By: Ron L'Esteve | Updated: 2023-01-25 | Comments | Related: > Cloud Strategy
Problem
Numerous organizations are either considering or have already embarked on their cloud transformation journey. It is important to note that many of these organizations have existed for decades or centuries. Throughout this time, these organizations have been growing and evolving while maintaining legacy platforms and developing employee skills along the way. Legacy skills and platforms may hinder their success with digital innovation and cloud transformation initiatives, especially without a clear understanding of the roles and responsibilities involved in the process. This could lead to confusion and misalignment among teams.
Solution
By clearly understanding the roles and responsibilities involved in an organization's cloud transformation journey and how they all fit together, leaders can ensure that their cloud transformation is well-planned, executed, and aligned as their teams work towards the same goals. This article will provide a clear overview of the key cloud roles and responsibilities involved in cloud platform transformation and administration. These roles include leadership, development, and support personas at both cloud and traditional levels that all play a role in advancing an organization's evolutionary and revolutionary goals.
There are multiple role-based hierarchies within an organization. The sample organizational chart shown in the image below depicts some of the leadership, development, and support roles which we will discuss further in the article. In general, the CEO is responsible for the overall leadership and direction of the organization, while the CIO and CTO are responsible for the organization's technology-related leadership. The Vice President of Engineering and the Directors are responsible for leading the different engineering teams, and the Managers are responsible for leading teams of engineers and technicians. Individual engineers and technicians are responsible for designing, developing, and maintaining the organization's technology systems and infrastructure.
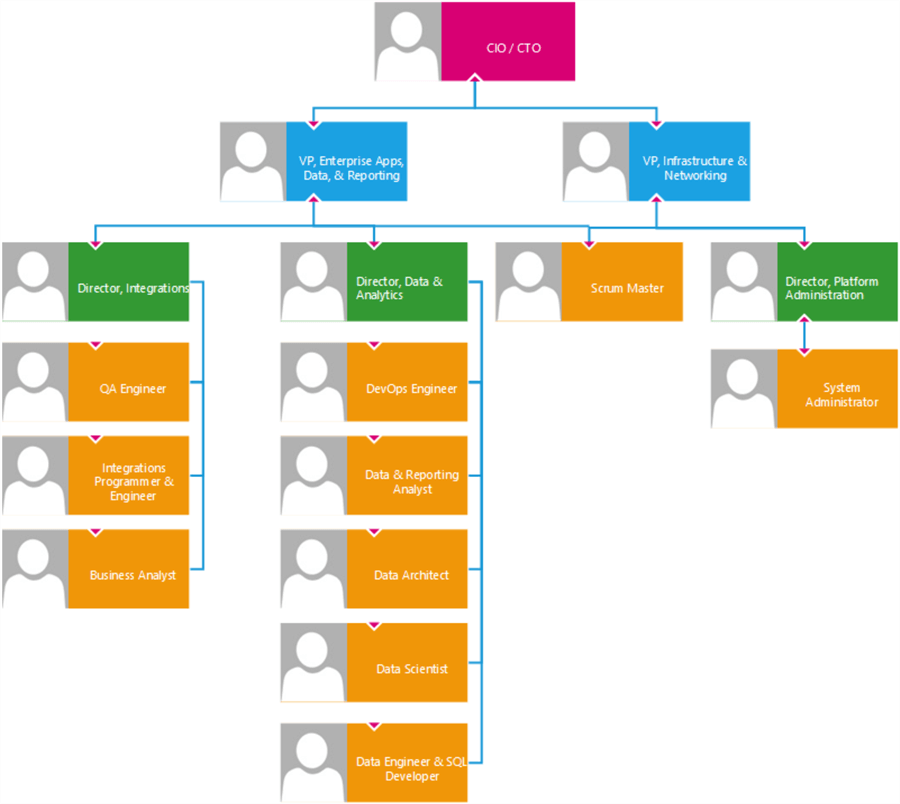
The Leaders
There are many levels of organizational leadership, including the C-Levels, Vice Presidents, and Directors. While cloud transformation's vision, strategy, and evangelism might be driven by the highest leadership levels, such as the CEO, the strategic and tactical responsibility, accountability, and ultimate charter of cloud transformation are driven by technology leadership. Technology Cloud leaders are responsible for managing the organization's use of cloud computing and ensuring its success.
The Cloud Leader's Responsibilities
While a Cloud Leader's specific responsibilities may vary depending on their role, some common responsibilities may include:
- Developing and Implementing a Cloud Strategy: Cloud leaders are responsible for developing and implementing a plan for the organization's use of cloud computing. This may involve working with the business to understand its needs, identifying the most appropriate cloud solutions, and developing a roadmap for implementation.
- Managing Cloud Projects: Cloud leaders may manage cloud-related projects, including coordinating with different teams and stakeholders, tracking progress, and ensuring that projects are completed on time and within budget.
- Ensuring Security and Compliance:Cloud leaders are responsible for ensuring that the organization's cloud computing environment is secure and compliant with relevant laws and regulations. This may involve implementing security measures, conducting regular security assessments, and responding to security incidents.
- Providing Technical Support: Cloud leaders may be responsible for providing technical support to users of the organization's cloud computing systems. This may involve troubleshooting issues, providing guidance and assistance, and answering customer questions.
- Managing Budgets and Resources: Cloud leaders may be responsible for managing the budget for the organization's cloud computing efforts and ensuring that resources are used efficiently.
- Staying Up-to-Date with Industry Trends and Developments: Cloud leaders should stay up-to-date with the latest developments in cloud computing and identify opportunities for the organization to take advantage of new technologies and innovations.
CIO, CTO, and Vice President
Chief Information Officers (CIO), Chief Technology Officers (CTO), and Vice Presidents (VP) are all senior-level executives within an organization. The CIO and CTO are executive-level positions involving strategic planning and decision-making for an organization's technology-related matters. The CIO is primarily responsible for the management and use of information and technology within an organization. At the same time, the CTO is responsible for the overall direction and oversight of an organization's technology-related matters. However, there are some key differences between the roles:
| CIO | CTO | VP | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scope of Responsibility | Responsible for the overall management and use of information and technology within an organization. This includes the implementation and maintenance of systems and processes, as well as the development and management of the IT budget. | Responsible for the overall direction and oversight of an organization's technology-related matters, including research and development, innovation, and the selection and implementation of new technologies. | Responsible for a specific area or function within the organization. The scope of their responsibility may vary depending on the specific role and industry. |
| Focus | Focus is on the overall internal IT strategy and on managing the internal IT systems and infrastructure. | Focus is more on the long-term strategy and direction of the organization's external technology-related efforts, including identifying and developing new technologies that could benefit the organization. | Focus is more on the practical, day-to-day aspects of managing an organization's IT infrastructure and systems. |
| Background & Expertise | May have more practical, hands-on experience with managing IT systems and infrastructure. | May have a more technical or research-oriented background. | May have a combination of practical, hands-on experience with managing IT systems and infrastructure and a technical research-oriented background. |
It is important to point out that some large modern organizations with ample budgets are beginning to create the Chief Cloud Officer (CCO) role. While often, in smaller or cost-conscious organizations, the CIO, CTO, or VP takes on this responsibility. The CCO is responsible for leading the overall strategy and direction of the organization's use of cloud computing. They work with the business to understand their needs and develop a plan for using the cloud to meet those needs.
Director and Manager
Directors and Managers are both leadership roles responsible for managing development and support teams. They have different areas of responsibility and levels of authority. Some key differences between the two roles are summarized in the following table:
| Director | Manager | |
|---|---|---|
| Scope of Responsibility | Responsible for leading a specific department or function within the organization. They may have a broad focus and are accountable for the overall strategy and direction of the department. | Responsible for leading a team or group of employees within the organization. They may have a narrower focus and be responsible for the team's day-to-day management. |
| Authority | Have more authority and decision-making power than managers. Directors may have the authority to make strategic decisions for the department or function that they lead. | Have more limited decision-making authority and may need to consult with their superiors before making certain decisions. |
| Reporting Relationship | Report to higher-level executives, such as vice presidents or the CEO. | Report to directors or other higher-level managers. |
Product Owner, Product Manager, and Program Manager
There are a few evolving managerial positions in many modern cloud organizations, including the Cloud Solutions Manager, Delivery Lead, Cloud Program Manager, Cloud Product Owner, and Cloud Strategist. These roles are responsible for managing the organization's overall cloud computing strategy and cloud portfolio. They work with the business to understand their needs and develop a plan that translates into a program or product for using the cloud to meet those needs. Depending on the organization, these responsibilities can be split across single or multiple roles.
A product owner, product manager, and program manager are all responsible for managing product development within an organization, but they have different roles and responsibilities. Some key differences between the three roles include:
| Product Owner | Product Manager | Program Manager | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scope of Responsibility | Responsible for defining and prioritizing the features and requirements for a specific product. They work closely with the development team to ensure the product is being built to meet the target market's needs. | Responsible for the overall strategy and direction of a product, including defining its vision and goals and making decisions about how to allocate resources to achieve those goals. | Responsible for managing multiple related projects or programs and ensuring they are completed on time and within budget. |
| Focus | Focus on defining and prioritizing the features and requirements for a specific product. | Focus on the overall strategy and direction of a product and on making decisions about allocating resources to achieve the product's goals. | Focus on managing multiple related projects or programs and ensuring they are completed on time and within budget. |
| Background & Expertise | May have more experience with product development, marketing, and discipline of the product they own. | May have more experience with product development, marketing, and discipline of the product they manage. | May have more experience with project management and coordinating complex projects. |
In summary, a product owner is responsible for defining and prioritizing the features and requirements for a specific product, a product manager is responsible for the overall strategy and direction of a product, and a program manager is responsible for managing multiple related projects or programs.
Scrum Master and Project Manager
A project manager and a scrum master are both responsible for managing projects but use different approaches and techniques. Some key differences between the two roles include:
| Project Manager | Scrum Master | |
|---|---|---|
| Methodology | Typically follows a traditional project management methodology, such as the Waterfall or PRINCE2 methods. This involves breaking the project into phases, creating a detailed plan, and following that plan closely to complete the project. | Follows the Scrum framework, which is an agile project management methodology. This involves breaking the project down into small increments called "sprints" and regularly reviewing and adjusting the project plan based on feedback and progress. |
| Role & Responsibilities | Responsible for managing the overall project and ensuring it is completed on time and within budget. They may create project plans, coordinate with different teams and stakeholders, and track progress. | Responsible for facilitating the Scrum process and helping the team follow the framework. They are not directly responsible for managing the project but for helping the team work together effectively and efficiently. |
| Team Dynamics | Responsible for leading and directing the team. | Focuses on facilitating and coaching the team while helping them self-organize and make decisions, rather than making decisions for them. |
In summary, a project manager follows a traditional project management methodology and manages the overall project. In contrast, a scrum master follows the Scrum framework and helps the team work together effectively and efficiently.
The Developers
Cloud development roles are responsible for building and deploying applications on the cloud. Some of the significant cloud development roles include:
- Cloud Developer: This person writes code to build and deploy applications on the cloud. They are responsible for creating and maintaining the organization's cloud-based applications focusing on one or many disciplines, including reporting, streaming, applications, integrations, and more.
- Cloud Solution Architect: This person is responsible for designing and building the cloud infrastructure for the organization. They work with the business to understand their needs and design a solution that meets them.
- Cloud DevOps Engineer: This person is responsible for managing the development, testing, and deployment of applications on the cloud. They may be responsible for tasks such as setting up and maintaining continuous integration and delivery pipelines, automating deployment processes, and monitoring the performance of applications.
- Cloud Data Engineer: This person is responsible for designing and building the data infrastructure for the organization's cloud-based applications. They may be responsible for tasks such as setting up and maintaining data warehouses and data lakes, designing and implementing data pipelines, and ensuring the data is secure and compliant.
- Cloud Security Engineer: This person is responsible for ensuring that the organization's cloud computing environment is secure. They work to prevent data breaches and unauthorized access to the system.
- Cloud AI Engineer: This person is responsible for building and deploying artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) models on the cloud. They may be involved in tasks such as designing and implementing cloud-based AI and ML systems, integrating AI and ML models into existing cloud-based systems, and optimizing the performance of AI and ML models on the cloud.
- Data Scientist: This person analyzes and interprets data to identify trends, patterns, and insights. They may be involved in tasks such as collecting and cleaning data, building and testing statistical models, and communicating the results of their analysis to stakeholders.
In summary, cloud development roles are responsible for building and deploying applications on the cloud and designing and building the infrastructure and data systems that support those applications.
The Support Team
Cloud support roles are responsible for supporting applications on the cloud. Some of the significant cloud support roles include:
- Cloud Administrator: This person manages the organization's cloud infrastructure and ensures it runs smoothly. They may be responsible for monitoring the system, configuring and maintaining servers, and providing technical support to users.
- Cloud Support Engineer: This person provides technical support to customers using the organization's cloud computing products and services. They may be responsible for troubleshooting issues, providing guidance and assistance, and answering customer questions.
- Cloud Sales Engineer: This person works with potential customers to explain the benefits of the organization's cloud computing products and services and helps them understand how the organization's cloud solutions can meet their needs.
- Cloud Project Manager: This person is responsible for managing cloud-related projects, including coordinating with different teams and stakeholders, tracking progress, and ensuring that projects are completed on time and within budget. They may also provide technical support to users by serving as a change manager.
In summary, cloud support roles are responsible for providing technical support to users of the organization.
The Analysts
Several analysts support cloud transformation. These include the following roles:
- Cloud Analyst: This person is responsible for analyzing and interpreting data related to the organization's use of the cloud. They may be involved in tasks such as monitoring the performance of cloud-based systems, identifying trends and patterns in cloud usage data, and providing recommendations for improving the efficiency and effectiveness of the organization's use of the cloud.
- Data Analyst: This person analyzes and interprets data to identify trends, patterns, and insights. They may be involved in tasks such as collecting and cleaning data, building and testing statistical models, and communicating the results of their analysis to stakeholders.
- Business Intelligence Analyst: This person is responsible for helping organizations make data-driven decisions. They may be involved in tasks such as gathering and analyzing data from various sources, creating reports and dashboards, and providing insights and recommendations based on their analysis.
- Business Analyst: This person is responsible for analyzing business processes and identifying opportunities for improvement. They may be involved in tasks such as gathering and analyzing data, creating models and simulations, and providing recommendations for improving efficiency and effectiveness.
In summary, a cloud analyst is responsible for analyzing and interpreting data related to the organization's use of the cloud, a data analyst is responsible for analyzing and interpreting data to identify trends and insights, a BI analyst is responsible for helping organizations make data-driven decisions, and a business analyst is responsible for analyzing business processes and identifying opportunities for improvement.
Conclusion
As an organization gains maturity on its cloud transformation journey, the skills of its leadership, development, support, and analyst teams continue to evolve and mature through the "growth-mindset philosophy." Understanding some of these traditional and cloud specialist roles will promote team alignment and success with digital innovation and cloud transformation initiatives. Additionally, these various traditional personas can upskill and transition to cloud-focused roles as part of their career progression and to further contribute to the organizational charter of "strategic innovation and digital transformation."
Next Steps
- Read more about How roles and responsibilities change in a cloud transition - Work Life by Atlassian
- To learn more about effective cloud change management strategies, read Gartner's article: Adopt This New 14x More Successful Change Management Strategy | Gartner
- Gain a deeper understanding of Cloud roles in the following article: What Are The Different Roles In The Cloud? A Beginners Guide. (openupthecloud.com)
- Read about how to Adapt roles, skills, and processes for the cloud - Cloud Adoption Framework | Microsoft Learn
About the author
 Ron L'Esteve is a trusted information technology thought leader and professional Author residing in Illinois. He brings over 20 years of IT experience and is well-known for his impactful books and article publications on Data & AI Architecture, Engineering, and Cloud Leadership. Ron completed his Master�s in Business Administration and Finance from Loyola University in Chicago. Ron brings deep tec
Ron L'Esteve is a trusted information technology thought leader and professional Author residing in Illinois. He brings over 20 years of IT experience and is well-known for his impactful books and article publications on Data & AI Architecture, Engineering, and Cloud Leadership. Ron completed his Master�s in Business Administration and Finance from Loyola University in Chicago. Ron brings deep tecThis author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips
Article Last Updated: 2023-01-25






