By: Eduardo Pivaral | Updated: 2023-07-18 | Comments | Related: > Azure Synapse Analytics
Problem
One of the premises of a modern warehouse is to be able to interconnect cloud services and process and analyze data from any provider with ease. Two of the top cloud services right now are Azure Synapse and Snowflake. Whatever your organization is implementing or if you need to transfer data from/to those services, it is important to know how to interconnect them and be able to transfer data between services.
Solution
Snowflake is a native-cloud, self-managed service for enterprise-level modern data applications. It is becoming one of the top data services in the world because of its capabilities and ease to use.
Azure Synapse is an enterprise-level analytics service. It provides analytics and big data capabilities using multiple languages and engines, with native support with other services like PowerBI, Databricks, and machine learning and cognitive services.
In a previous tip, we discussed how to pull data from Snowflake to Azure and in this tip will have two simple examples showing how to copy data from Azure Blob Storage (or any other source if you understand the basic steps) to Snowflake.
Setting Up the Example
For this example, we assume we have a Synapse Analytics service running, a Snowflake account, and at least one blob storage account.
How to create a Synapse Analytics service is outside the scope of this tip, but you can go to your Azure account at https://portal.azure.com and create a Synapse service:
For a Snowflake account, you can go to https://www.snowflake.com and create a new account using the Start for Free button:

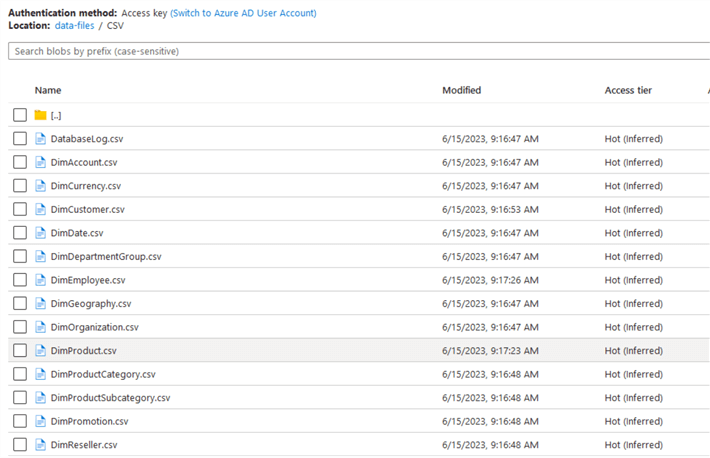
For this example, I have some sample CSV files in my Azure Blob storage that we will use to load into Snowflake.
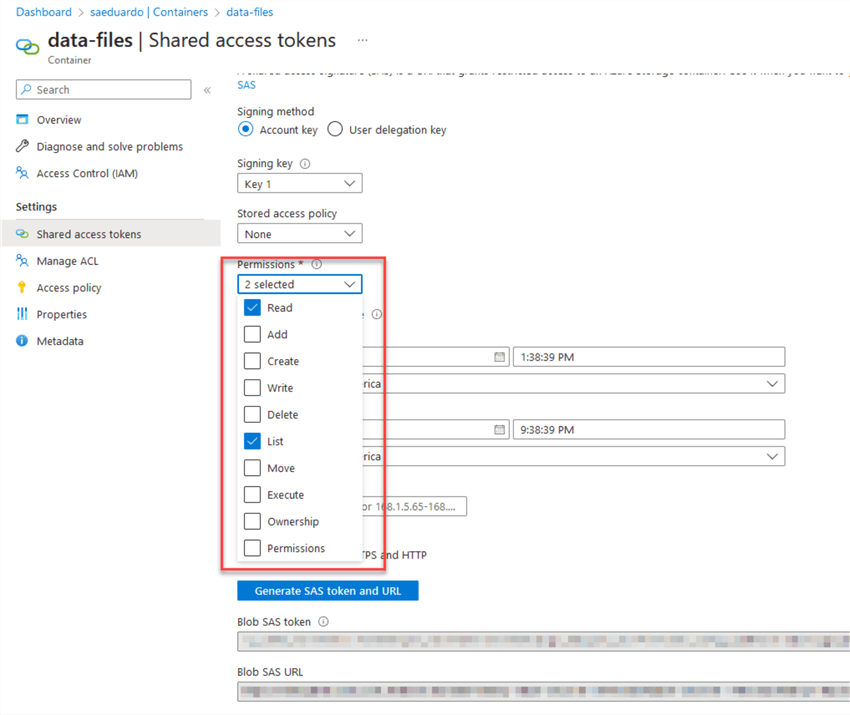
Also, we will use a SAS token and URL to access the blob storage for this example. You can configure it in the Azure portal here; for permissions, we will use Read and List:
Example: Load File from Azure to Snowflake Using Snowflake Stages
Setting Up Snowflake Stage
A stage is a place in Snowflake where the data files can be stored before loading them to a table. For our first example, manually loading files directly into Snowflake, we must define a stage to Azure blob storage.
Login to Snowflake and create a new worksheet if you plan to use web GUI:
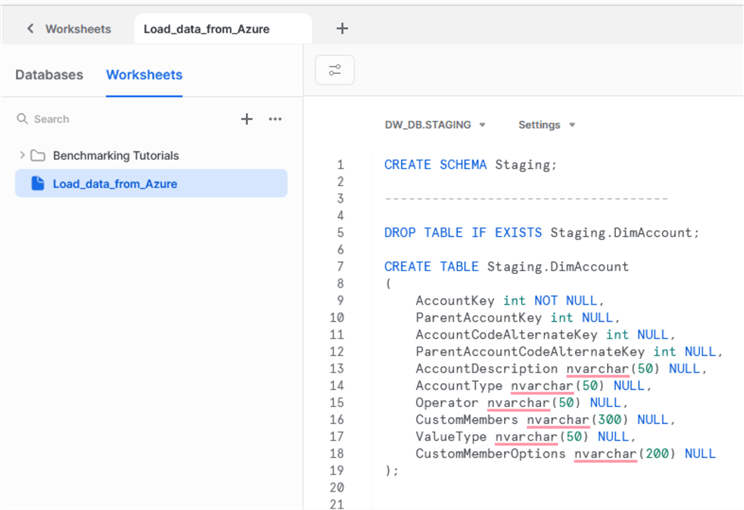
First, we need to create a schema and a table if you don’t have it yet:
CREATE SCHEMA Staging; ------------------------------------ DROP TABLE IF EXISTS Staging.DimAccount; CREATE TABLE Staging.DimAccount ( AccountKey int NOT NULL, ParentAccountKey int NULL, AccountCodeAlternateKey int NULL, ParentAccountCodeAlternateKey int NULL, AccountDescription nvarchar(50) NULL, AccountType nvarchar(50) NULL, Operator nvarchar(50) NULL, CustomMembers nvarchar(300) NULL, ValueType nvarchar(50) NULL, CustomMemberOptions nvarchar(200) NULL );
Remember that the table should match the format of the file you plan to use.
Then we create a file format where we will define the CSV properties. Use this link to learn more about Snowflake file formatting: Create File Format.
----------------------------------
CREATE OR REPLACE FILE FORMAT CSV_tips
TYPE = CSV
FIELD_DELIMITER = '|'
SKIP_HEADER = 0
NULL_IF = ('NULL', 'null')
EMPTY_FIELD_AS_NULL = true;
In our case, no header and a pipe delimiter.
Then, and this is one of the most important parts of the example, we set up the stage.
For URL, we use the location of our blob storage + the folders we want to retrieve the data and replace the “HTTPS://” part with “azure://”.
In my case, this is my URL:
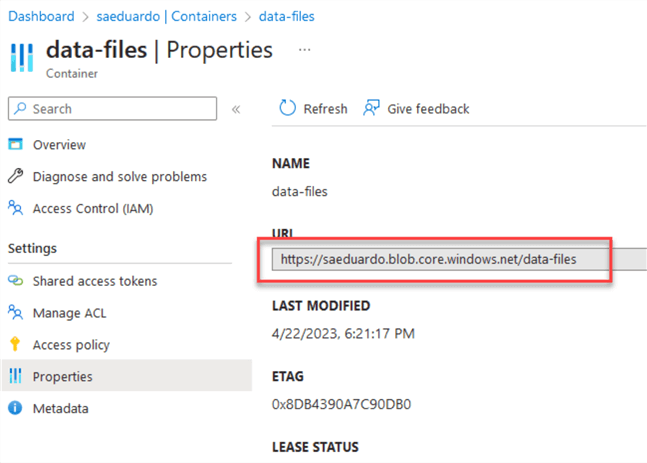
So, I need to add /CSV/ at the end of it and replace the https for azure.
For the Azure SAS token, use the one we generated earlier (BLOB SAS TOKEN).
And last, for file format, use the one we created in the previous step:
CREATE OR REPLACE STAGE Staging_files
url='azure://saeduardo.blob.core.windows.net/data-files/CSV/'
credentials=(azure_sas_token='<your blob SAS token>')
file_format = CSV_tips;
Once created, and if the permissions and path are ok, you can verify that you can access the files by listing the stage:
list '@Staging_files';
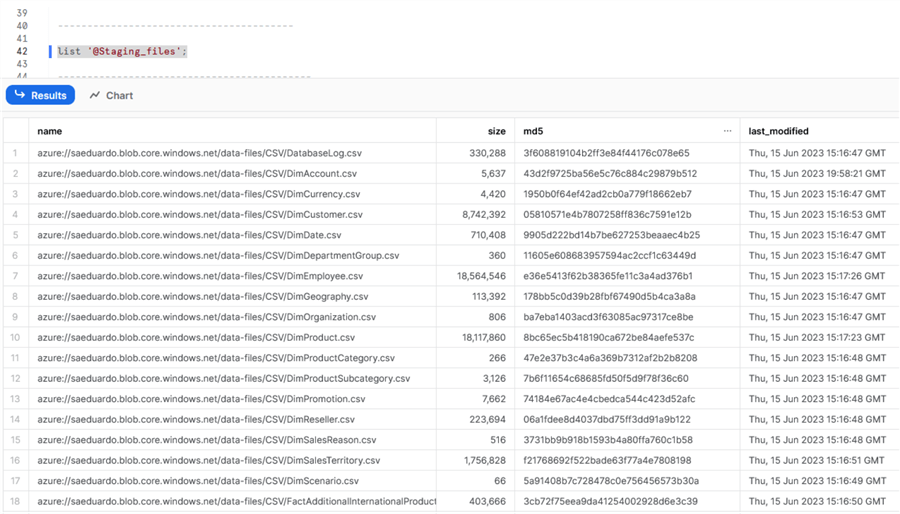
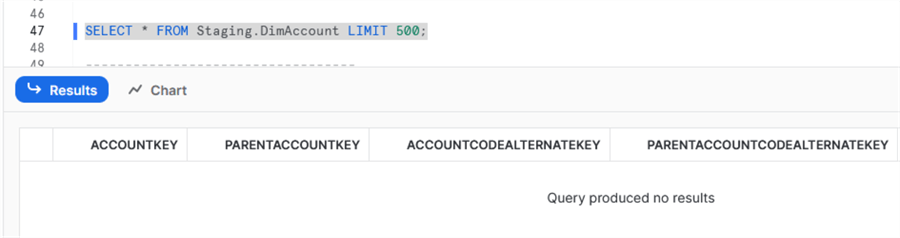
Once you have validated your access, we can copy the file to the table. First, we validate that the table is empty:
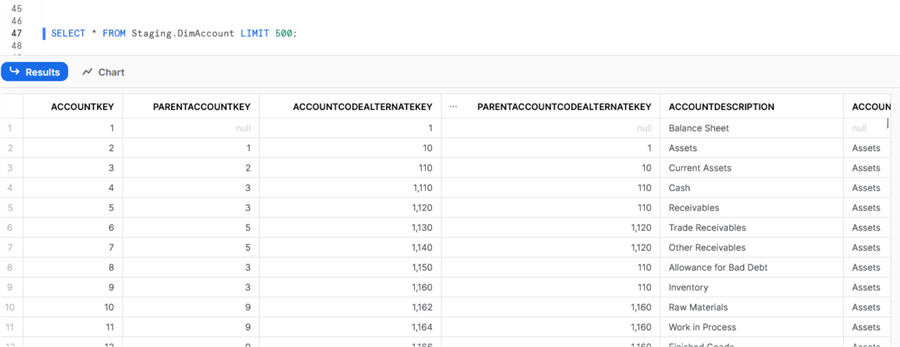
SELECT * FROM Staging.DimAccount LIMIT 500;
Next, we load the data from the stage to the actual table using the COPY INTO command:
COPY INTO Staging.DimAccount FROM '@Staging_files/DimAccount.csv';
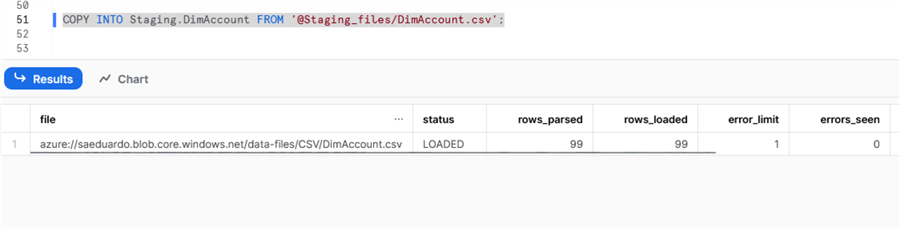
We can see that the copy was successful. We can browse the data by running the SELECT again:
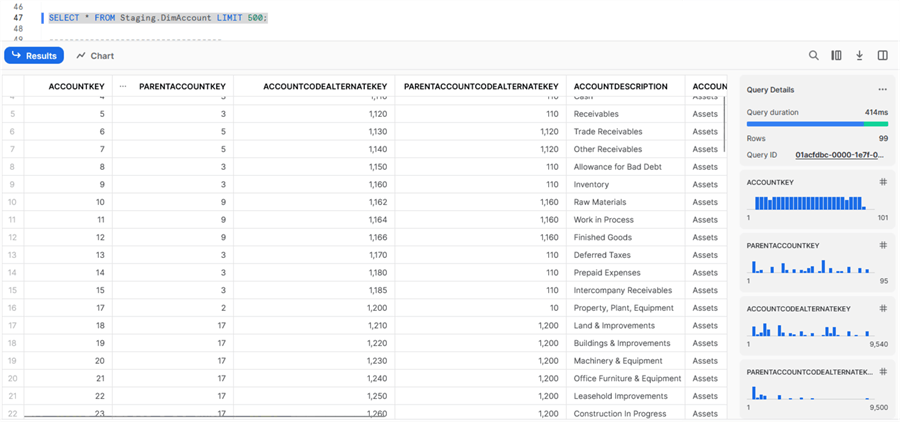
Our first example was successful.
If this meets your needs and you want to schedule this simple approach, you can use TASKS inside Snowflake.
Example: Copying Data from Snowflake to Blob Storage Using Synapse Analytics
We have validated that we have communication from Azure to Snowflake and verified that the information is ok.
What if, like the title of this tip, you want to add the copy task inside a Synapse pipeline?
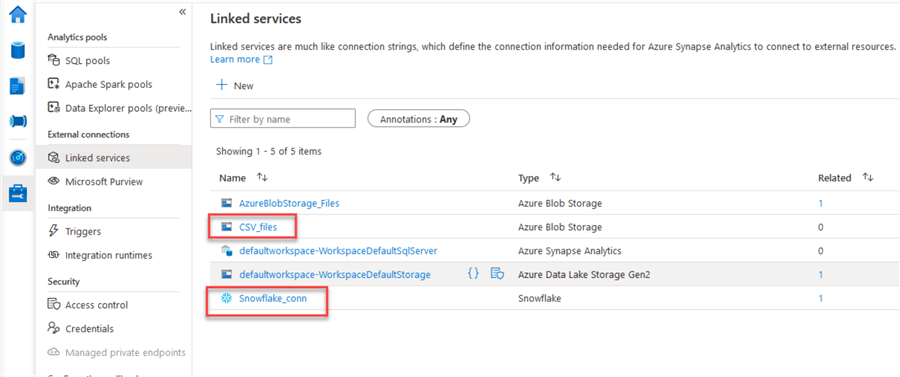
We need to create the linked services for our blob storage and Snowflake. Check out how to do this in this tip: Data Transfer from Snowflake to Azure Blob using Synapse Analytics.
Note: A the time of this writing, only SAS authentication is supported to direct copy from Blob Storage to Snowflake. You need to add these permissions in the storage account for this to work from Synapse:
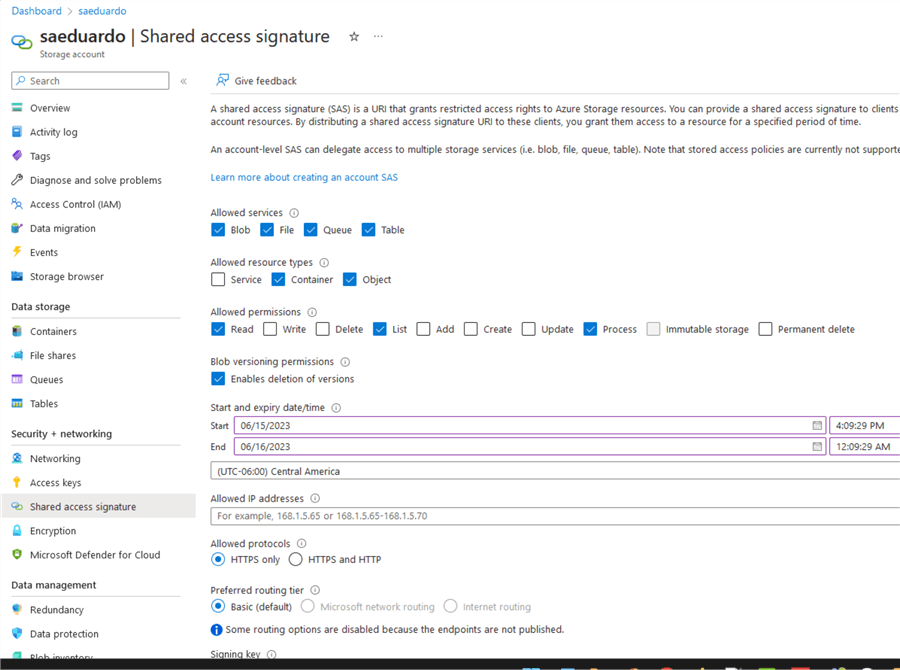
Once you have created your linked services, we can create the test pipeline.
Creating the Pipeline
In Synapse Studio, go to Integrate, and create a new pipeline:
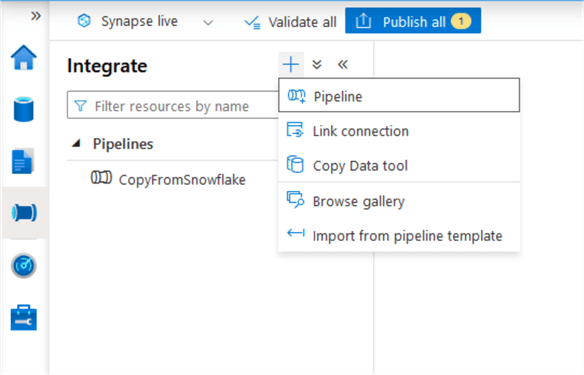
Provide a descriptive name:
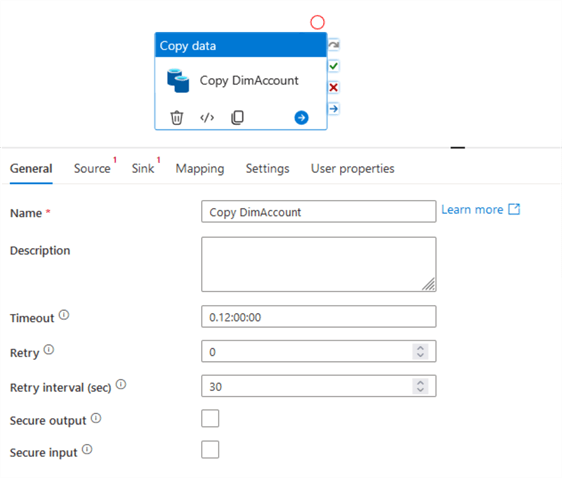
Add a copy data task and add a meaningful description:
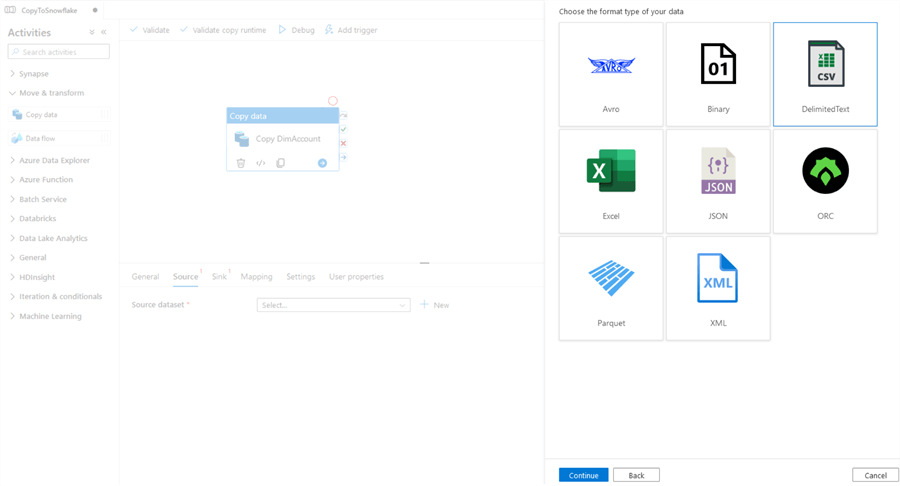
In Source, select a new blob storage, and select CSV file:
Create the file with the linked service selected, and configure the CSV file format:
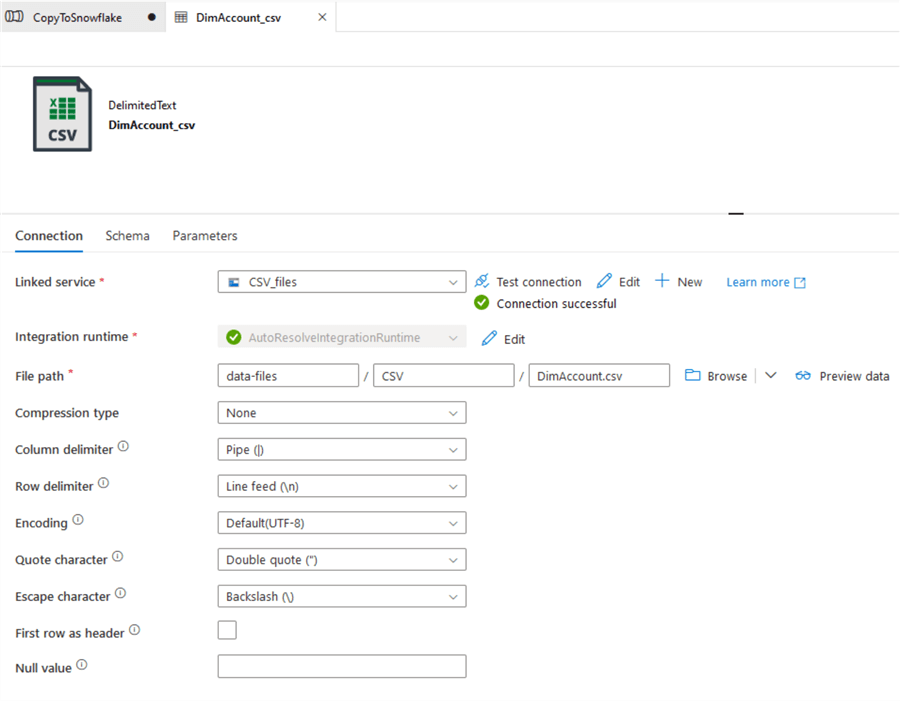
TIP: You can use the Detect Format option to help fill in the fields.
For the Sink, select the Snowflake connection, locate your linked service, and select the table where you want to load the data:
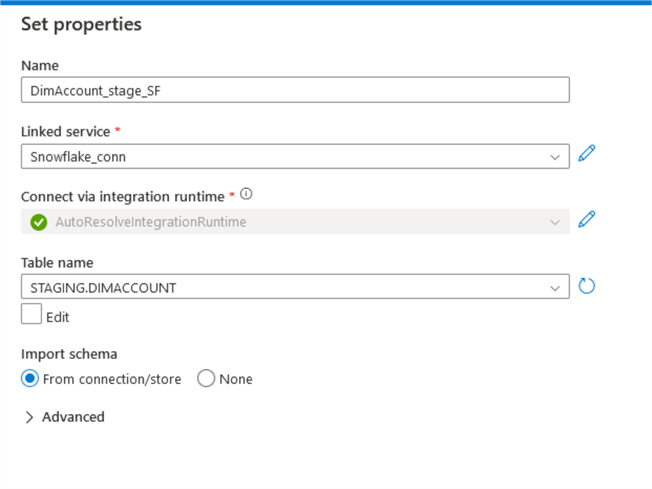
Leave everything else as default and validate/publish your pipeline:
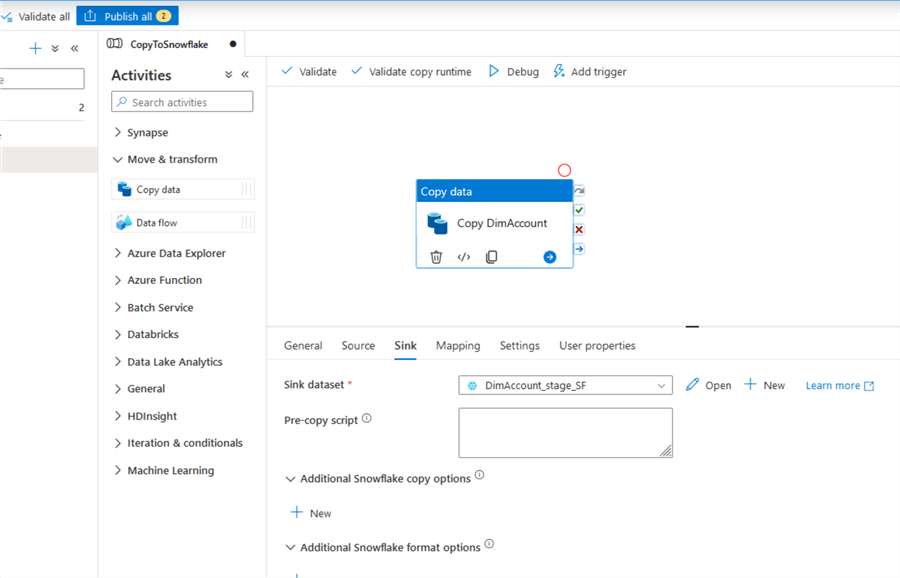
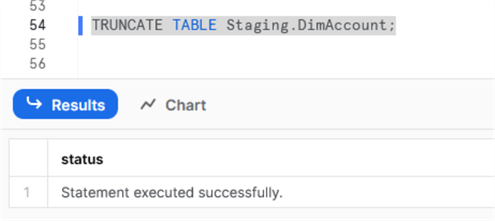
Once the pipeline is published, we can test it with a manual trigger. But before that, since we are using the same Snowflake table, we need to truncate it in our worksheet:
Run a manual trigger or a debug, as you prefer:
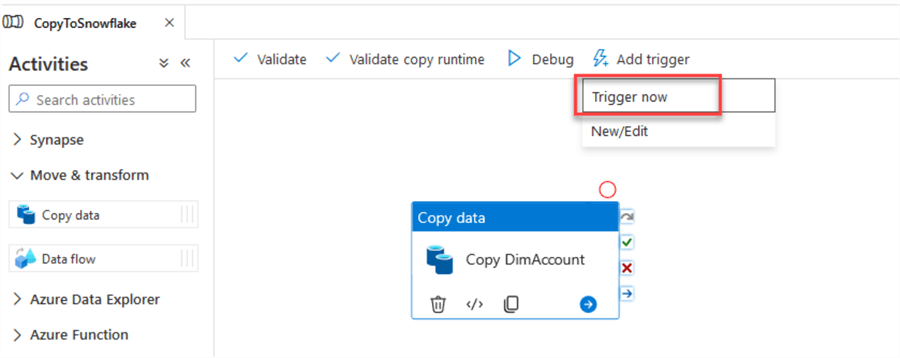
If everything is ok, the pipeline will execute successfully:
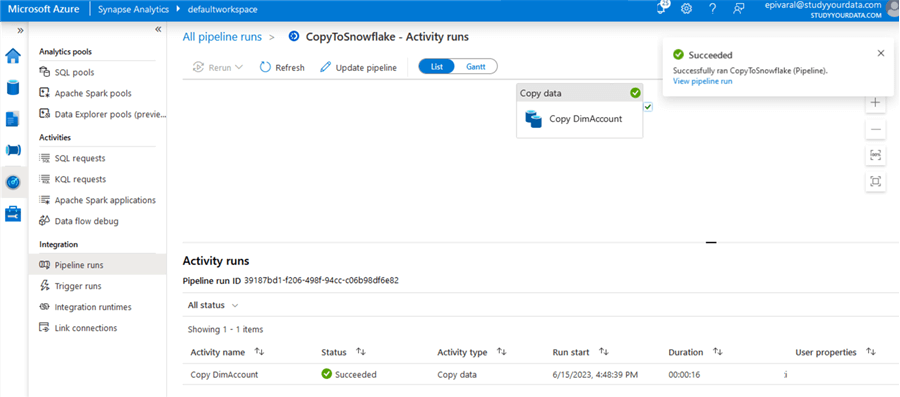
Now, we need to validate it again inside Snowflake. We have the data copied:
Next Steps
- Now that you know how to copy data from/to Snowflake to Synapse, you can create more robust pipelines, for example, incremental or with additional business logic and validations.
- The basic idea was explained using blob storage, but you can easily change it to use any other service (AzureSQLDB, CosmoDB, etc).
- You can check Azure Synapse documentation.
- You can check Snowflake documentation.
- Check other Synapse tips.
About the author
 Eduardo Pivaral is an MCSA, SQL Server Database Administrator and Developer with over 15 years experience working in large environments.
Eduardo Pivaral is an MCSA, SQL Server Database Administrator and Developer with over 15 years experience working in large environments. This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips
Article Last Updated: 2023-07-18






