By: Rajendra Gupta | Comments (5) | Related: > Identities
Problem
SQL Server 2017 provides many exciting features and enhancements over previous versions of SQL Server. Consider a scenario where we are running a transaction inserting identity values in a column and an unexpected restart occurs for the SQL Server services due to a crash, a failover or a shutdown. What will happen to the identity values in case we retry the transaction after the restart? We will explore this scenario with SQL Server 2017 and compare this behavior with previous versions of SQL Server.
Solution
SQL Server has a lot of configuration options that can be only enabled globally at the SQL Server instance level. Microsoft provides us a huge number of Trace Flags that change the internal behavior of SQL Server. SQL Server 2016 contains many existing configuration options that we can configure at the database level without using any specific Trace Flags at the instance level. These database level configuration can be done with database scoped configuration options.
Database Scoped Configurations allow configuring individual database level behavior without changing the entire instance level behavior. In SQL Server 2016 these database scope configurations are available:
- Legacy Cardinality Estimation
- MAX DOP
- Parameter Sniffing
- Query Optimizer Fixes
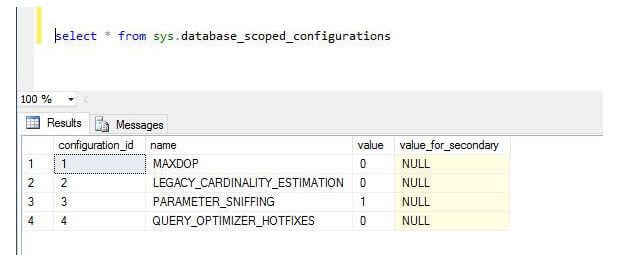
SQL Server 2017 introduced a new database scoped configuration option IDENTITY_CACHE.
Below are the database scoped connection options in SQL Server 2017:
- Legacy Cardinality Estimation
- MAX DOP
- Parameter Sniffing
- Query Optimizer Fixes
- IDENTITY_CACHE
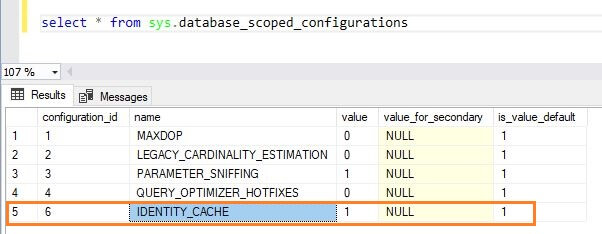
As we can see, SQL Server 2017 provides a new database scoped configuration option IDENTITY_CACHE. By default, this option is set to ON. In SQL Server, the database engine stores a series of values for the identity columns and it uses them as needed. The database engine generates identity values in a batch to reduce transaction log write and it only logs the max value of the batch. Sometimes when the identity column is being populated and an unexpected SQL Server restart/failover occurs, after a restart the next value of last batch max identity value will be used, so there will be a gap between identity columns values before the restart and after the restart. This feature was introduced in SQL Server 2012.
In SQL Server 2012 and later, we can use Trace Flag 272 to disable this feature, but the trace flag is set at the server instance level, not at the database level.
Example: IDENTITY_CACHE set to ON (default) in SQL Server 2017
First, let's look at the IDENTITY_CACHE database scoped operation with an ON state and see the behavior.
Let's create a table having an identity column and add some records.
CREATE TABLE MSSQLTips_Demo
(ID INT IDENTITY(1,1) PRIMARY KEY,
EmpName varchar(50));
GO
Insert Into MSSQLTips_Demo (EmpName) Values ('Rajendra')
Insert Into MSSQLTips_Demo (EmpName) Values ('Kashish')
Insert Into MSSQLTips_Demo (EmpName) Values ('Sonu')
Insert Into MSSQLTips_Demo (EmpName) Values ('Kusum')
Insert Into MSSQLTips_Demo (EmpName) Values ('Akshita')
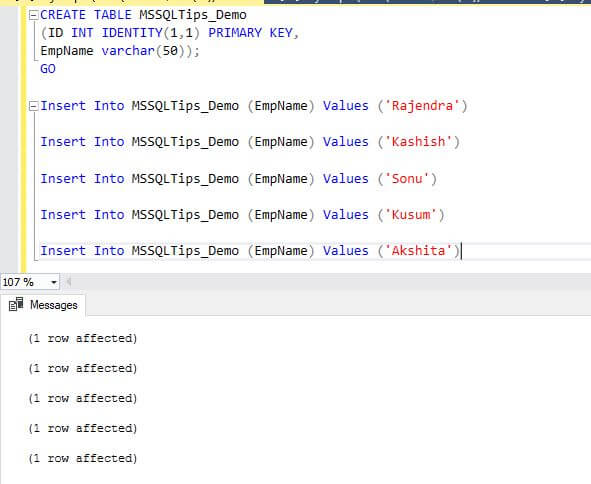
Now we have a table with 5 records in the table. We can see that the identity values are set and the max value for column ID is 5.
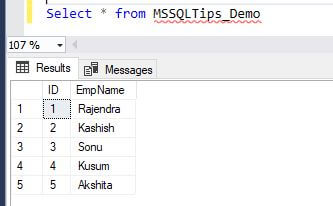
Now let's insert more records under an explicit transaction without doing a commit.
Begin tran
Insert Into MSSQLTips_Demo (EmpName) Values ('Shyam')
Insert Into MSSQLTips_Demo (EmpName) Values ('Ram')
Insert Into MSSQLTips_Demo (EmpName) Values ('Mohan')
Insert Into MSSQLTips_Demo (EmpName) Values ('Guddu')
Now we need to stop the SQL Server services. We can do it in two ways:
- From SQL Server Configuration Manager
- Using SHUTDOWN WITH NOWAIT command
We will use the SHUTDOWN WITH NOWAIT option here to stop the SQL Server services.
In another query window run the following to perform an uncontrolled shutdown of the SQL Server instance.
SHUTDOWN WITH NOWAIT
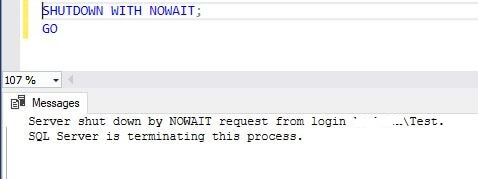
Execute the above command twice and you will see the below message.
Once it completes, we need to start the SQL Server instance via SQL Server Configuration Manager and again try to insert records in the table. To start the services, launch SQL Server Configuration Manager and go to SQL Server Services. Right click on the SQL Server service and select Start.

Now let's execute more insert statements.
Insert Into MSSQLTips_Demo (EmpName) Values ('Shyam')
Insert Into MSSQLTips_Demo (EmpName) Values ('Ram')
Insert Into MSSQLTips_Demo (EmpName) Values ('Mohan')
Insert Into MSSQLTips_Demo (EmpName) Values ('Guddu')
Let's see the records in the table for the identity values. We can see the results below, there is a gap in the identity values:
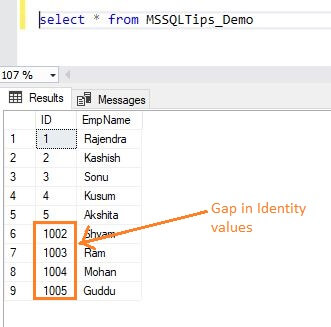
To overcome this scenario, SQL Server 2017 has the facility to disable the Identity Cache at the database level which prevents the gap in identity values.
Example: IDENTITY_CACHE set to OFF in SQL Server 2017
In SQL Server 2017, we can disable the identity cache at the database level using ALTER DATABASE SCOPED CONFIGURATION. To disable the IDENTITY_CACHE, use the below query.
ALTER DATABASE SCOPED CONFIGURATION SET IDENTITY_CACHE = OFF
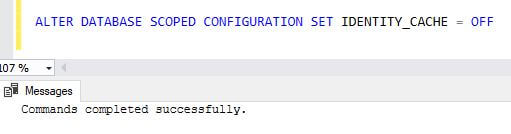
We can see below IDENTITY_CACHE is disabled now.
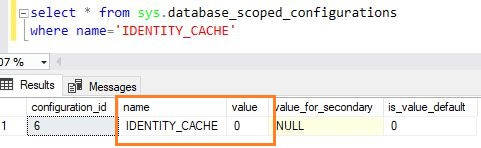
Since we have disabled the IDENTITY_CACHE, this will show the behavior as in older versions of SQL Server.
To perform the tests again, drop the table and repeat the same steps.
USE [MSSQLTIPS] GO DROP TABLE [dbo].[MSSQLTips_Demo] GO CREATE TABLE [dbo].[MSSQLTips_Demo]( [ID] [int] IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL, [EmpName] [varchar](50) NULL ) GO
Now with the IDENTITY_CACHE disabled, insert the records into the table.
Insert Into MSSQLTips_Demo (EmpName) Values ('Rajendra')
Insert Into MSSQLTips_Demo (EmpName) Values ('Kashish')
Insert Into MSSQLTips_Demo (EmpName) Values ('Sonu')
Insert Into MSSQLTips_Demo (EmpName) Values ('Kusum')
Insert Into MSSQLTips_Demo (EmpName) Values ('Akshita')
Now insert more records under an explicit transaction with an uncommitted transaction.
Begin tran
Insert Into MSSQLTips_Demo (EmpName) Values ('Shyam')
Insert Into MSSQLTips_Demo (EmpName) Values ('Ram')
Insert Into MSSQLTips_Demo (EmpName) Values ('Mohan')
Insert Into MSSQLTips_Demo (EmpName) Values ('Guddu')
Now perform the uncontrolled shutdown.
SHUTDOWN WITH NOWAIT
Now, let's restart the SQL instance and run more INSERTs.
Insert Into MSSQLTips_Demo (EmpName) Values ('Shyam')
Insert Into MSSQLTips_Demo (EmpName) Values ('Ram')
Insert Into MSSQLTips_Demo (EmpName) Values ('Mohan')
Insert Into MSSQLTips_Demo (EmpName) Values ('Guddu')
Let's view the identity values after disabling the Identity_Cache option.
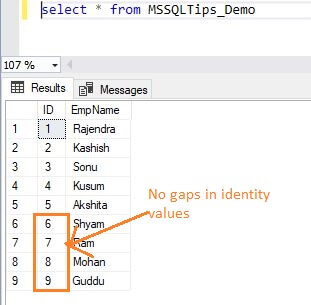
We can see the sequence of identity values is continuous despite the unexpected server shutdown.
So, in SQL Server 2017 we have an option for preventing gaps in an identity field without having to use Trace Flag 272 at the instance level. This looks like a promising feature to avoid identity value gaps.
Note: The IDENTITY_CACHE option needs to be executed via T-SQL script, there is not a GUI option available.
Next Steps
- SQL Server 2017 officially launched on October 2nd, 2017, check out the SQL Server 2017 release notes.
- Explore SQL Server 2017 What's new in SQL Server 2017.
- Read more SQL Server 2017 tips.
- Explore Database Scope Options in SQL Server.
About the author
 Rajendra Gupta is a Consultant DBA with 14+ years of extensive experience in database administration including large critical OLAP, OLTP, Reporting and SharePoint databases.
Rajendra Gupta is a Consultant DBA with 14+ years of extensive experience in database administration including large critical OLAP, OLTP, Reporting and SharePoint databases.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips






