By: Joe Gavin | Updated: 2024-03-28 | Comments | Related: > Indexing
Problem
Indexes are very helpful to improve SQL Server query performance, but sometimes indexes get created that are not helpful or no longer needed. In this article, we look at various ways to delete a SQL Server index.
Solution
The most common reasons to drop an index are because it's either unused or a duplicate of another index. While indexes can (and usually do) improve performance, unused or duplicate indexes take up storage space unnecessarily. They can slow things down, which is the opposite of what we, as DBAs and Developers, are trying to accomplish.
Key Details About Disabling and Dropping SQL Server Indexes
Let's look at some "must-know" information about disabling and dropping indexes.
- Be aware if you disable a clustered index
- Prevents access to the data.
- The data remains intact but inaccessible until the clustered index is dropped or rebuilt.
- An index may be part of a foreign key constraint.
- Understanding the relationships and constraints involved with the index is imperative.
- An index may still be in use.
- Be sure you're tracking index data for a reasonable period of time. Remember, unless you're capturing Dynamic Management View (DMV) data, they only hold data going back to the last server restart.
- Create and store an index creation script for any index you plan to drop somewhere safe, such as in source control, just in case. Recreating an index from a known good script is much easier than restoring an old backup to a test server.
- An application, stored procedure, view, or function may be using an index
hint(s).
- The definitions for stored procedures, views, or functions are easily searched, but you may not have access to every app's source code, especially if it's a vendor application.
- You may violate a vendor support contract.
- Some application vendors take the position that there are no changes of any kind to be made in their databases.
- The methods pointed out can still be used to make a case for dropping them to present to the vendor for their approval.
- Disabled indexes are not maintained.
- A disabled index prohibits creating another index with the same name.
- The optimizer does not consider disabled indexes.
- A disabled index can be dropped.
- Disabling an index associated with primary keys, foreign keys, or constraints disables them on the other table(s).
- Foreign key constraints on underlying tables are also disabled when a clustered index is disabled.
- Non-clustered indexes are disabled when an associated clustered index is disabled.
- Statistics cannot be successfully updated on a table with a disabled clustered index.
Finding Unused SQL Server Indexes
The following tips show ways to help find unused indexes:
- Discovering Unused Indexes
- Find Unused SQL Server Indexes with Policy Based Management
- Deeper Insight into Used and Unused Indexes for SQL Server
- How to Get Index Usage Information in SQL Server
Finding Duplicate SQL Server Indexes
These tips will show you ways to find duplicate indexes:
- Identify SQL Server Indexes With Duplicate Columns
- Over 40 Queries to Find SQL Server Tables With or Without a Certain Property
- SQL Server Index Basics
Disabling SQL Server Indexes
It's safer to disable an index than to drop it. As cautious DBAs, we may want to consider disabling what we believe is an unused or duplicate index as a first step. Re-enabling an index is quicker and easier than recreating them.
The minimum permission to disable an index is ALTER permission on the table or view. You already have permission if you are in the sysadmin server role or db_ddladmin or db_owner roles in the database.
For our examples, we'll work with a non-clustered index, IX_ExpectedDeliveryDate, on the Purchasing.PurchaseOrders table in the WideWorldImporters sample database.
To disable with SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS), expand down to the index in the Object Explorer
- Right-click on the index to disable.
- Click Disable.
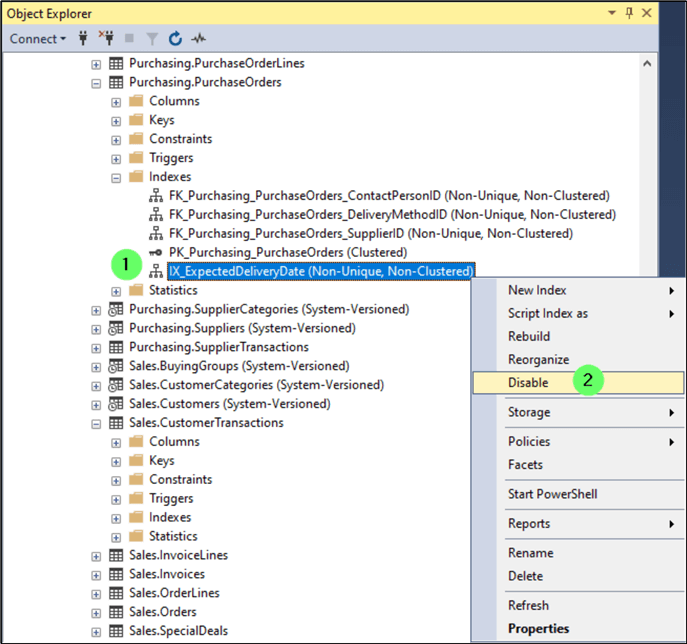
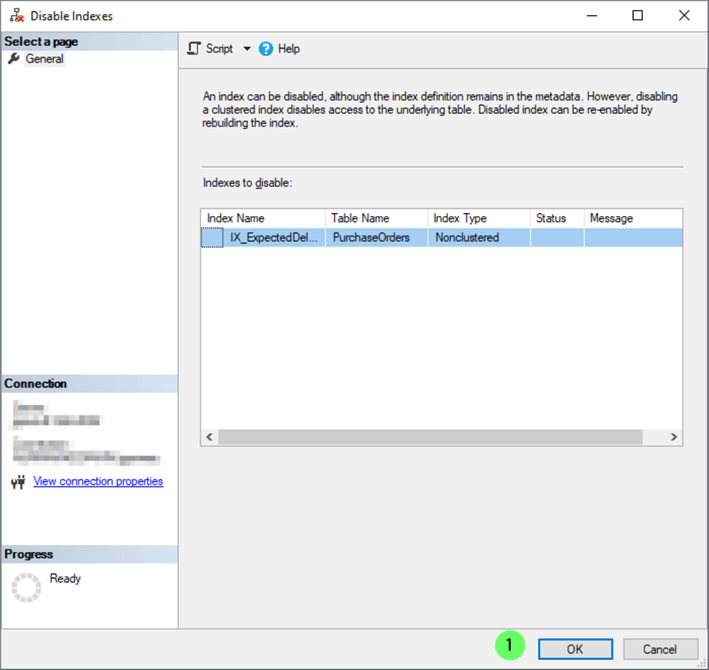
You're presented with the Disable Indexes confirmation window.
- Click OK.
Or you can disable the index with SQL:
USE [WideWorldImporters] GO ALTER INDEX [IX_ExpectedDeliveryDate] ON [Purchasing].[PurchaseOrders] DISABLE; GO
Enabling a Disabled SQL Server Index
If it's determined late that the index is needed, we must rebuild it to re-enable.
- Right-click on the index.
- Click Rebuild.
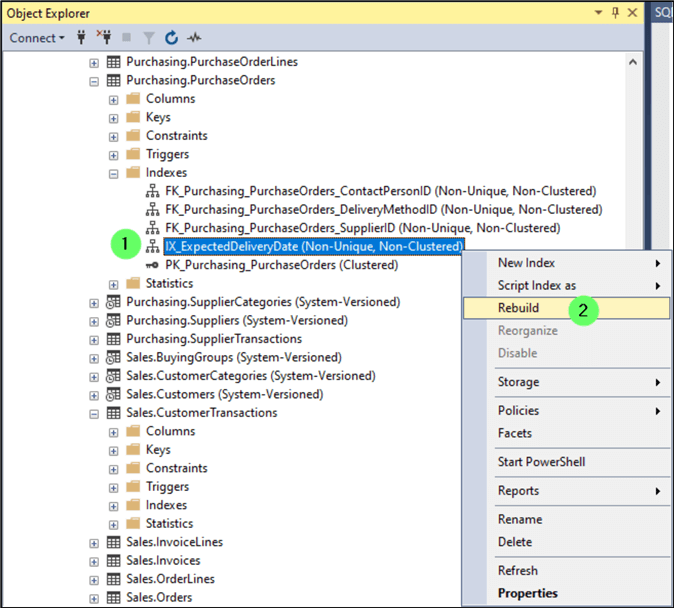
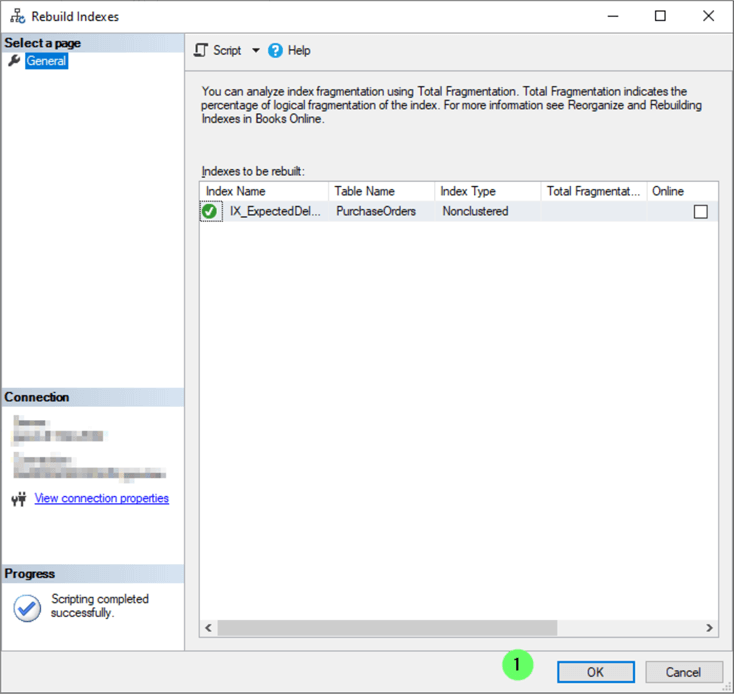
You're presented with the Rebuild Indexes confirmation window.
- Click OK.
Or rebuild to re-enable the index with T-SQL:
USE [WideWorldImporters]
GO
ALTER INDEX [IX_ExpectedDeliveryDate] ON [Purchasing].[PurchaseOrders]
REBUILD PARTITION = ALL
WITH (PAD_INDEX = OFF, STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, SORT_IN_TEMPDB = OFF, ONLINE = OFF,
ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON)
GO
Dropping SQL Server Indexes
The minimum permission needed to drop an index is also ALTER permission on the table or view.
Script Index Before Dropping
Where we can't simply rebuild an index as we did with a disabled index as the index no longer exists. It's highly advisable to archive a script to recreate it, if need be, before dropping it. You just never know.
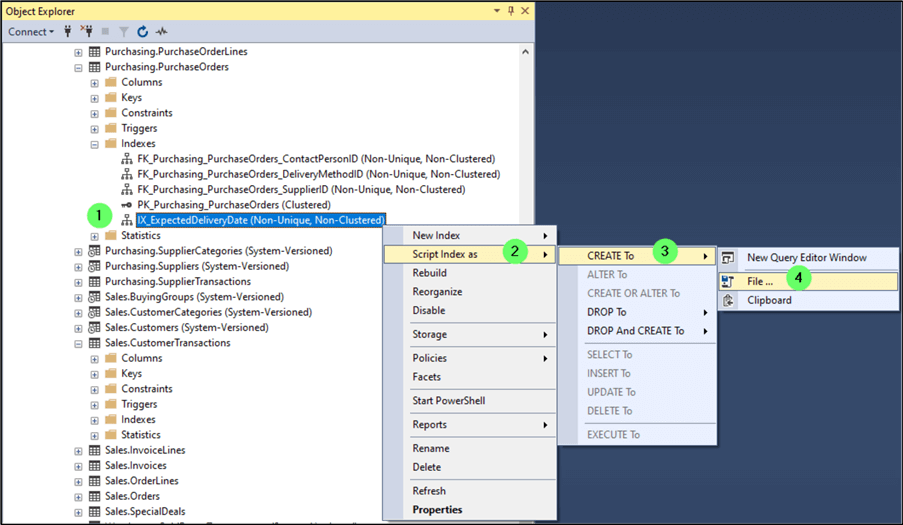
- Right-click on the index.
- Click on Script Index as.
- Click CREATE To.
- Click on File…
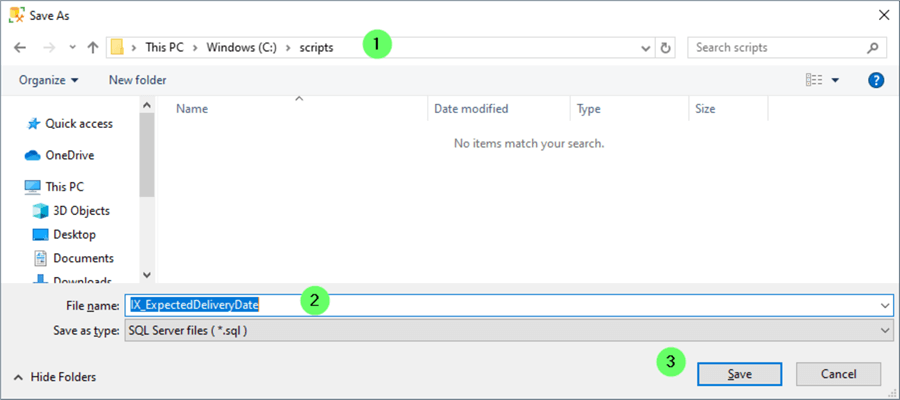
- Choose a directory to write a file to.
- Name the script.
- Click Save.
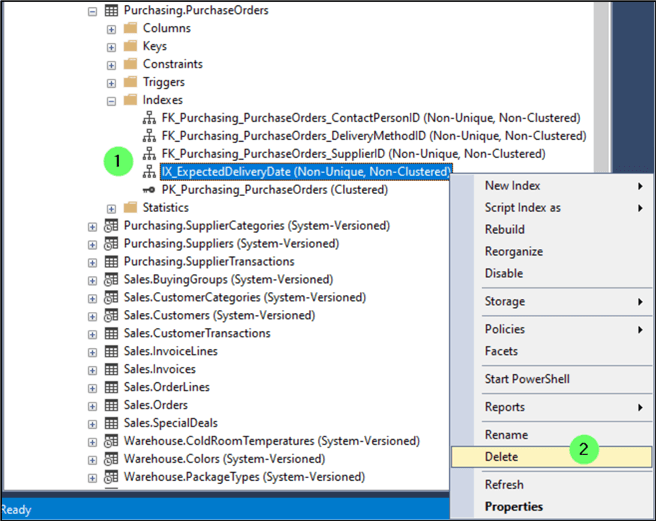
Now, drop the index.
- Right-click on the index.
- Click Delete.
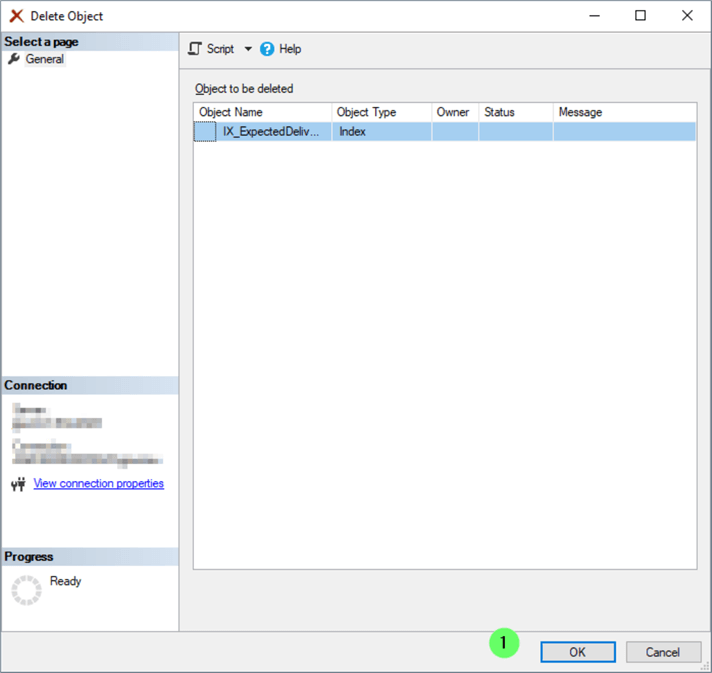
You're presented with the Delete Object confirmation window.
- Click OK.
Or drop the index with T-SQL:
USE [WideWorldImporters]; GO DROP INDEX [IX_ExpectedDeliveryDate] ON [Purchasing].[PurchaseOrders]; GO
Recreate the Index if needed
To recreate the index, open the script you saved and run it.
Next Steps
Here are additional links to index related tips:
- Safely Dropping Unused SQL Server Indexes
- New Drop If Exists Syntax in SQL Server 2016
- Script out all SQL Server Indexes in a Database using T-SQL
- Script to Disable Non Used SQL Server Indexes
- Creating Indexes with SQL Server Management Studio
- SQL Server Non-clustered Indexes
- SQL Server Index Tutorial Overview
- How to Get Index Usage Information in SQL Server
- SQL Server Index Properties in Management Studio
- Types of SQL Server Indexes
About the author
 Joe Gavin is from the Greater Boston area. He started working with SQL Server and Sybase in 1998 in the financial services industry and has been a SQL Server Database Administrator for a dairy cooperative since 2011. He graduated from Northeastern University in Boston with a Bachelor of Science in Engineering Technology (BSET) degree in Computer Technology. Joe has spoken at the Boston and Providence SQL Saturday events.
Joe Gavin is from the Greater Boston area. He started working with SQL Server and Sybase in 1998 in the financial services industry and has been a SQL Server Database Administrator for a dairy cooperative since 2011. He graduated from Northeastern University in Boston with a Bachelor of Science in Engineering Technology (BSET) degree in Computer Technology. Joe has spoken at the Boston and Providence SQL Saturday events. This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips
Article Last Updated: 2024-03-28






