By: Daniel Calbimonte | Comments | Related: > Analysis Services Development
Problem
I have a Tabular Database and I'd like to know how to use some common functions and expressions used in DAX as well as how to format the display of the data?
Solution
In this tip, we will show you some common expressions in DAX using a Tabular Database as well as how to format columns.
Requirements
- SQL Server 2016 (most of the functions will work on SQL Server 2014, but some are exclusive for SQL Server 2016 and future versions).
- SSDT should be installed.
- A Tabular Instance installed.
- Some Tables with Dates, Strings and Numbers.
Introduction
Here are some typical DAX expression and function examples for a Tabular Database.
DISTINCTCOUNT DAX Expression
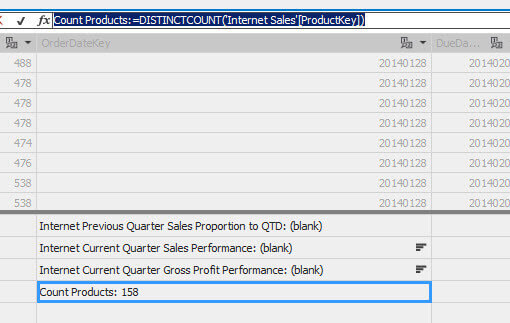
A very common function is the DISTINCTCOUNT. We can count the number of distinct rows. In this example, we will count the number of different Products using ProductKey:
Count Products:=DISTINCTCOUNT('Internet sales'[ProductKey])
SUM DAX Expression
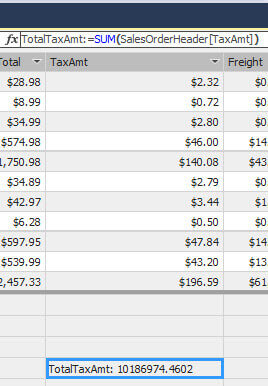
With SUM, you can add numbers of a specified column. The following example adds the values of the TaxAmt column in the SalesOrderHeader table:
TotalTaxAmt:=SUM(SalesOrderHeader[TaxAmt])
DATEDIFF DAX Expression
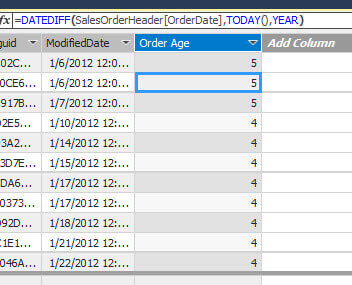
DATEDIFF is a new function in SQL Server 2016. It shows the difference between two dates. In this example, we will show the number of years of an OrderDate. It shows the difference between Today and the OrderDate:
=DATEDIFF(SalesOrderHeader[OrderDate],TODAY(),YEAR)
Concatenate Strings DAX Expression
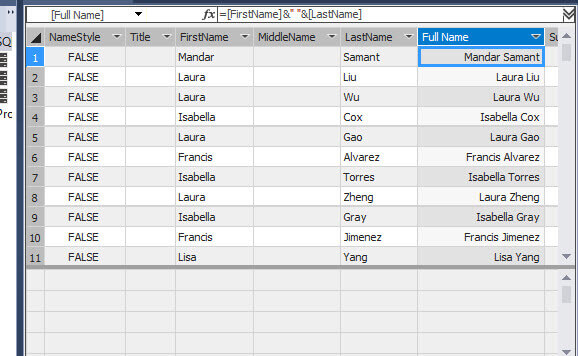
We can concatenate strings or other values using the &. The following example concatenates the FirstName and LastName with a space between them:
=[FirstName]&" "&[LastName]
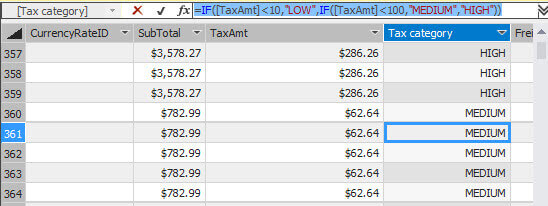
IF DAX Expression
IF allows conditional operations. The following example will show LOW if the TaxAmt is lower than 10, MEDIUM if the value is lower than 100, else HIGH:
=IF([TaxAmt]<10,"LOW",IF([TaxAmt]<100,"MEDIUM","HIGH"))
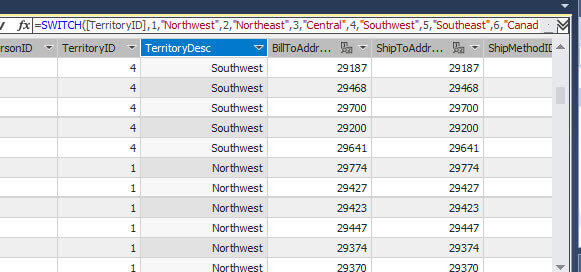
SWITCH DAX Expression
IF is used for conditional operations of 2 or 3 values usually. For more values, use SWITCH. The following example shows the Region Description according to a specific numeric value. For example if Territory ID is 1, the value will be Northwest, if the value is 2 then Northeast and so on:
=SWITCH([TerritoryID],1,"Northwest",2,"Northeast",3,"Central",4,"Southwest",5,"Southeast",6,"Canada",7,"France",8,"Germany",9,"Australia",10,"United Kingdom","Other")
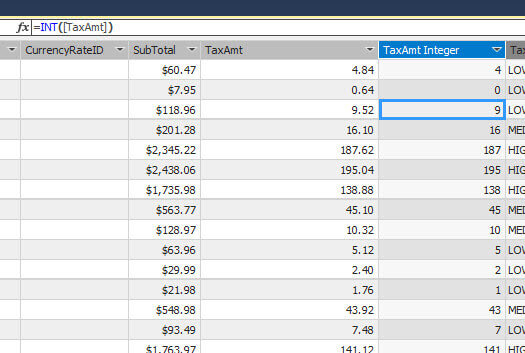
INT DAX Expression
The INT function displays the integer value of a specified number:
=INT([TaxAmt])
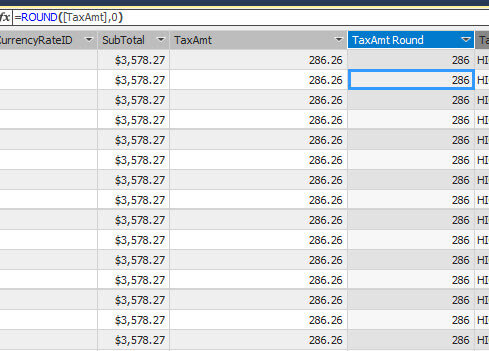
ROUND DAX Expression
If you need to round to the closest integer value, you can use the ROUND function. The following function rounds to an integer value with 0 decimals:
=ROUND([TaxAmt],0)
The following example rounds to a value with 3 decimals:
=ROUND([TaxAmt],3)
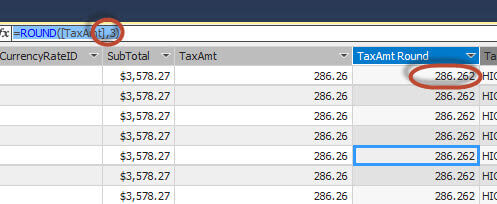
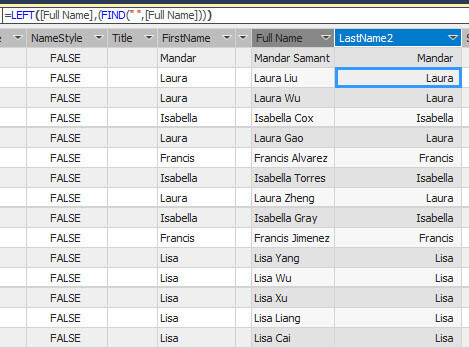
Parsing Strings DAX Expression
The following example gets the lastname from the fullname. The FIND function detects the position of the space and the function returns the string starting from the space until the end of the string:
=LEFT([Full Name],(FIND(" ",[Full Name])))
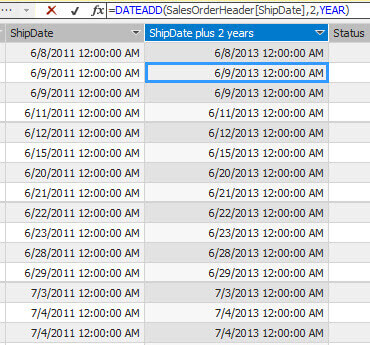
DATEADD DAX Expression
The example shows how to add 2 years to a specified data using the DATEADD function:
=DATEADD(SalesOrderHeader[ShipDate],2,YEAR)
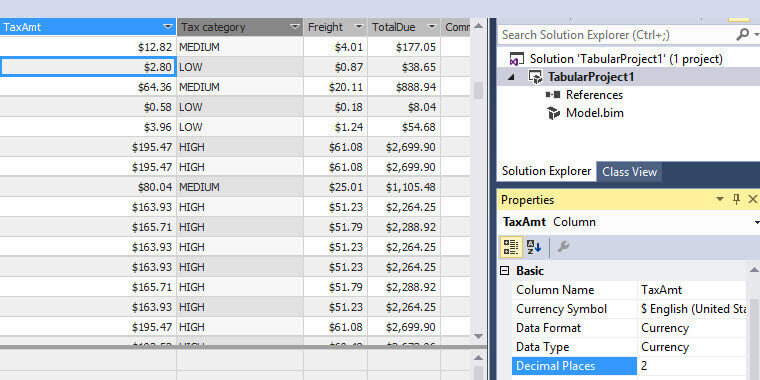
Formatting Column Display DAX Expression
Format Decimal Places
To format the display output there are several functions. However, the easiest way to handle the format is to go to properties. In this example, we are selecting 2 decimal places for TaxAmt:
Format Currency Display in DAX
It is also possible to select the currency symbol using the properties. In this example, we are using British pounds as the currency symbol:
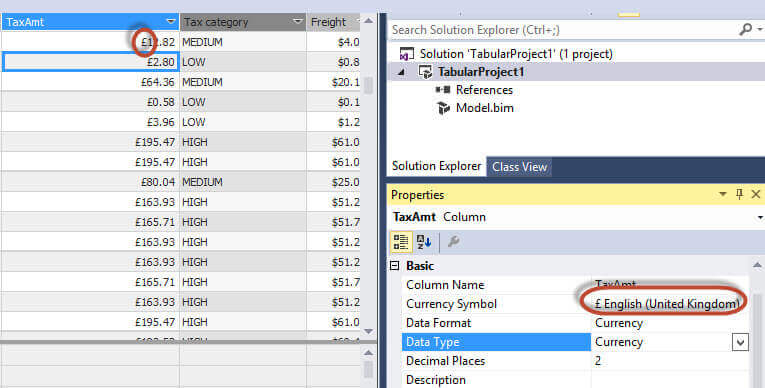
Change Data Format and Type in DAX
You can change the format from currency to decimal or other data types:
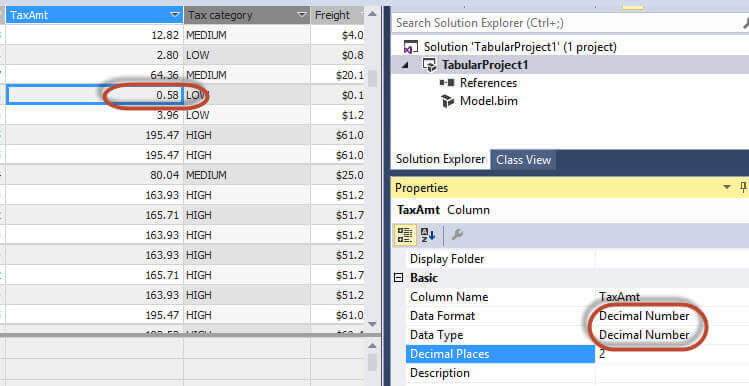
Conclusion
DAX includes functions and expressions very similar to Excel. The main idea of DAX was to create a more familiar language to create functions and expressions. DAX is simple for basic calculations, but it can be complex for some calculations.
Next Steps
For more information, refer to the following links:- DAX Function Reference
- DAX Operator Reference
- Getting Started with the DAX queries for SQL Server Analysis Services
- New DAX functions in SQL Server 2016
About the author
 Daniel Calbimonte is a Microsoft SQL Server MVP, Microsoft Certified Trainer and 6-time Microsoft Certified IT Professional. Daniel started his career in 2001 and has worked with SQL Server 6.0 to 2022. Daniel is a DBA as well as specializes in Business Intelligence (SSIS, SSAS, SSRS) technologies.
Daniel Calbimonte is a Microsoft SQL Server MVP, Microsoft Certified Trainer and 6-time Microsoft Certified IT Professional. Daniel started his career in 2001 and has worked with SQL Server 6.0 to 2022. Daniel is a DBA as well as specializes in Business Intelligence (SSIS, SSAS, SSRS) technologies.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips






