By: Edwin Sarmiento | Comments (7) | Related: 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | > Clustering
Problem
In a previous tip on Validating a Windows Cluster Prior to Installing SQL Server 2014, I have seen how to install SQL Server 2014 on a Windows Server 2012 R2 failover cluster (WSFC). With Windows Server 2016 already publicly available, I would like to upgrade and migrate my SQL Server 2008 failover clusters to SQL Server 2016 running on Windows Server 2016. How do I go about building a Windows Server 2016 failover cluster for SQL Server 2016 and eventually upgrade and migrate my databases?
Solution
Windows Server 2008 has made installation and configuration of failover clusters a lot easier compared to previous versions of Windows Server, making it the standard for the setup experience for later versions. Not much has changed with the installation and configuration but newer features were introduced that made Windows Server 2016 the platform of choice for providing high availability for SQL Server workloads - both for failover clustered instances and Availability Groups.
Some of the Windows Server 2016 failover clustering features that apply to SQL Server 2016 are listed below:
- Active Directory Domain-independent failover clusters. This enables you to deploy WSFC without an Active Directory domain.
- Site-awareness for multi-site WSFCs. With support for multi-site, geographically dispersed WSFCs starting with Windows Server 2008, failover cluster nodes can now be grouped according to their physical locations - whether for local high availability or for disaster recovery.
- Site-awareness for quorum configuration. With the introduction of site-awareness for multi-site WSFCs, the quorum configuration now interacts with the preferred site configuration. Dynamic quorum will favor the preferred site.
- Witness type using Azure Blob Storage. The ability to place a witness in Azure blob storage for multi-site WSFC deployments makes it a cost-effective option than having a dedicated third data center.
- Quarantine of problematic nodes. Unhealthy nodes are quarantined and no longer allowed to join the WSFC, preventing them from negatively affecting the overall health of the WSFC.
- Storage Replica. The ability to natively do block-level replication without the need for proprietary storage-based replication technology allows for easier deployments of SQL Server failover clustered instances for both local high availability and disaster recovery.
- Storage Spaced Direct (S2D). This enables creation of highly available storage from locally attached storage that can be used for SQL Server failover clustered instances.
- In-place OS upgrade. The ability to perform in-place OS upgrades from Windows Server 2012 R2 to Windows Server 2016 failover clusters with minimal to no downtime reduces the need for additional hardware required for side-by-side migration and upgrades and extra effort reinstalling and configuring the workloads running on top of the existing WSFC.
In this series of tips, you will install a SQL Server 2016 failover clustered instance on a Windows Server 2016 failover cluster the traditional way - with Active Directory-joined servers and shared storage for the SQL Server databases. Configuring TCP/IP and joining the servers to your Active Directory domain is outside the scope of this tip. Consult your systems administrators on how to perform these tasks. It is assumed that the servers that you will join to the WSFC are already joined to an Active Directory domain and that the domain user account that you will use to perform the installation and configuration has local Administrative privileges on all of the servers.
We will cover the other features in future tips.
Preparing the shared disks
Similar to this previous tip, you need to provision your shared storage depending on your requirement. This tip assumes that the underlying shared storage has already been physically attached to all of the WSFC nodes and that the hardware meets the requirements defined in the Microsoft TechNet article Failover Clustering Hardware Requirements and Storage Options.
Managing shared storage requires an understanding of your specific storage product which is outside the scope of this tip. Consult your storage vendor for more information.
In my environment, I've configured four (4) shared storage volumes - SQL_DATA_H, SQL_DATA_I and SQL_DATA_J allocated for the SQL Server databases and DISK_W for the witness disk.
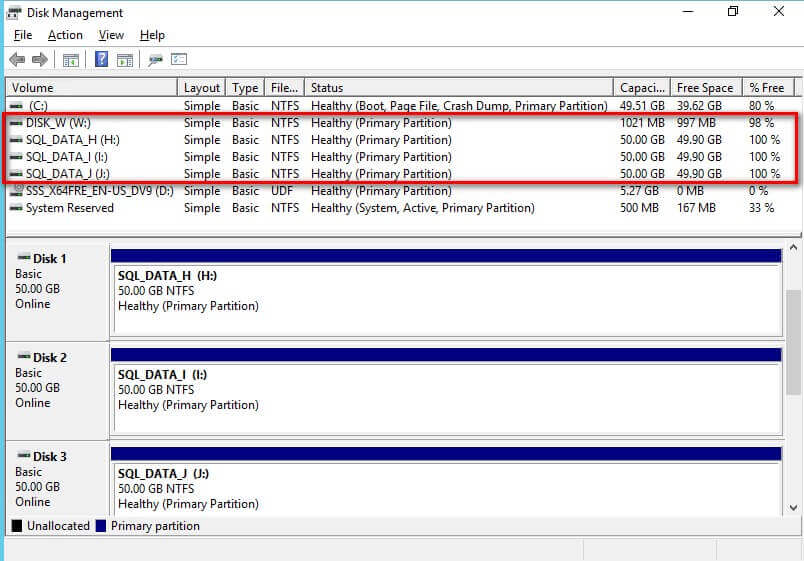
The goal here is to provision shared storage both for capacity and performance. Perform the necessary storage stress tests to make sure that you are getting the appropriate amount of IOPs as promised by your storage vendor. You can use the DiskSpd utility for this purpose.
Adding the Failover Clustering Feature
Before you can create a failover cluster, you must install the Failover Clustering feature on all servers that you want to include in the WSFC. The Failover Clustering feature is not enabled, by default. If you plan to deploy several servers to be members of a WSFC, you can create a generic server OS deployment image that includes this feature. This can be done by using the Sysprep utility built into the Windows Server operating system.
To add the Failover Clustering feature:
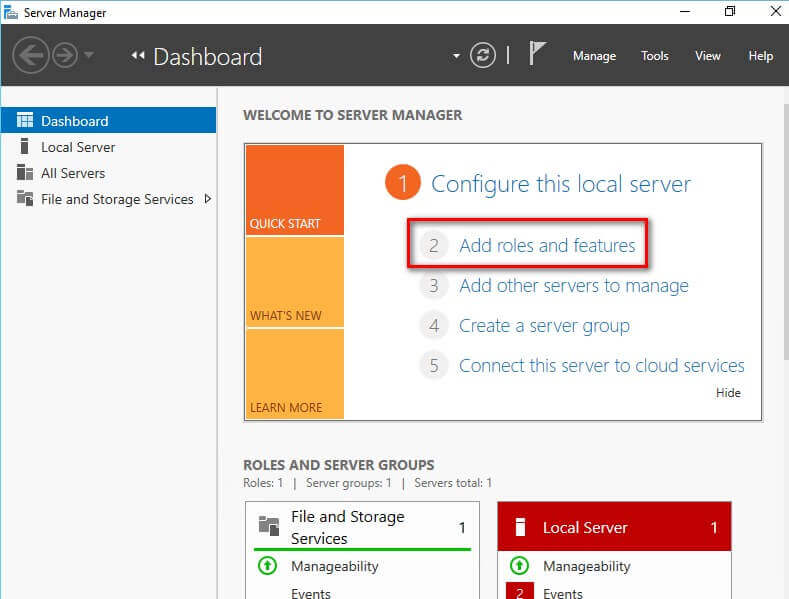
- Open the Server Manager Dashboard and click the
Add roles and features link. This will run the Add Roles and
Features Wizard.
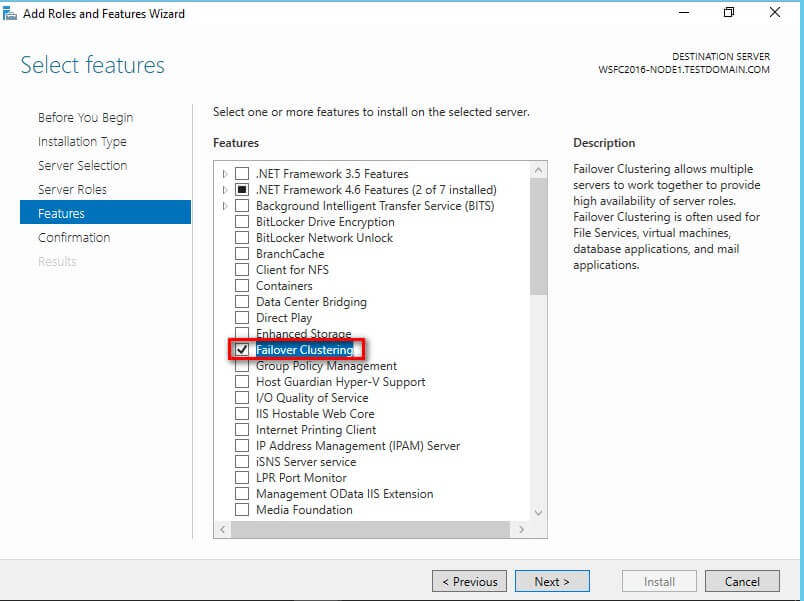
- Click thru the different dialog boxes until you reach the Select
features dialog box. In the Select features dialog
box, select the Failover Clustering checkbox and click
Next.
- In the Confirm installation selections dialog box, click
Install to confirm the selection and proceed to do the installation.
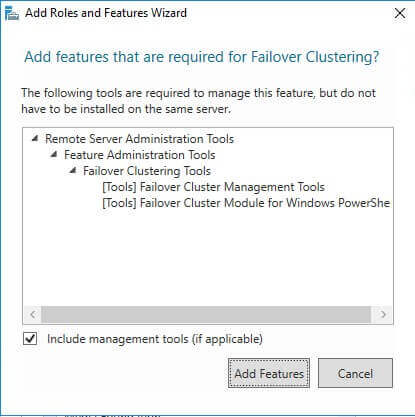
When prompted with the Add features that are required for Failover Clustering dialog box, click Add Features. Click Next.
NOTE: In previous versions of SQL Server, you were required to install the .NET Framework 3.5 with SP 1. This is no longer the case with SQL Server 2016.
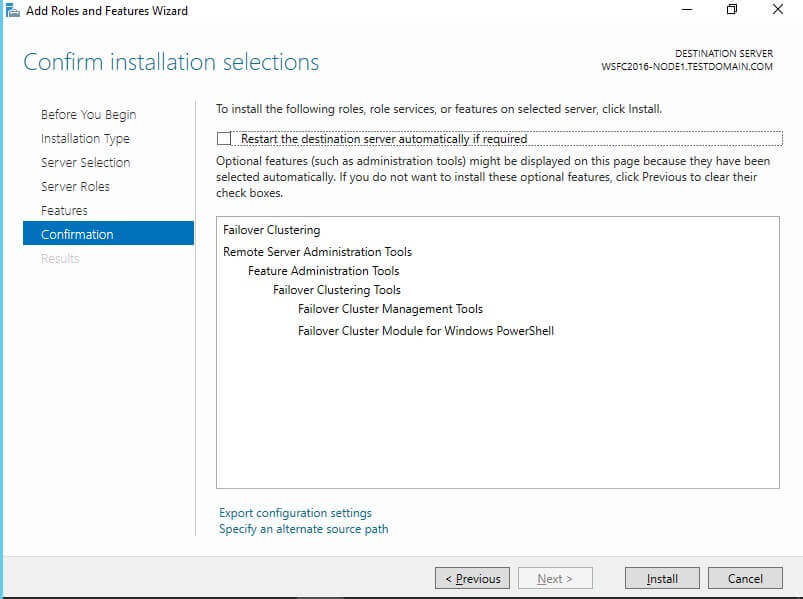
NOTE: Perform these steps on all of the servers that you intend to join in your WSFC.
Running the Failover Cluster Validation Wizard
Next, you need to run the Failover Cluster Validation Wizard from the Failover Cluster Management console as described in this previous tip. You can launch the tool from the Server Manager dashboard, under Tools and select Failover Cluster Manager.
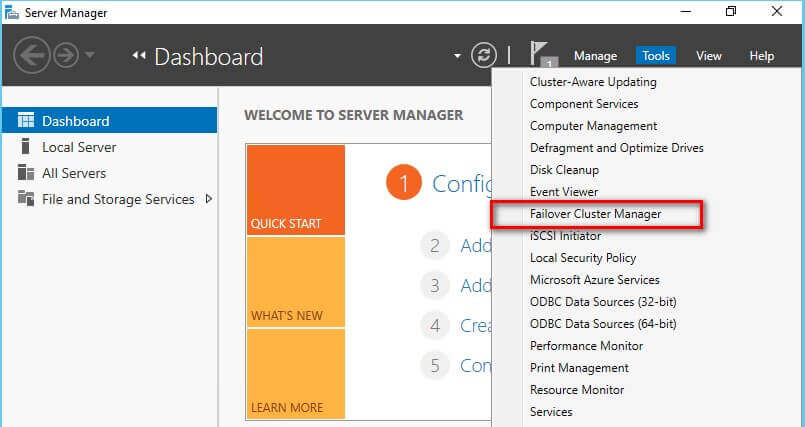
NOTE: These steps can be performed on any of the servers that will act as nodes in your WSFC.
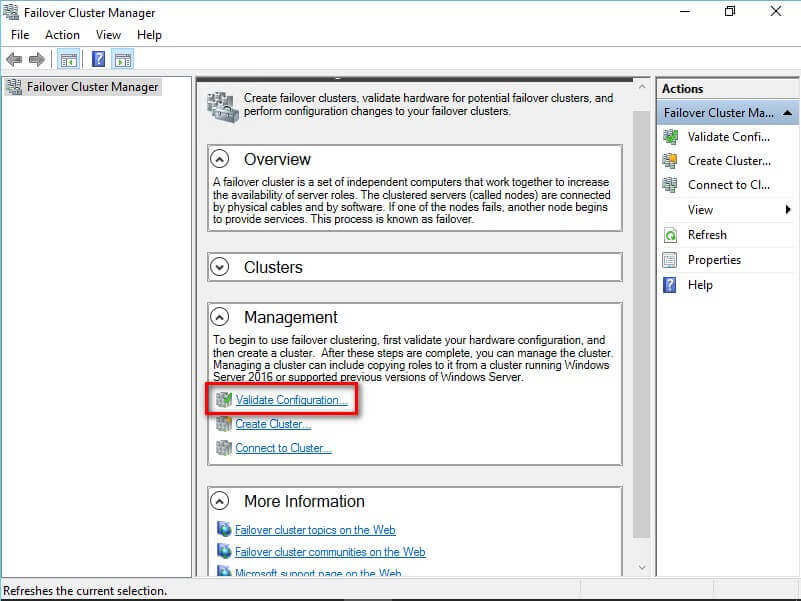
- In the Failover Cluster Management console, under the
Management section, click the Validate Configuration
link. This will run the Validate a Configuration Wizard.
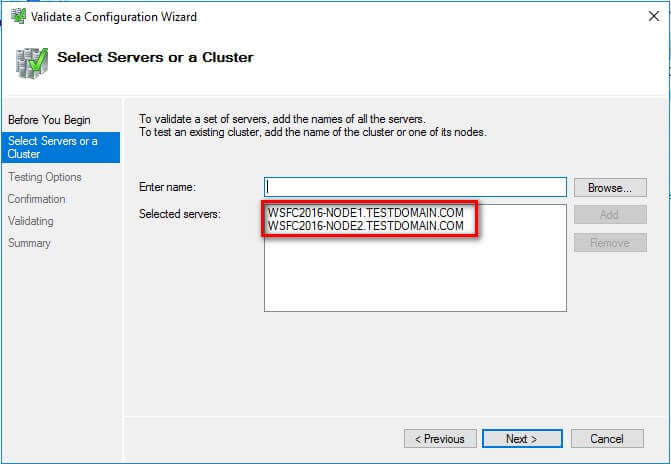
- In the Select Servers or a Cluster dialog box, enter the
hostnames of the nodes that you want to add as members of your WSFC. Click
Next.
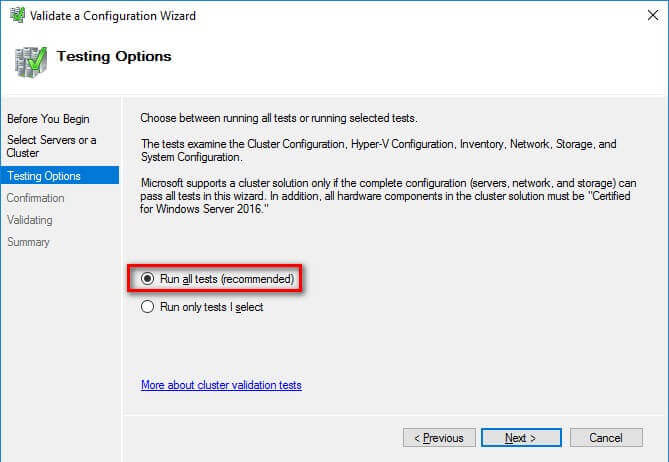
- In the Testing Options dialog box, accept the default option
Run all tests (recommended) and click Next.
This will run all the necessary tests to validate whether or not the nodes are
OK for the WSFC.
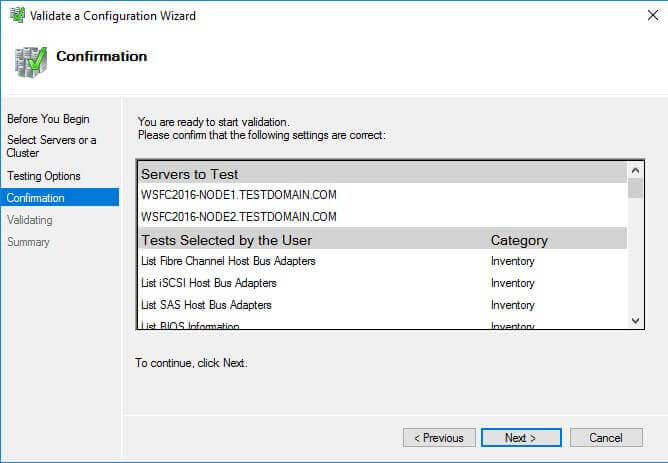
- In the Confirmation dialog box, click Next.
This will run all the necessary validation tests.
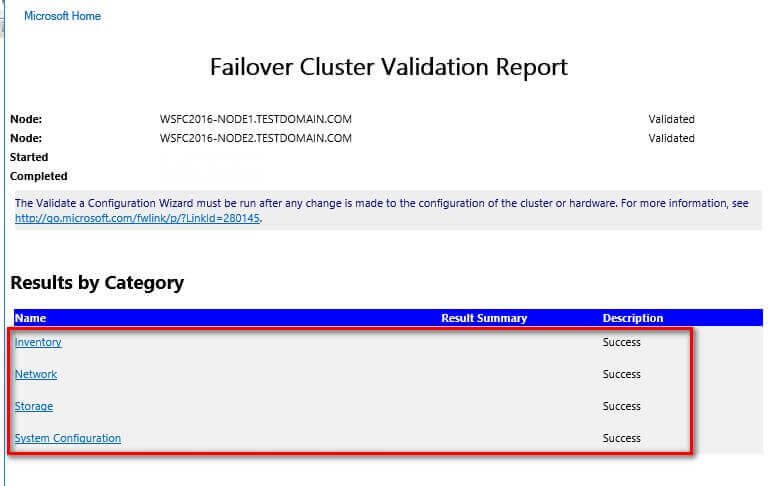
- In the Summary dialog box, verify that all the selected
checks return successful results.
- To create the WSFC using the servers you've just validated, select the Create the cluster now using the validated nodes... checkbox and click Finish.
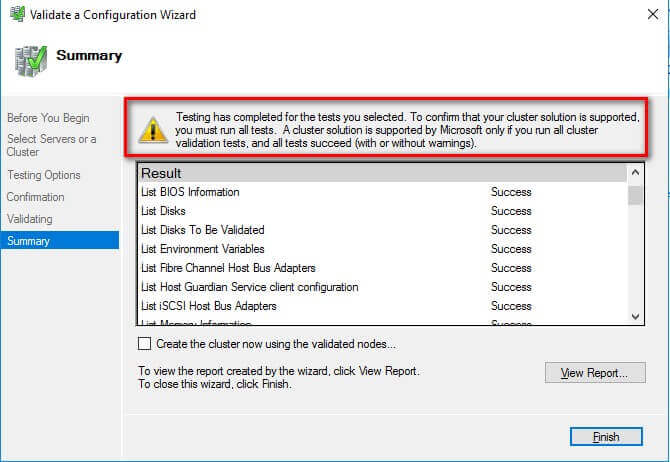
A note on the results: In the past, the Cluster Validation Wizard may report Warning messages pertaining to network and disk configuration issues, missing security updates, incompatible drivers, etc. The general recommendation has always been to resolve all errors and issues that the Cluster Validation Wizard reports prior to proceeding with the next steps. And it still is.
With Windows Server 2016, checks for Storage Spaces Direct have been included in the Cluster Validation Wizard. Despite choosing the Run all tests (recommended) option, the Cluster Validation Wizard will exclude those checks.
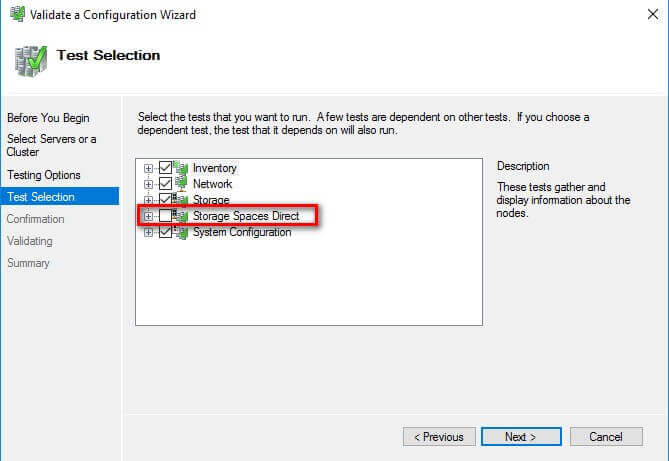
This is why you will get a Warning message in the cluster validation report despite having all selected default checks return successful results.
Another way of running the Failover Cluster Validation is by using the Test-Cluster PowerShell cmdlet as described in this previous tip.
In this tip, you've:
- Seen some of the new Windows Server 2016 failover clustering features that apply to SQL Server workloads
- Had an idea of how to provision shared storage for your WSFC
- Added the Failover Clustering feature on all of the servers that you intend to join in a WSFC
- Tan the Failover Cluster Validation Wizard and
- Have seen the new validation checks for Storage Spaces Direct that can cause a Warning message when running the Failover Cluster Validation Wizard
In the next tip in this series, you will go thru the process of creating the WSFC and configure the cluster quorum settings using the new Windows Server 2016 failover clustering features. Once you've manage to create a working Windows Server 2016 failover cluster, that's the only time you can proceed to install SQL Server 2016.
Next Steps
- Review the previous tips on Install SQL Server 2008 on a Windows Server 2008 Cluster Part 1, Part 2, Part 3 and Part 4 to see the difference in the setup experience between Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2016.
- Read more on the following topics:
About the author
 Edwin M Sarmiento is a Microsoft SQL Server MVP and Microsoft Certified Master from Ottawa, Canada specializing in high availability, disaster recovery and system infrastructures.
Edwin M Sarmiento is a Microsoft SQL Server MVP and Microsoft Certified Master from Ottawa, Canada specializing in high availability, disaster recovery and system infrastructures.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips






