By: Daniel Calbimonte | Updated: 2022-05-16 | Comments | Related: More > Database Administration
Problem
Learn about what a SQL database is, what is stored in a database and how to interact with a database.
Solution
The following SQL tutorial gives you an idea of what a SQL database is and some of the things that can be done with a SQL database.
What is a SQL Database?
A SQL database is a logical container to hold a collection of data and code. It is stored in a computer and most of the time it is managed by a RDBMS (Relational Database Management System). To interact with the data and the code we typically use SQL (Structured Query Language) to manage the data, objects, security, and more.
There are several important RDBMS in the industry. MSSQLTips is mainly focused on Microsoft SQL Server, but other popular database systems (open source too) include Oracle, MySQL, PostgreSQL, DB2, and MariaDB. There are other also NoSQL databases like MongoDB, Amazon DynamoDB and Redis (these databases do not use SQL and are outside the scope of this tutorial).
SQL Database - Logical and Physical
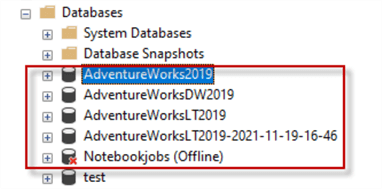
Using SQL Server as an example, the container which we interact with is the logical name of the database as shown below in the screen shot from SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS).
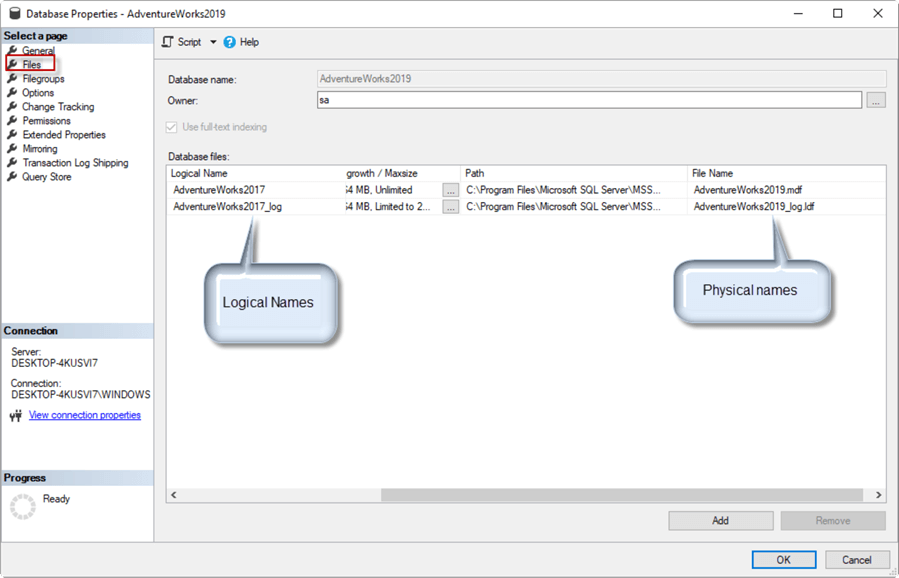
Each database also has physical files that are assigned to the logical database name. If you right click on a database and select Properties from within SSMS and go to the Files page you can see the physical location of the files. As you can see below, each physical file also has a logical name with SQL Server.
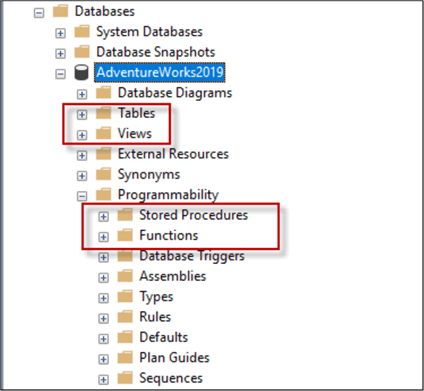
SQL Database Objects
There are several types of database objects and the most used are the following:
Tables
The table object is an entity that stores information in columns and rows. It can be a list of customers, employees, invoices, sales data, etc. This is the actual SQL data that gets keyed into systems or loaded into systems from external sources. In addition to tables that you might create, there are also system tables that the database system uses to track and organize all of the database objects.
- How to create a table using SQL Server Management Studio
- Create Tables in SQL Server with T-SQL
- How To Create a Table in SQL Server
Views
A view is a virtual table defined by a query. A view can be a query from a table, multiple tables, from another view or multiple views, and can include one or many columns. There are also system views that exist to help you easily retrieve data about various objects in a database.
Stored Procedures
A stored procedure is nothing more than prepared SQL code that is saved and can be reused over and over again. This allows for reuse of code and these stored procedures are stored within the database. There are also system stored procedures that allow you to interact with the database.
Functions
Functions are also prepared SQL statements that execute specific tasks. This allows you to write a function one time and reuse it over and over in various places within your code. There are also system functions that can be used to simplify processing such as GETDATE() that returns the current date and time.
SQL Database Operations
In order to work with a MS SQL Server database, the following shows simple examples of creating a table and interacting with the table using SQL code.
Create Table
The following SQL command will create a table called dbo.student (i.e. schema dot table name) with numerous column names and data types specified.
CREATE TABLE dbo.student ( id smallint, firstname varchar(60), lastname varchar(60), email varchar(60), address varchar(60), phone varchar(15), )
For more information and examples about creating tables please refer to these links:
- How to create a table using SQL Server Management Studio
- Create Tables in SQL Server with T-SQL
- How To Create a Table in SQL Server
- SQL Server Primary Key
- How to create a SQL Server foreign key
- SQL Server Data Types Quick Reference Guide
Create Indexes
Indexes allow for faster access (i.e. optimization) to specific data stored in a table. It is like an index you find in a book to quickly find the page you want to read.
The following syntax creates an index on the dbo.student table:
CREATE NONCLUSTERED INDEX [IX_student] ON [dbo].[student] ( [id] ASC )
For more information about indexes, please review this tutorial:
- SQL Server Index Tutorial Overview
- SQL Server Index Basics
- Types of SQL Server Indexes
- All SQL Server Index Tips
Insert Data
Another important operation is inserting data into a table. The following example will insert two rows in the table we previously created.
INSERT INTO dbo.student VALUES (1,'John','Rambo','[email protected]','Mount Street 234','1-2345533434'), (2,'John','McClaine','[email protected]','Great Valley Street 234','1-2347783434')
For more information about the SQL INSERT command, please check this tutorial:
Select Data
The SELECT statement is used to get data from the table. The following SQL query will return all columns and rows from the table dbo.student.
SELECT * FROM dbo.student
The following SQL query shows how to get specific columns from the table.
SELECT firstname, lastname FROM dbo.student
The following SQL query shows how to get the email of the student with lastname equal to 'McClaine'.
SELECT email FROM dbo.student WHERE lastname = 'McClaine'
For more information about SELECT statements, refer to these links:
- Advice for Learning T-SQL SELECT Statement Step By Step
- SQL Server Join Example
- SQL Server SELECT Examples
Update Data
We can also update the data in a table. The following example will change John Rambo’s phone number from '1-2345533434' to '1-2345533435'.
UPDATE dbo.student SET phone = '1-2345533435' WHERE lastname = 'Rambo'
For more about UPDATES refer to this link:
Delete Data
Lastly, we can also delete data from a table. The following example shows how to delete student McClaine:
DELETE FROM [dbo].[student] WHERE lastname = 'McClaine'
For more information about the DELETE statement, refer to this link:
SQL Database Security
In SQL Server, we have two main types of authentication, SQL authentication and Windows authentication. SQL Authentication uses a login created inside of SQL Server and is specific to SQL Server. Windows authentication uses operating system authentication (such as Active Directory or a local Windows user).
In order to interact with the database and SQL Server a user has to login to SQL Server using one of these two authentication methods. There is then server level permissions and database level permissions.
There is also the ability to grant, revoke and deny permissions to objects, so only authorized users have access.
Server Roles
These provide different types of permissions at the SQL Server level.
Database Roles
These provide different types of permissions at the database level.
Next Steps
For more information refer to the following:
- Create SQL Server Database using SQL Server Management Studio
- SQL Server Create Database Examples
- Create SQL Server Database with PowerShell
About the author
 Daniel Calbimonte is a Microsoft SQL Server MVP, Microsoft Certified Trainer and 6-time Microsoft Certified IT Professional. Daniel started his career in 2001 and has worked with SQL Server 6.0 to 2022. Daniel is a DBA as well as specializes in Business Intelligence (SSIS, SSAS, SSRS) technologies.
Daniel Calbimonte is a Microsoft SQL Server MVP, Microsoft Certified Trainer and 6-time Microsoft Certified IT Professional. Daniel started his career in 2001 and has worked with SQL Server 6.0 to 2022. Daniel is a DBA as well as specializes in Business Intelligence (SSIS, SSAS, SSRS) technologies.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips
Article Last Updated: 2022-05-16






