15 digit precision output SELECT @MyFLoat AS MyFloat

Real Data Type
- Real is an approximate number data type equivalent to a float(24) used to store a floating-point number
- Range of values: - 3.40E + 38 to -1.18E - 38, 0 and 1.18E - 38 to 3.40E + 38
- Storage size: 4 Bytes
-- real DECLARE @MyReal real = 0.1111111111111111111111111111111111111 -- 7 digit precision output SELECT @MyReal AS MyReal

Date and Time SQL Server Data Types
Date Data Type
- Defines a date in the format yyyy-mm-dd
- Range of values: 0001-01-01 through 9999-12-31
- Storage size: 3 Bytes
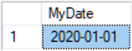
-- declare variable and set to Jan 1 2020 DECLARE @MyDate date = '2020-01-01' SELECT @MyDate
Time Data Type
- Defines a time
- Range of values: 00:00:00.0000000 through 23:59:59.9999999
- Storage size: 5 Bytes
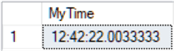
-- declare time variable and set to current time DECLARE @MyTime time = GETDATE() SELECT @MyTime AS MyTime
Datetime Data Type
- Define a date and time
- Range of values: 0001-01-01 through 9999-12-31 - 00:00:00.0000000 through 23:59:59.9999999
- Storage size: 8 Bytes
-- declare datetime variable and set to current time DECLARE @MyDateTime datetime = GETDATE() SELECT @MyDateTime AS MyDatetime
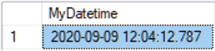
Datetime2 Data Type
- Define a date and time with higher precision than datetime
- DECLARE @VarName(n) where n is a value from 1 to 7 defining precision with default of 7
- Range of values: 1753-01-01 through 9999-12-31 - 00:00:00.0000000 through 23:59:59.9999999
- Storage
size:
- precision < 3 6 Bytes
- precision = 3 or 4 7 Bytes
- precision > 4 8 Bytes
-- declare datetime2 variable and set to current time DECLARE @MyDatetime2 datetime2(7) = GETDATE() SELECT @MyDatetime2 AS MyDatetime2
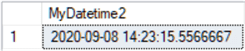
Smalldatetime Data Type
- Define a date and time without fractional seconds
- Range of values: 1900-01-01 through 2079-06-06 - 00:00:00 through 23:59:59
- Storage size: 4 Bytes
-- declare smalltime variable and set to current time DECLARE @MySmalldatetime smalldatetime = GETDATE() SELECT @MySmalldatetime AS MySmalldatetime

Datetimeoffset Data Type
- Defines a date and time with time zone awareness
- DECLARE @VarName datetimeoffset(n) where n is a value from 1 to 7 defining precision with default of 7
- Range of values: 0001-01-01 through 9999-12-31 - 00:00:00 through 23:59:59.9999999 - -14:00 through +14:00
- Storage size: 10 Bytes
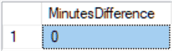
-- compare times in 2 timezones DECLARE @Edt datetimeoffset = CAST('2020-01-01 08:00:00.000 -00:00' AS datetimeoffset) DECLARE @Pdt datetimeoffset = CAST('2020-01-01 05:00:00.000 -03:00' AS datetimeoffset) SELECT DATEDIFF(minute, @Edt, @Pdt) as MinutesDifference
Character Strings SQL Server Data Types
Char Data Type
- Char is fixed size string used to store characters
- Char(n | max) – where n is the fixed length of the string in Byte pairs from 1 through 8,000 and max is 8,000
- Storage size: n
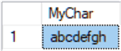
-- char DECLARE @MyChar char(20) = 'abcdefgh' -- 20 bytes used SELECT @MyChar AS MyChar
Varchar Data Type
- Varchar is a variable size string used to store characters
- Varchar(n | max) – where n is the fixed length of the string in Byte pairs from 1 through 8,000 and max is 8,000
- Storage size: up to n or max
-- char DECLARE @MyChar char(20) = 'abcdefgh' -- 20 bytes used SELECT @MyChar AS MyChar

Text Data Type
- Test is a variable length string up to 2,147,483,647 Bytes
- Invalid for local variable
- Storage size: to 2,147,483,647 Bytes
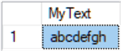
-- create a table with 1 field of type text CREATE TABLE dbo.MyTable(MyText text NULL) --insert value INSERT dbo.MyTable VALUES('abcdefgh') SELECT MyText FROM dbo.MyTable
Unicode Character Strings SQL Server Data Types
Nchar Data Type
- Nchar is fixed size string
- Use to store string of fixed length characters
- Nchar(n | max) – where n is the fixed length of the string in Byte pairs from 1 through 4,000 and max is 4,000
- Storage size: n or max
-- nchar DECLARE @MyNchar char(10) = 'abcdefgh' -- 20 bytes used SELECT @MyNchar AS MyNchar

Nvarchar Data Type
- Nvarchar is a variable size string
- Can store text in multiple languages
- Nvarchar(n | max) – where n is the fixed length of the string in Byte pairs from 1 through 4,000 and max is 4,000
- Storage size: up to n or max
-- nvarchar DECLARE @MyNvarchar char(10) = 'abcdefgh' -- 8 bytes used SELECT @MyNvarchar AS MyNvarchar

Binary Strings SQL Server Data Types
Binary Data Type
- Binary is a fixed length data type
- Can be used to store any kind of binary data of fixed length like files, etc.
- Binary(n) – where n is from 1 to 8,000
- Storage size: n
-- binary DECLARE @MyBinary binary(2) = 100 SELECT CAST(@MyBinary AS int) AS MyBinary

Varbinary Data Type
- Varbinary is a variable length data type that can be used to store any kind of binary data of varied length like files, etc.
- Varbinary(n | max) – where n is from 1 to 8,000 and max is 8,000
- Storage size: n
-- varbinary DECLARE @MyVarbinary varbinary(2) = 100 SELECT CAST(@MyVarbinary AS int) AS MyVarbinary

Next Steps
Following are some links with further info on data types:
About the author
 Joe Gavin is from the Greater Boston area. He started working with SQL Server and Sybase in 1998 in the financial services industry and has been a SQL Server Database Administrator for a dairy cooperative since 2011. He graduated from Northeastern University in Boston with a Bachelor of Science in Engineering Technology (BSET) degree in Computer Technology. Joe has spoken at the Boston and Providence SQL Saturday events.
Joe Gavin is from the Greater Boston area. He started working with SQL Server and Sybase in 1998 in the financial services industry and has been a SQL Server Database Administrator for a dairy cooperative since 2011. He graduated from Northeastern University in Boston with a Bachelor of Science in Engineering Technology (BSET) degree in Computer Technology. Joe has spoken at the Boston and Providence SQL Saturday events. This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips






