By: Ken Simmons | Comments | Related: 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | > Partitioning
Problem
I am using partitioning in my database. Is there an easy way for me to identify partitions that may have too much data so they can be split? Check out the examples and scripts in this tip to find out.
Solution
Even though you try to setup partitioning in a way that will be evenly populated, it is very easy for business rules to change in a way that may distribute data unevenly throughout your partitions. For example, you can use the following script to create an unevenly loaded partition.
--Create partition function
CREATE PARTITION FUNCTION TestPartitionFunction (Datetime)
AS RANGE RIGHT FOR VALUES ('1/1/2000', '1/1/2005');
GO
--Create partition scheme
CREATE PARTITION SCHEME TestPartitionScheme
AS PARTITION TestPartitionFunction
TO ([PRIMARY], [PRIMARY], [PRIMARY]);
GO
--Create partition table
CREATE TABLE TestPartitionTable
(ID INT IDENTITY NOT NULL,
SomeDateColumn DATETIME)
ON TestPartitionScheme (SomeDateColumn);
CREATE CLUSTERED INDEX PK_SamplePartitionTable ON TestPartitionTable (ID)
GO
SET NOCOUNT ON
--DELETE FROM TestPartitionTable
--Insert sample data
INSERT INTO TestPartitionTable (SomeDateColumn)
SELECT '1/1/1999'
GO 500
INSERT INTO TestPartitionTable (SomeDateColumn)
SELECT '1/1/1998'
GO 500
SET NOCOUNT ON
INSERT INTO TestPartitionTable (SomeDateColumn)
SELECT '1/1/1997'
GO 500
INSERT INTO TestPartitionTable (SomeDateColumn)
SELECT '1/1/1996'
GO 500
INSERT INTO TestPartitionTable (SomeDateColumn)
SELECT '1/1/1995'
GO 500
INSERT INTO TestPartitionTable (SomeDateColumn)
SELECT '1/1/2001'
GO 500
INSERT INTO TestPartitionTable (SomeDateColumn)
SELECT '1/1/2006'
GO 500
Now, you can use the following script to search for overloaded partitions throughout your database.
;WITH cteUsedPartitions AS
(
SELECT object_id,
SUM(rows) TotalNbrRows,
COUNT(*) TotalUsedPartitions
from sys.partitions
where index_id = 1 AND rows > 0
GROUP BY OBJECT_ID
HAVING COUNT(*) > 1
)
SELECT DISTINCT
OBJECT_NAME(sp.object_id) TableName,
pf.name PartitionFunction,
ps.name PartitionScheme,
sp.partition_number,
rows,
TotalNbrRows,
(SELECT COUNT(*)
FROM sys.partitions
WHERE object_id = sp.object_id AND
index_id = 1) TotalPartitions,
TotalUsedPartitions,
CAST((rows / (TotalNbrRows * 1.0)) *
100 AS DECIMAL(10,2)) AS PrcentOfTotal,
CAST(((TotalNbrRows * 1.0/TotalUsedPartitions) /
(TotalNbrRows * 1.0)) *
100 AS DECIMAL(10,2)) AS IdealPrcentOfTotal
FROM sys.data_spaces d
JOIN sys.indexes i ON
d.data_space_id = i.data_space_id
JOIN cteUsedPartitions p ON
i.object_id = p.object_id
JOIN sys.partitions sp ON
p.object_id = sp.object_id
AND sp.index_id = i.index_id
JOIN sys.partition_schemes ps ON
d.data_space_id = ps.data_space_id
JOIN sys.partition_functions pf ON
ps.function_id = pf.function_id
JOIN sys.index_columns ic ON
i.index_id = ic.index_id
AND i.object_id = ic.object_id
JOIN sys.columns c ON
c.object_id = ic.object_id
AND c.column_id = ic.column_id
WHERE i.index_id = 1 AND
CAST((rows / (TotalNbrRows * 1.0)) *
100 AS DECIMAL(10,2)) > --PercentOf Total
(CAST(((TotalNbrRows/TotalUsedPartitions) /
(TotalNbrRows * 1.0)) *
100 AS DECIMAL(10,2)) * 2)--Ideal Percent * 2
You can see by the following image that the query found the overloaded partition.

Since there are three partitions, the ideal percentage would be 33.33, but partition 1 has 71.43 percent of the total rows. The above script is looking for anything that is over double the ideal percentage, but you can change that. For example, you could modify the WHERE clause to look for partitions where the percent of the total rows are greater than the ideal percent * 1.5. Now I can run the following code to split the overloaded partition and correct the issue.
ALTER PARTITION SCHEME TestPartitionScheme NEXT USED [PRIMARY]
ALTER PARTITION FUNCTION TestPartitionFunction()
SPLIT RANGE('1/1/1999')
ALTER PARTITION SCHEME TestPartitionScheme NEXT USED [PRIMARY]
ALTER PARTITION FUNCTION TestPartitionFunction()
SPLIT RANGE('1/1/1998')
ALTER PARTITION SCHEME TestPartitionScheme NEXT USED [PRIMARY]
ALTER PARTITION FUNCTION TestPartitionFunction()
SPLIT RANGE('1/1/1997')
ALTER PARTITION SCHEME TestPartitionScheme NEXT USED [PRIMARY]
ALTER PARTITION FUNCTION TestPartitionFunction()
SPLIT RANGE('1/1/1996')
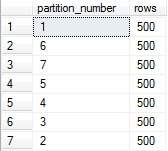
--Verify the rows are balanced
SELECT partition_number, rows
FROM sys.partitions
WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID('TestPartitionTable')
You can see by the following results that the rows are now balanced.
Next Steps
- Review some other tips on partitioning:
- Partitioning Category - http://www.mssqltips.com/category.asp?catid=65
- Creating a table with horizontal partitioning in SQL Server
- Handling Large SQL Server Tables with Data Partitioning
- Managing multiple partitions in multiple filegroups in SQL 2005 for cleanup purposes
- SQL Server Database Partitioning Myths and Truths
- Switching data in and out of a SQL Server 2005 data partition
- Check out the following partitioning white paper - http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd578580.aspx
- Review the partitioned tables and indexes in Books Online. - http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms175533.aspx
About the author
 Ken Simmons is a database administrator, developer, SQL Server book author and Microsoft SQL Server MVP.
Ken Simmons is a database administrator, developer, SQL Server book author and Microsoft SQL Server MVP.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips






