By: Scott Murray | Comments (29) | Related: > Reporting Services Administration
Problem
The ReportServer database stores all the details concerning the SSRS datasources, datasets, and reports and includes details about their parameters, location, run statistics, subscriptions, and queries. Much of the information needed to maintain SSRS can be gleaned from the Report Manager or by connecting to SSRS in Management studio. However, sometimes you need more details than is provided by these methods. What options are available?
Solution
SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS) installs a ReportServer database which house the nuts and bolts of the Reporting Services Infrastructure. In a previous post, we covered the ExecutionLog table and views included in the ReportServer database which describes the ExecutionLogStorage and related views ExecutionLog, ExecutionLog2, and ExecutionLog3, so we will not cover those areas in depth. However many other tables exist in that database which will be introduced in this article. Although these queries can be extremely helpful for specific needs, PLEASE NOTE that these queries are not supported by Microsoft and future updates and upgrades could break their functionality. Testing an upgrade is, of course, the key when dealing with unsupported queries.
The main tables to be used in the queries include:
- Catalog: This table contains the main details about SSRS reports and folders. Many of the below queries will center around this table.
- Datasources: This table contains the root details about how the report datasets connect to its related resource.
- Subscriptions, Schedule, Notifications, & ActiveSubscriptions: These tables contain information about scheduled report subscriptions.
- Users: This table contains details about access details for users of the report server including those users running the reports and those users publishing the reports.
Example Queries
Query 1
This provides a basic layer of the reports, folders, and other objects that make up the folder structure of the Report Server.
--QUERY 1 USE ReportServer GO SELECT CASE WHEN C.Name = '' THEN 'Home' ELSE C.Name END AS ItemName, C.Description as Report_Description, LEN(C.Path) - LEN(REPLACE(C.Path, '/', '')) AS ItemLevel, CASE WHEN C.type = 1 THEN '1-Folder' WHEN C.type = 2 THEN '2-Report' WHEN C.type = 3 THEN '3-File' WHEN C.type = 4 THEN '4-Linked Report' WHEN C.type = 5 THEN '5-Datasource' WHEN C.type = 6 THEN '6-Model' WHEN C.type = 7 Then '7-ReportPart' WHEN C.type = 8 Then '8-Shared Dataset' ELSE '9-Unknown' END AS ItemType, CASE WHEN C.Path = '' THEN 'Home' ELSE C.Path END AS Path, ISNULL(CASE WHEN CP.Name = '' THEN 'Home' ELSE CP.Name END, 'Home') AS ParentName, ISNULL(LEN(CP.Path) - LEN(REPLACE(CP.Path, '/', '')), 0) AS ParentLevel, ISNULL(CASE WHEN CP.Path = '' THEN ' Home' ELSE CP.Path END, ' Home') AS ParentPath FROM dbo.Catalog AS CP RIGHT OUTER JOIN dbo.Catalog AS C ON CP.ItemID = C.ParentID
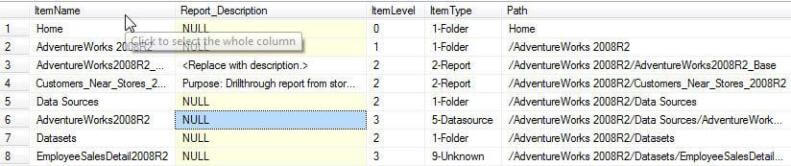
Query 1 Example Results
As noted in the below query results, the item name (folder name, report name, etc), the item type, the item path in the folder structure, and the item's parent are returned in the result set..
Query 2
This provides more report level detail about a reports including who created and modified it, when was it last executed and conveys some basic subscription details. Scott Herbent's SQL Ninja blog provided the initial basis for this query, although extensive modification has been made..
--Query 2 Complex Catalog Query USE ReportServer GO SELECT CAT_PARENT.Name AS ParentName, CAT.Name AS ReportName, ReportCreatedByUsers.UserName AS ReportCreatedByUserName, CAT.CreationDate AS ReportCreationDate, ReportModifiedByUsers.UserName AS ReportModifiedByUserName, CAT.ModifiedDate AS ReportModifiedDate, CountExecution.CountStart AS ReportExecuteCount, EL.InstanceName AS LastExecutedServerName, EL.UserName AS LastExecutedbyUserName, EL.TimeStart AS LastExecutedTimeStart, EL.TimeEnd AS LastExecutedTimeEnd, EL.Status AS LastExecutedStatus, EL.ByteCount AS LastExecutedByteCount, EL.[RowCount] AS LastExecutedRowCount, SubscriptionOwner.UserName AS SubscriptionOwnerUserName, SubscriptionModifiedByUsers.UserName AS SubscriptionModifiedByUserName, SUB.ModifiedDate AS SubscriptionModifiedDate, SUB.Description AS SubscriptionDescription, SUB.LastStatus AS SubscriptionLastStatus, SUB.LastRunTime AS SubscriptionLastRunTime FROM dbo.Catalog CAT INNER JOIN dbo.Catalog CAT_PARENT ON CAT.ParentID = CAT_PARENT.ItemID INNER JOIN dbo.Users ReportCreatedByUsers ON CAT.CreatedByID = ReportCreatedByUsers.UserID INNER JOIN dbo.Users ReportModifiedByUsers ON CAT.ModifiedByID = ReportModifiedByUsers.UserID LEFT OUTER JOIN ( SELECT ReportID, MAX(TimeStart) LastTimeStart FROM dbo.ExecutionLog GROUP BY ReportID ) AS LatestExecution ON CAT.ItemID = LatestExecution.ReportID LEFT OUTER JOIN ( SELECT ReportID, COUNT(TimeStart) CountStart FROM dbo.ExecutionLog GROUP BY ReportID ) AS CountExecution ON CAT.ItemID = CountExecution.ReportID LEFT OUTER JOIN dbo.ExecutionLog AS EL ON LatestExecution.ReportID = EL.ReportID AND LatestExecution.LastTimeStart = EL.TimeStart LEFT OUTER JOIN dbo.Subscriptions SUB ON CAT.ItemID = SUB.Report_OID LEFT OUTER JOIN dbo.Users SubscriptionOwner ON SUB.OwnerID = SubscriptionOwner.UserID LEFT OUTER JOIN dbo.Users SubscriptionModifiedByUsers ON SUB.ModifiedByID = SubscriptionModifiedByUsers.UserID ORDER BY CAT_PARENT.Name, CAT.Name
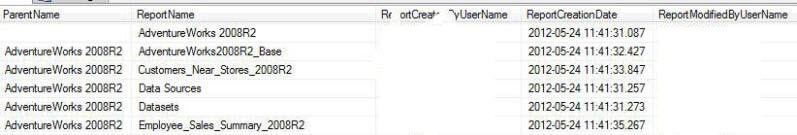
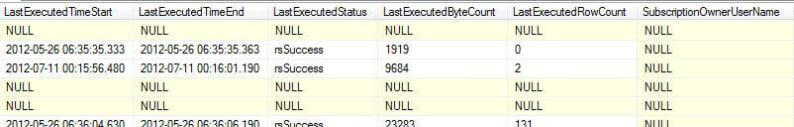
Query 2 Example Results
Note in the results below, that a Blank Parent Name is actually the "Home" directory on the report server.
Query 3
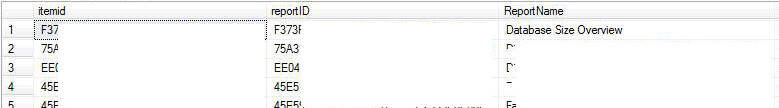
This provides the scheduling details for our subscription and the related SQLAgent JobID. The SQLAgent JobID can be used to run the "Subscription on an adhoc basis or for 1 time report runs. Additionally, Query 3A is from the SQLServer Central Forums http://www.sqlservercentral.com/Forums/Topic1131922-150-1.aspx#bm1132607 and provides details about the subscription report's parameters, output method and location, and the last run date.
--Query 3 Subscription Query USE REPORTSERVER CAT.itemid, REP_SCH.reportID, CAT.Name AS 'ReportName', sub.Report_OID, REP_SCH.ScheduleID AS 'SQLJobID', CASE SCH.recurrencetype WHEN 1 THEN 'Once' WHEN 3 THEN CASE SCH.daysinterval WHEN 1 THEN 'Every day' ELSE 'Every other ' + CAST(SCH.daysinterval AS varchar) + ' day.' END WHEN 4 THEN CASE SCH.daysofweek WHEN 1 THEN 'Every ' + CAST(SCH.weeksinterval AS varchar) + ' week on Sunday' WHEN 2 THEN 'Every ' + CAST(SCH.weeksinterval AS varchar) + ' week on Monday' WHEN 4 THEN 'Every ' + CAST(SCH.weeksinterval AS varchar) + ' week on Tuesday' WHEN 8 THEN 'Every ' + CAST(SCH.weeksinterval AS varchar) + ' week on Wednesday' WHEN 16 THEN 'Every ' + CAST(SCH.weeksinterval AS varchar) + ' week on Thursday' WHEN 32 THEN 'Every ' + CAST(SCH.weeksinterval AS varchar) + ' week on Friday' WHEN 64 THEN 'Every ' + CAST(SCH.weeksinterval AS varchar) + ' week on Saturday' WHEN 42 THEN 'Every ' + CAST(SCH.weeksinterval AS varchar) + ' week on Monday, Wednesday, and Friday' WHEN 62 THEN 'Every ' + CAST(SCH.weeksinterval AS varchar) + ' week on Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday and Friday' WHEN 126 THEN 'Every ' + CAST(SCH.weeksinterval AS varchar) + ' week from Monday to Saturday' WHEN 127 THEN 'Every ' + CAST(SCH.weeksinterval AS varchar) + ' week on every day' END WHEN 5 THEN CASE SCH.daysofmonth WHEN 1 THEN 'Day ' + '1' + ' of each month' WHEN 2 THEN 'Day ' + '2' + ' of each month' WHEN 4 THEN 'Day ' + '3' + ' of each month' WHEN 8 THEN 'Day ' + '4' + ' of each month' WHEN 16 THEN 'Day ' + '5' + ' of each month' WHEN 32 THEN 'Day ' + '6' + ' of each month' WHEN 64 THEN 'Day ' + '7' + ' of each month' WHEN 128 THEN 'Day ' + '8' + ' of each month' WHEN 256 THEN 'Day ' + '9' + ' of each month' WHEN 512 THEN 'Day ' + '10' + ' of each month' WHEN 1024 THEN 'Day ' + '11' + ' of each month' WHEN 2048 THEN 'Day ' + '12' + ' of each month' WHEN 4096 THEN 'Day ' + '13' + ' of each month' WHEN 8192 THEN 'Day ' + '14' + ' of each month' WHEN 16384 THEN 'Day ' + '15' + ' of each month' WHEN 32768 THEN 'Day ' + '16' + ' of each month' WHEN 65536 THEN 'Day ' + '17' + ' of each month' WHEN 131072 THEN 'Day ' + '18' + ' of each month' WhEN 262144 THEN 'Day ' + '19' + ' of each month' WHEN 524288 THEN 'Day ' + '20' + ' of each month' WHEN 1048576 THEN 'Day ' + '21' + ' of each month' WHEN 2097152 THEN 'Day ' + '22' + ' of each month' WHEN 4194304 THEN 'Day ' + '23' + ' of each month' WHEN 8388608 THEN 'Day ' + '24' + ' of each month' WHEN 16777216 THEN 'Day ' + '25' + ' of each month' WHEN 33554432 THEN 'Day ' + '26' + ' of each month' WHEN 67108864 THEN 'Day ' + '27' + ' of each month' WHEN 134217728 THEN 'Day ' + '28' + ' of each month' WHEN 268435456 THEN 'Day ' + '29' + ' of each month' WHEN 536870912 THEN 'Day ' + '30' + ' of each month' WHEN 1073741824 THEN 'Day ' + '31' + ' of each month' END WHEN 6 THEN 'The ' + CASE SCH.monthlyweek WHEN 1 THEN 'first' WHEN 2 THEN 'second' WHEN 3 THEN 'third' WHEN 4 THEN 'fourth' WHEN 5 THEN 'last' ELSE 'UNKNOWN' END + ' week of each month on ' + CASE SCH.daysofweek WHEN 2 THEN 'Monday' WHEN 4 THEN 'Tuesday' ELSE 'Unknown' END ELSE 'Unknown' END + ' at ' + LTRIM(RIGHT(CONVERT(varchar, SCH.StartDate, 100), 7)) AS 'ScheduleDetails' ,SCH.RecurrenceType ,CAT.Path AS 'ReportPath' FROM dbo.Catalog AS cat INNER JOIN dbo.ReportSchedule AS REP_SCH ON CAT.ItemID = REP_SCH.ReportID INNER JOIN dbo.Schedule AS SCH ON REP_SCH.ScheduleID = SCH.ScheduleID INNER JOIN dbo.Subscriptions AS sub ON sub.SubscriptionID = REP_SCH.SubscriptionID WHERE (LEN(CAT.Name) > 0) --AND --CAT.Name like 'Name of Report%' --Can add the Report Name ORDER BY 'ReportName' --OR --Query 3 Subscription Query --This code is from: http://www.sqlservercentral.com/Forums/Topic1131922-150-1.aspx#bm1132607 SELECT CAT.[Name] AS RptName , U.UserName , CAT.[Path] , res.ScheduleID AS JobID , sub.LastRuntime , sub.LastStatus , LEFT(CAST(sch.next_run_date AS CHAR(8)) , 4) + '-' + SUBSTRING(CAST(sch.next_run_date AS CHAR(8)) , 5 , 2) + '-' + RIGHT(CAST(sch.next_run_date AS CHAR(8)) , 2) + ' ' + CASE WHEN LEN(CAST(sch.next_run_time AS VARCHAR(6))) = 5 THEN '0' + LEFT(CAST(sch.next_run_time AS VARCHAR(6)) , 1) ELSE LEFT(CAST(sch.next_run_time AS VARCHAR(6)) , 2) END + ':' + CASE WHEN LEN(CAST(sch.next_run_time AS VARCHAR(6))) = 5 THEN SUBSTRING(CAST(sch.next_run_time AS VARCHAR(6)) , 2 , 2) ELSE SUBSTRING(CAST(sch.next_run_time AS VARCHAR(6)) , 3 , 2) END + ':00.000' AS NextRunTime , CASE WHEN job.[enabled] = 1 THEN 'Enabled' ELSE 'Disabled' END AS JobStatus , sub.ModifiedDate , sub.Description , sub.EventType , sub.Parameters , sub.DeliveryExtension , sub.Version FROM dbo.Catalog AS cat INNER JOIN dbo.Subscriptions AS sub ON CAT.ItemID = sub.Report_OID INNER JOIN dbo.ReportSchedule AS res ON CAT.ItemID = res.ReportID AND sub.SubscriptionID = res.SubscriptionID INNER JOIN msdb.dbo.sysjobs AS job ON CAST(res.ScheduleID AS VARCHAR(36)) = job.[name] INNER JOIN msdb.dbo.sysjobschedules AS sch ON job.job_id = sch.job_id INNER JOIN dbo.Users U ON U.UserID = sub.OwnerID ORDER BY U.UserName , RptName
Query 3 Example Results
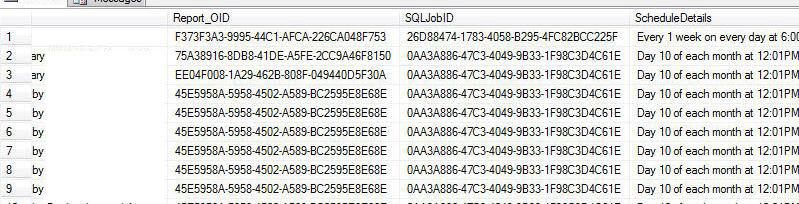
Query 4
The below provides information about who has access to folders and reports and describes the role / level of access the user or group have to that report.
--Query 4 Permissions/Roles USE ReportServer GO SELECT CAT.Name ,U.UserName ,ROL.RoleName ,ROL.Description ,U.AuthType FROM dbo.Users U INNER JOIN dbo.PolicyUserRole PUR ON U.UserID = PUR.UserID INNER JOIN dbo.Policies POLICY ON POLICY.PolicyID = PUR.PolicyID INNER JOIN dbo.Roles ROL ON ROL.RoleID = PUR.RoleID INNER JOIN dbo.Catalog CAT ON CAT.PolicyID = POLICY.PolicyID ORDER BY CAT.Name
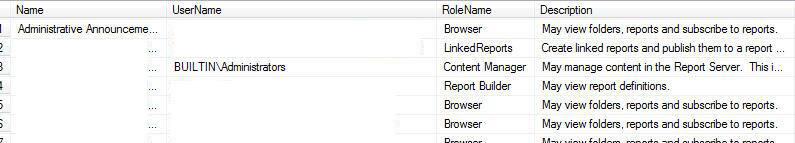
Query 4 Example Results
Note in the below results that not only is the role name displayed but also the roles description.
Other Hints
In reviewing the various tables, you will quickly notice that several tables contain XML formated fields. If you need to parse out these details, I would recommend reviewing Sankar Reddy's MSSQLTip: Script to determine SQL Server Reporting Services parameters, path and default values. Make sure you change the XMLNAMESPACE to 2008 in order for the XML to be parsed correctly.
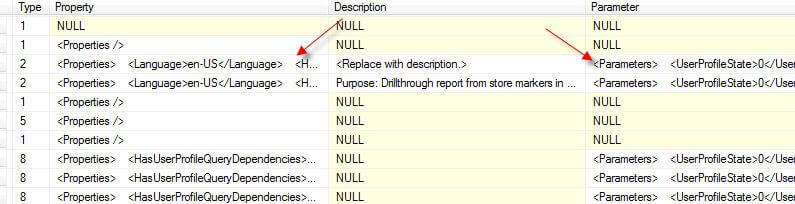
Let us review some of the tables in the ReportServer database. First, the Configuration table provides specifics on the Report Server setup; however, I would caution you to not make updates directly to this table, and instead use the SSRS Configuration Manager
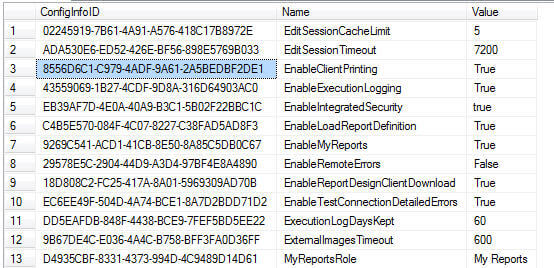
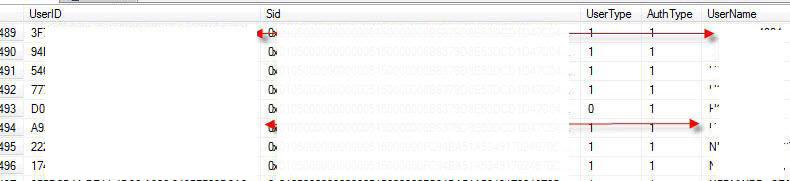
Next, the Users table, displayed below, is the link between the UserID that is assigned by SSRS and the actual UserName (active directory or local) who logs into the Report Server to run or maintain a report. You could use the User Name field to link up to Active Directory, if used, to get additional details concerning a user. Brady Upton's tip, Querying Active Directory Data from SQL Server will get you started querying Active Directory which you could link up to this UserName field.
Conclusion-Creating an Execution Log SSRS Report
In this tutorial, several of the ReportServer database tables, most importantly Catalog, Subscription, and Users, were reviewed. Several example queries showed some of the powerful information that could be gleamed from these tables, but be cautious about using these tables as they could change in future versions of SQL Server.
Next Steps
- CodePlex Project with various sample queries: http://ssrscatalogqueries.codeplex.com/
- SSRS Query Details: http://gallery.technet.microsoft.com/scriptcenter/42440a6b-c5b1-4acc-9632-d608d1c40a5c
- Check out these related resources:
About the author
 Scott Murray has a passion for crafting BI Solutions with SharePoint, SSAS, OLAP and SSRS.
Scott Murray has a passion for crafting BI Solutions with SharePoint, SSAS, OLAP and SSRS.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips






